simplify docs/install and merge docs/hardware
docs/hardware is redundant, because it now mostly contains installation instructions, and docs/install also contains hardware information. therefore, in practise, they are both the same kind of information. merge the two, and streamline everything. a lot of redundant information has been removed. docs/install/ has been re-structured in such a way as to enable more chronological reading, to make it easier for the average user to install Canoeboot. This is part of a larger series of changes I'm working on for the documentation. I'm massively auditing the entire Canoeboot documentation. Signed-off-by: Leah Rowe <info@minifree.org>master
parent
c35da8dc01
commit
633dbebbc6
|
|
@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ASUS Chromebook C201
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This page is absolete. Refer to these pages instead:
|
||||
|
||||
* [C201 flashing instructions](../install/c201.md)
|
||||
* [Chromebook flashing instructions](../install/chromebooks.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Intel D510MO and D410PT desktop boards
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
![Intel D510MO]()
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Intel |
|
||||
| **Name** | D510MO/D410PT |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2010 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel NM10 Express (Mount Olive) |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Atom |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Integrated |
|
||||
| **Display** | None. |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 4GB |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | Intel BIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Not present. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | ? |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | - |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | P+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | P+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | - |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
This is a desktop board using intel hardware (circa \~2009, ICH7
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the ThinkPad X200. It can make
|
||||
for quite a nifty desktop. Powered by Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: D410PT is another name and it's the same board. Flash the exact same
|
||||
ROM and it should work.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This board has a working framebuffer in Grub, but in GNU+Linux in
|
||||
native resolution the display is unusable due to some raminit issues.
|
||||
This board can however be used for building a headless server.
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/d510mo.md](../install/d510mo.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,124 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Intel D945GCLF desktop board
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 alt="D945GCLF" class="p" src="https://av.canoeboot.org/d945gclf/d945gclf.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.canoeboot.org/d945gclf/d945gclf.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Intel |
|
||||
| **Name** | D945GCLF/D945GCLF2D |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2008 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Calistoga 945GC |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Atom |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | ? |
|
||||
| **Display** | None. |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 2GB |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | Intel BIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Not present. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8 512KiB |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works without blobs;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
W*: Works with blobs;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
P*: Partially works with blobs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | | Notes |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|-------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N | |
|
||||
| **Display** | - | |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ | |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ | |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ | |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | - | |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Doesn't work |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Doesn't work |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
If you just want flashing instructions, go to
|
||||
[../install/d945gclf.md](../install/d945gclf.md)
|
||||
|
||||
D945GCLF2D also reported working by a user.
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This board is a mini-itx desktop board for 2008. It uses an atom 230,
|
||||
which is a singe core CPU but it is hyperthreaded so it appears to have
|
||||
2 thread to the OS. The flash chip is very small, 512KiB, so grub2 does
|
||||
not fit, which is why Canoeboot has to use seabios on this target. Full
|
||||
disk encryption like on other supported targets will not be possible, so
|
||||
plan accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
This board has a 945gc chipset which is the desktop equivalent of 945gm
|
||||
which can be found in the Lenovo x60/t60 or macbook2,1. This chipset
|
||||
features an ICH7 southbridge. It has 1 DIMM slot that can accommodate up
|
||||
to 2G of DDR2 RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
Connectivity-wise it has 1 PCI slot, a 10/100 ethernet port, 4 usb slot
|
||||
and 4 usb ports, with one internal header and 2 SATA ports.
|
||||
|
||||
The D945GCLF2 is an upgraded version of this board. The differences are:
|
||||
1 more USB header, 10/100/1000 ethernet and a dual core cpu (also
|
||||
hyperthreaded). Since the board is almost identical (and coreboot code
|
||||
seem to indicate that it works, since MAX\_CPU=4 is set), it is believed
|
||||
that it should also work but this is untested.
|
||||
|
||||
Remarks about vendor bios:
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Without a coreboot firmware this board is completely useless, since the
|
||||
vendor bios is very bad. It cannot boot from any HDD whether it is
|
||||
connected to the SATA port or USB. With Canoeboot, it works just
|
||||
fine.
|
||||
|
||||
- The vendor bios write protects the flash so it requires external
|
||||
flashing to install Canoeboot on this device. Once Canoeboot is
|
||||
flashed there is no problem to update the firmware internally
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an image of the board:\
|
||||
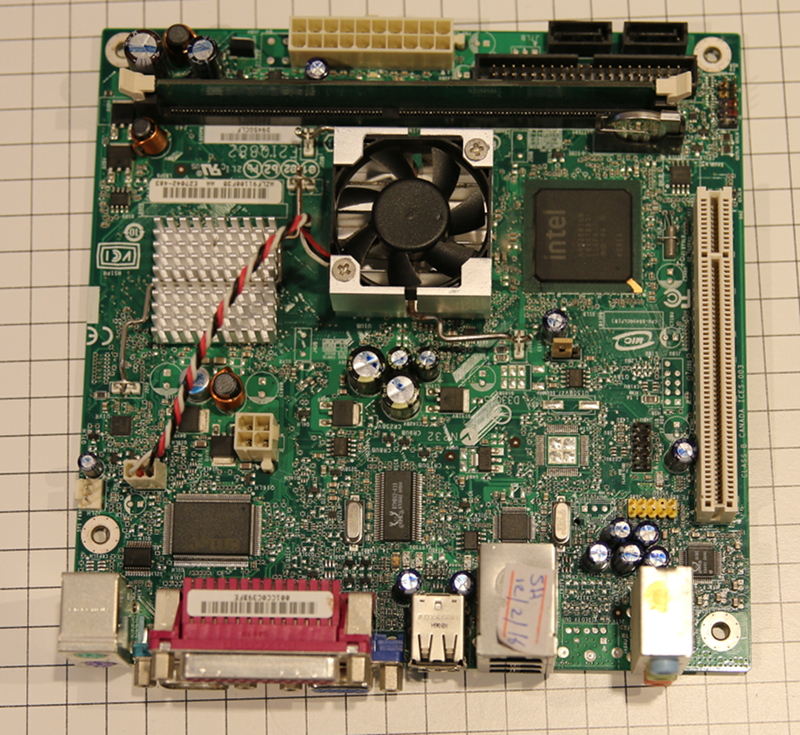\
|
||||
Here is an image of the D945GCLF2 board:\
|
||||
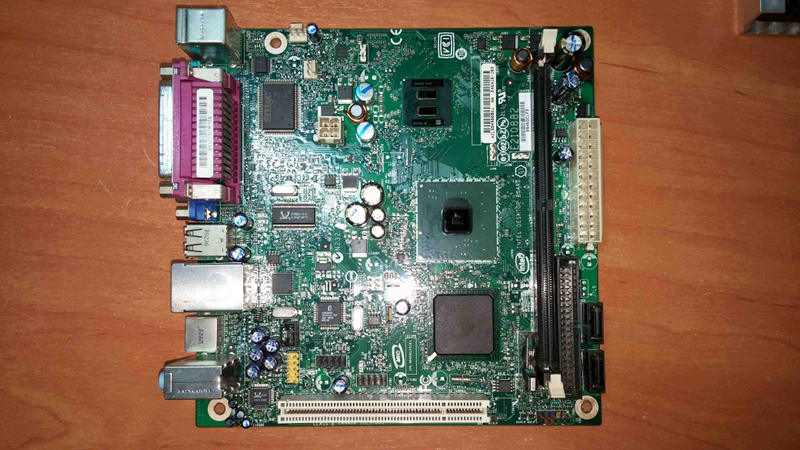{width="80%" height="80%"}\
|
||||
And SPI SOIC8 flash chip\
|
||||
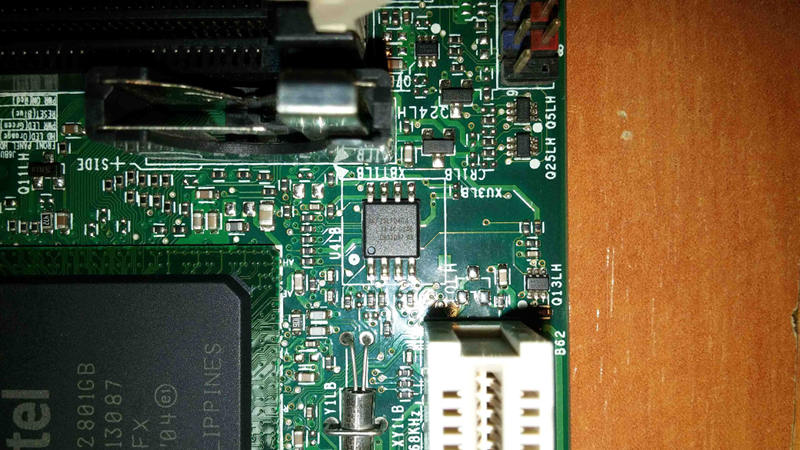{width="50%" height="50%"}
|
||||
|
||||
How to replace thermal paste and fan
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
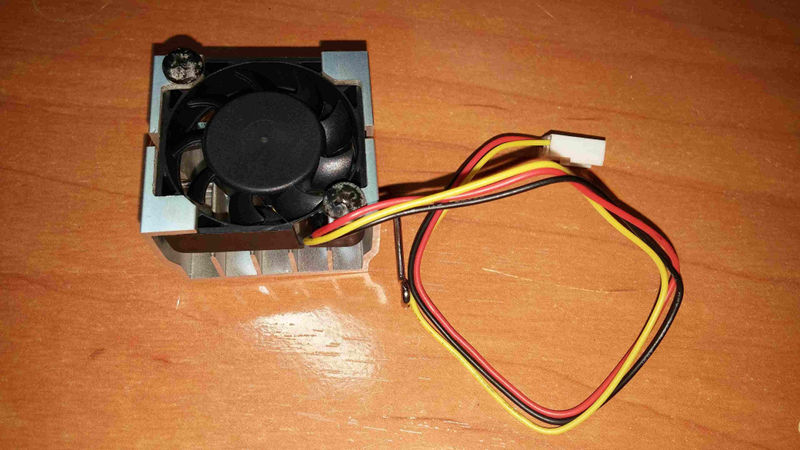
This board comes with very crappy disposable loud fan, that one has no
|
||||
bearings, which can not be repaired or oiled properly, do not waste your
|
||||
time trying to fix it, just buy one chinese same size fan\
|
||||
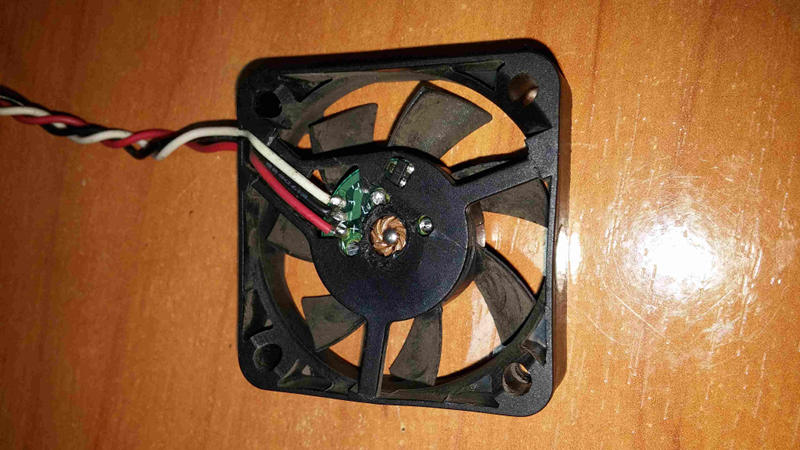{width="50%" height="50%"}
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Make sure that new one has same wiring\
|
||||
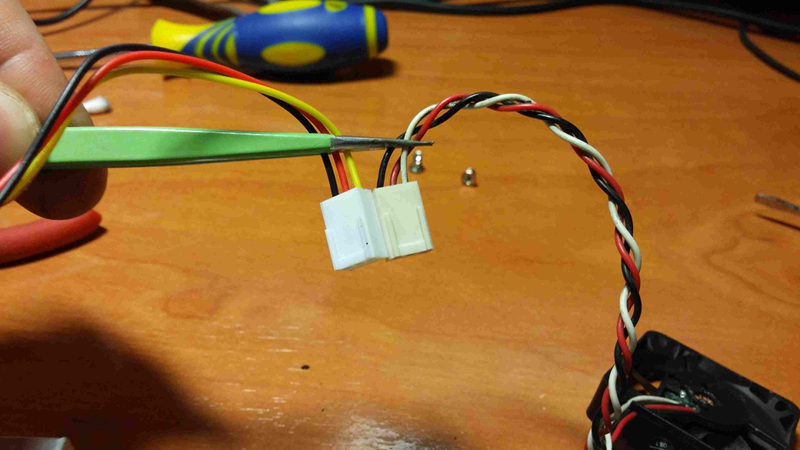{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
This is a new one, with bearing and maintenable\
|
||||
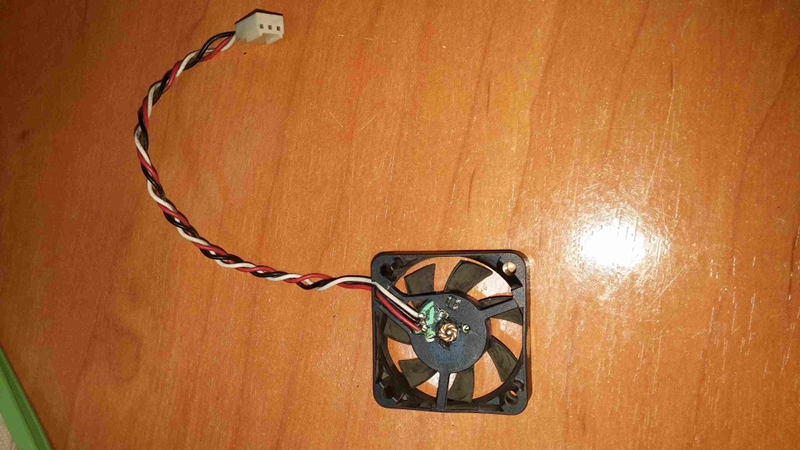
{width="50%" height="50%"}
|
||||
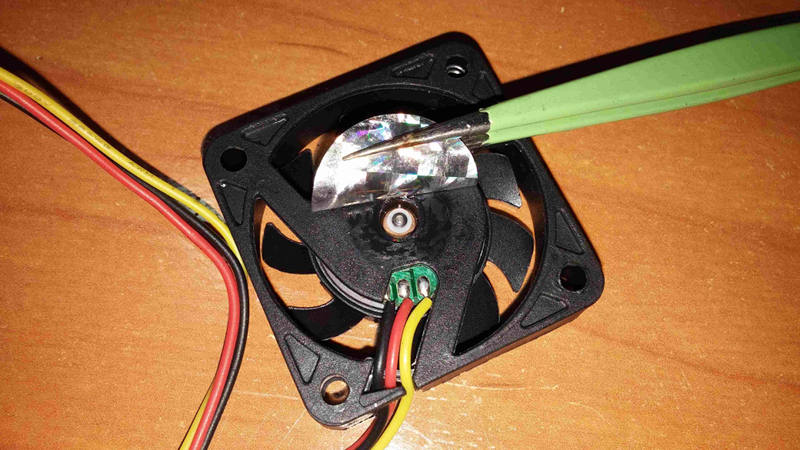{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Now remove the both coolers rotating them a bit, slowly, then clean both
|
||||
silicons and both coolers (removing cmos battery first is recommended)\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Put a little bit of non conductive thermal paste on both silicons (only
|
||||
cpu silicon iis shown on that image)\
|
||||
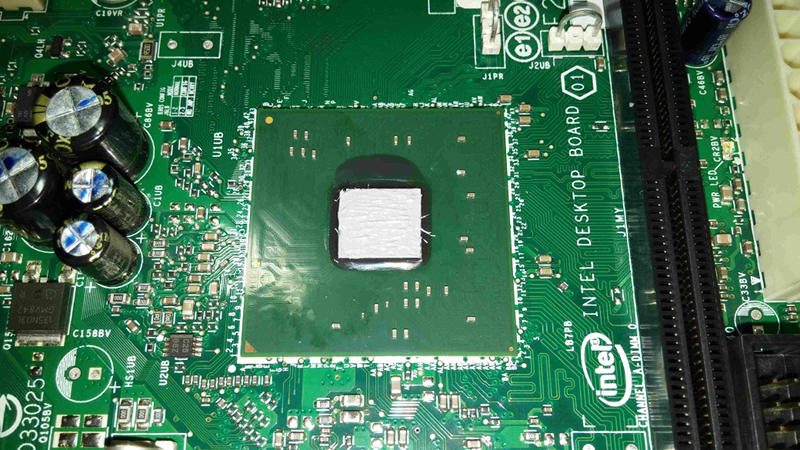{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
|
||||
Before assembling new fan, some need new longer screws, make sure having
|
||||
these (on the left is original one, too short for new fan)\
|
||||
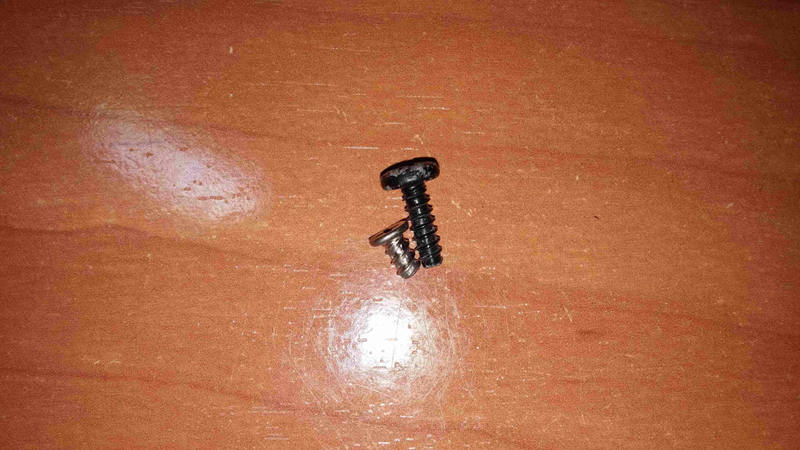{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
After that, assemble your new fan into CPU cooler\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Finally assemle both coolers on both chips, do not forget put in the CPU
|
||||
fan connector back, and you are done.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L desktop board
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
![GA-G41M-ES2L]()
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Gigabyte |
|
||||
| **Name** | GA-G41M-ES2L |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel G41 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Extreme/Quad/Duo,
|
||||
Pentium Extreme/D/4 Extreme/4/Celeron |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Integrated |
|
||||
| **Display** | None. |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 8GB (2x4GB DDR2-800) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | AWARD BIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be disabled |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | 2x8Mbit |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display** | - |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | P+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | P+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | - |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Slow! |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
This is a desktop board using intel hardware (circa \~2009, ICH7
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the ThinkPad X200. It can make
|
||||
for quite a nifty desktop. Powered by Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
In recent Canoeboot releases, only SeaBIOS payload is provided in ROMs
|
||||
for this board. According to user reports, they work quite well. GRUB was
|
||||
always buggy on this board, so it was removed from cbmk.
|
||||
|
||||
IDE on the board is untested, but it might be possible to use a SATA HDD
|
||||
using an IDE SATA adapter. The SATA ports do work, but it's IDE emulation. The
|
||||
emulation is slow in DMA mode sia SeaBIOS, so SeaBIOS is configured to use PIO
|
||||
mode on this board. This SeaBIOS configuration does not affect the GNU+Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
You need to set a custom MAC address in GNU+Linux for the NIC to work.
|
||||
In /etc/network/interfaces on debian-based systems like Debian or
|
||||
Devuan, this would be in the entry for your NIC:\
|
||||
hwaddress ether macaddressgoeshere
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively:
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool canoeboot.rom extract -n rt8168-macaddress -f rt8168-macaddress
|
||||
|
||||
Modify the MAC address in the file `rt8168-macaddress` and then:
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool canoeboot.rom remove -n rt8168-macaddress
|
||||
cbfstool canoeboot.rom add -f rt8168-macaddress -n rt8168-macaddress -t raw
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have a different MAC address hardcoded. In the above example, the ROM
|
||||
image is named `canoeboot.rom` for your board. You can find cbfstool
|
||||
under `coreboot/default/util/cbfstool/` after running the following command
|
||||
in the build system:
|
||||
|
||||
./update trees -d coreboot TREENAME
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about using the build system, cbmk, here:\
|
||||
[Canoeboot build instructions](../build/)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/](../install/)
|
||||
|
||||
RAM
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**This board is very picky with RAM. If it doesn't boot, try an EHCI debug
|
||||
dongle, serial usb adapter and null modem cable, or spkmodem, to get a
|
||||
coreboot log to see if it passed raminit.**
|
||||
|
||||
Kingston 8 GiB Kit KVR800D2N6/8G with Elpida Chips E2108ABSE-8G-E
|
||||
|
||||
this is a 2x4GB setup and these work quite well, according to a user on IRC.
|
||||
|
||||
Nanya NT2GT64U8HD0BY-AD with 2 GiB of NT5TU128M8DE-AD chips works too.
|
||||
|
||||
Many other modules will probably work just fine, but raminit is very picky on
|
||||
this board. Your mileage *will* fluctuate, wildly.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# biosdecode 2.12
|
||||
VPD present.
|
||||
BIOS Build ID: 6DET65WW
|
||||
Box Serial Number: L3AAR0B
|
||||
Motherboard Serial Number: 1ZFDS89N4DD
|
||||
Machine Type/Model: 7459GW4
|
||||
SMBIOS 2.4 present.
|
||||
Structure Table Length: 2464 bytes
|
||||
Structure Table Address: 0x000E0010
|
||||
Number Of Structures: 68
|
||||
Maximum Structure Size: 120 bytes
|
||||
BIOS32 Service Directory present.
|
||||
Revision: 0
|
||||
Calling Interface Address: 0x000FDC80
|
||||
ACPI 2.0 present.
|
||||
OEM Identifier: LENOVO
|
||||
RSD Table 32-bit Address: 0x79B5B843
|
||||
XSD Table 64-bit Address: 0x0000000079B5B8AB
|
||||
PNP BIOS 1.0 present.
|
||||
Event Notification: Not Supported
|
||||
Real Mode 16-bit Code Address: E2CA:1868
|
||||
Real Mode 16-bit Data Address: 0040:0000
|
||||
16-bit Protected Mode Code Address: 0x000F97BD
|
||||
16-bit Protected Mode Data Address: 0x00000400
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,208 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Codec: Conexant CX20561 (Hermosa)
|
||||
Address: 0
|
||||
AFG Function Id: 0x1 (unsol 1)
|
||||
MFG Function Id: 0x2 (unsol 1)
|
||||
Vendor Id: 0x14f15051
|
||||
Subsystem Id: 0x17aa20ff
|
||||
Revision Id: 0x100000
|
||||
Modem Function Group: 0x2
|
||||
Default PCM:
|
||||
rates [0x160]: 44100 48000 96000
|
||||
bits [0xe]: 16 20 24
|
||||
formats [0x1]: PCM
|
||||
Default Amp-In caps: N/A
|
||||
Default Amp-Out caps: N/A
|
||||
State of AFG node 0x01:
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3 CLKSTOP
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
GPIO: io=4, o=0, i=0, unsolicited=1, wake=0
|
||||
IO[0]: enable=0, dir=0, wake=0, sticky=0, data=0, unsol=0
|
||||
IO[1]: enable=0, dir=0, wake=0, sticky=0, data=0, unsol=0
|
||||
IO[2]: enable=0, dir=0, wake=0, sticky=0, data=0, unsol=0
|
||||
IO[3]: enable=0, dir=0, wake=0, sticky=0, data=0, unsol=0
|
||||
Node 0x10 [Audio Output] wcaps 0xc1d: Stereo Amp-Out R/L
|
||||
Control: name="Speaker Playback Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=Out, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Control: name="Speaker Playback Switch", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=Out, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Device: name="CX20561 Analog", type="Audio", device=0
|
||||
Amp-Out caps: ofs=0x4a, nsteps=0x4a, stepsize=0x03, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-Out vals: [0x4a 0x4a]
|
||||
Converter: stream=8, channel=0
|
||||
PCM:
|
||||
rates [0x560]: 44100 48000 96000 192000
|
||||
bits [0xe]: 16 20 24
|
||||
formats [0x1]: PCM
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Node 0x11 [Audio Output] wcaps 0xc1d: Stereo Amp-Out R/L
|
||||
Control: name="Headphone Playback Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=Out, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Control: name="Headphone Playback Switch", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=Out, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Amp-Out caps: ofs=0x4a, nsteps=0x4a, stepsize=0x03, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-Out vals: [0x4a 0x4a]
|
||||
Converter: stream=8, channel=0
|
||||
PCM:
|
||||
rates [0x560]: 44100 48000 96000 192000
|
||||
bits [0xe]: 16 20 24
|
||||
formats [0x1]: PCM
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Node 0x12 [Audio Output] wcaps 0x211: Stereo Digital
|
||||
Control: name="IEC958 Playback Con Mask", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Control: name="IEC958 Playback Pro Mask", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Control: name="IEC958 Playback Default", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Control: name="IEC958 Playback Switch", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Control: name="IEC958 Default PCM Playback Switch", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Device: name="CX20561 Digital", type="SPDIF", device=1
|
||||
Converter: stream=8, channel=0
|
||||
Digital:
|
||||
Digital category: 0x0
|
||||
IEC Coding Type: 0x0
|
||||
PCM:
|
||||
rates [0x160]: 44100 48000 96000
|
||||
bits [0xe]: 16 20 24
|
||||
formats [0x5]: PCM AC3
|
||||
Node 0x13 [Beep Generator Widget] wcaps 0x70000c: Mono Amp-Out
|
||||
Control: name="Beep Playback Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=1, dir=Out, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Control: name="Beep Playback Switch", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=1, dir=Out, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Amp-Out caps: ofs=0x03, nsteps=0x03, stepsize=0x17, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-Out vals: [0x00]
|
||||
Node 0x14 [Audio Input] wcaps 0x100d1b: Stereo Amp-In R/L
|
||||
Device: name="CX20561 Analog", type="Audio", device=0
|
||||
Amp-In caps: ofs=0x4a, nsteps=0x50, stepsize=0x03, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-In vals: [0x50 0x50] [0x50 0x50]
|
||||
Converter: stream=4, channel=0
|
||||
SDI-Select: 0
|
||||
PCM:
|
||||
rates [0x160]: 44100 48000 96000
|
||||
bits [0xe]: 16 20 24
|
||||
formats [0x1]: PCM
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 2
|
||||
0x1d* 0x17
|
||||
Node 0x15 [Audio Input] wcaps 0x100d1b: Stereo Amp-In R/L
|
||||
Control: name="Capture Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=In, idx=1, ofs=0
|
||||
Amp-In caps: ofs=0x4a, nsteps=0x50, stepsize=0x03, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-In vals: [0x50 0x50]
|
||||
Converter: stream=0, channel=0
|
||||
SDI-Select: 0
|
||||
PCM:
|
||||
rates [0x160]: 44100 48000 96000
|
||||
bits [0xe]: 16 20 24
|
||||
formats [0x1]: PCM
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 1
|
||||
0x18
|
||||
Node 0x16 [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x400581: Stereo
|
||||
Control: name="Headphone Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Pincap 0x0000001c: OUT HP Detect
|
||||
Pin Default 0x042140f0: [Jack] HP Out at Ext Right
|
||||
Conn = 1/8, Color = Green
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0xc0: OUT HP
|
||||
Unsolicited: tag=02, enabled=1
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 2
|
||||
0x10 0x11*
|
||||
Node 0x17 [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x40048b: Stereo Amp-In
|
||||
Control: name="Dock Mic Boost Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=In, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Control: name="Dock Mic Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Amp-In caps: ofs=0x00, nsteps=0x04, stepsize=0x27, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-In vals: [0x00 0x00]
|
||||
Pincap 0x00001224: IN Detect
|
||||
Vref caps: 50 80
|
||||
Pin Default 0x61a190f0: [N/A] Mic at Sep Rear
|
||||
Conn = 1/8, Color = Pink
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x24: IN VREF_80
|
||||
Unsolicited: tag=03, enabled=1
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Node 0x18 [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x40048b: Stereo Amp-In
|
||||
Control: name="Mic Boost Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=In, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Control: name="Mic Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Amp-In caps: ofs=0x00, nsteps=0x04, stepsize=0x27, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-In vals: [0x00 0x00]
|
||||
Pincap 0x00001224: IN Detect
|
||||
Vref caps: 50 80
|
||||
Pin Default 0x04a190f0: [Jack] Mic at Ext Right
|
||||
Conn = 1/8, Color = Pink
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x24: IN VREF_80
|
||||
Unsolicited: tag=04, enabled=1
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Node 0x19 [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x400581: Stereo
|
||||
Control: name="Dock Headphone Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Pincap 0x00000014: OUT Detect
|
||||
Pin Default 0x612140f0: [N/A] HP Out at Sep Rear
|
||||
Conn = 1/8, Color = Green
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x40: OUT
|
||||
Unsolicited: tag=01, enabled=1
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 2
|
||||
0x10 0x11*
|
||||
Node 0x1a [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x400501: Stereo
|
||||
Control: name="Speaker Phantom Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Pincap 0x00010010: OUT EAPD
|
||||
EAPD 0x2: EAPD
|
||||
Pin Default 0x901701f0: [Fixed] Speaker at Int N/A
|
||||
Conn = Analog, Color = Unknown
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Misc = NO_PRESENCE
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x40: OUT
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 2
|
||||
0x10* 0x11
|
||||
Node 0x1b [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x400500: Mono
|
||||
Pincap 0x00010010: OUT EAPD
|
||||
EAPD 0x2: EAPD
|
||||
Pin Default 0x40f001f0: [N/A] Other at Ext N/A
|
||||
Conn = Unknown, Color = Unknown
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Misc = NO_PRESENCE
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x40: OUT
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 2
|
||||
0x10* 0x11
|
||||
Node 0x1c [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x400701: Stereo Digital
|
||||
Control: name="SPDIF Phantom Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Pincap 0x00000010: OUT
|
||||
Pin Default 0x40f001f0: [N/A] Other at Ext N/A
|
||||
Conn = Unknown, Color = Unknown
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Misc = NO_PRESENCE
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x40: OUT
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Connection: 1
|
||||
0x12
|
||||
Node 0x1d [Pin Complex] wcaps 0x40040b: Stereo Amp-In
|
||||
Control: name="Internal Mic Boost Volume", index=0, device=0
|
||||
ControlAmp: chs=3, dir=In, idx=0, ofs=0
|
||||
Control: name="Internal Mic Phantom Jack", index=0, device=0
|
||||
Amp-In caps: ofs=0x00, nsteps=0x04, stepsize=0x2f, mute=0
|
||||
Amp-In vals: [0x00 0x00]
|
||||
Pincap 0x00000020: IN
|
||||
Pin Default 0x90a601f0: [Fixed] Mic at Int N/A
|
||||
Conn = Digital, Color = Unknown
|
||||
DefAssociation = 0xf, Sequence = 0x0
|
||||
Misc = NO_PRESENCE
|
||||
Pin-ctls: 0x20: IN
|
||||
Power states: D0 D1 D2 D3
|
||||
Power: setting=D0, actual=D0
|
||||
Node 0x1e [Vendor Defined Widget] wcaps 0xf00000: Mono
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
|||
processor : 0
|
||||
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
|
||||
cpu family : 6
|
||||
model : 23
|
||||
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU P8600 @ 2.40GHz
|
||||
stepping : 6
|
||||
microcode : 0x60c
|
||||
cpu MHz : 800.000
|
||||
cache size : 3072 KB
|
||||
physical id : 0
|
||||
siblings : 2
|
||||
core id : 0
|
||||
cpu cores : 2
|
||||
apicid : 0
|
||||
initial apicid : 0
|
||||
fpu : yes
|
||||
fpu_exception : yes
|
||||
cpuid level : 10
|
||||
wp : yes
|
||||
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts nopl aperfmperf pni dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr pdcm sse4_1 lahf_lm dtherm tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority
|
||||
bogomips : 4787.97
|
||||
clflush size : 64
|
||||
cache_alignment : 64
|
||||
address sizes : 36 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
|
||||
power management:
|
||||
|
||||
processor : 1
|
||||
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
|
||||
cpu family : 6
|
||||
model : 23
|
||||
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU P8600 @ 2.40GHz
|
||||
stepping : 6
|
||||
microcode : 0x60c
|
||||
cpu MHz : 1600.000
|
||||
cache size : 3072 KB
|
||||
physical id : 0
|
||||
siblings : 2
|
||||
core id : 1
|
||||
cpu cores : 2
|
||||
apicid : 1
|
||||
initial apicid : 1
|
||||
fpu : yes
|
||||
fpu_exception : yes
|
||||
cpuid level : 10
|
||||
wp : yes
|
||||
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts nopl aperfmperf pni dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr pdcm sse4_1 lahf_lm dtherm tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority
|
||||
bogomips : 4787.97
|
||||
clflush size : 64
|
||||
cache_alignment : 64
|
||||
address sizes : 36 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
|
||||
power management:
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
|
|
@ -1,587 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# dmidecode 2.12
|
||||
SMBIOS 2.4 present.
|
||||
68 structures occupying 2464 bytes.
|
||||
Table at 0x000E0010.
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0000, DMI type 0, 24 bytes
|
||||
BIOS Information
|
||||
Vendor: LENOVO
|
||||
Version: 6DET65WW (3.15 )
|
||||
Release Date: 08/24/2010
|
||||
Address: 0xE0000
|
||||
Runtime Size: 128 kB
|
||||
ROM Size: 8192 kB
|
||||
Characteristics:
|
||||
PCI is supported
|
||||
PC Card (PCMCIA) is supported
|
||||
PNP is supported
|
||||
BIOS is upgradeable
|
||||
BIOS shadowing is allowed
|
||||
ESCD support is available
|
||||
Boot from CD is supported
|
||||
Selectable boot is supported
|
||||
BIOS ROM is socketed
|
||||
EDD is supported
|
||||
ACPI is supported
|
||||
USB legacy is supported
|
||||
BIOS boot specification is supported
|
||||
Targeted content distribution is supported
|
||||
BIOS Revision: 3.21
|
||||
Firmware Revision: 1.6
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0001, DMI type 1, 27 bytes
|
||||
System Information
|
||||
Manufacturer: LENOVO
|
||||
Product Name: 7459GW4
|
||||
Version: ThinkPad X200
|
||||
Serial Number: L3AAR0B
|
||||
UUID: 93861E01-4A15-11CB-8F2C-D4BC407E0839
|
||||
Wake-up Type: Power Switch
|
||||
SKU Number: Not Specified
|
||||
Family: ThinkPad X200
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0002, DMI type 2, 8 bytes
|
||||
Base Board Information
|
||||
Manufacturer: LENOVO
|
||||
Product Name: 7459GW4
|
||||
Version: Not Available
|
||||
Serial Number: 1ZFDS89N4DD
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0003, DMI type 3, 13 bytes
|
||||
Chassis Information
|
||||
Manufacturer: LENOVO
|
||||
Type: Notebook
|
||||
Lock: Not Present
|
||||
Version: Not Available
|
||||
Serial Number: Not Available
|
||||
Asset Tag: 1S7459GW4L3AAR0B
|
||||
Boot-up State: Unknown
|
||||
Power Supply State: Unknown
|
||||
Thermal State: Unknown
|
||||
Security Status: Unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0004, DMI type 126, 13 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0005, DMI type 126, 13 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0006, DMI type 4, 35 bytes
|
||||
Processor Information
|
||||
Socket Designation: None
|
||||
Type: Central Processor
|
||||
Family: Other
|
||||
Manufacturer: GenuineIntel
|
||||
ID: 76 06 01 00 FF FB EB BF
|
||||
Signature: Type 0, Family 6, Model 23, Stepping 6
|
||||
Flags:
|
||||
FPU (Floating-point unit on-chip)
|
||||
VME (Virtual mode extension)
|
||||
DE (Debugging extension)
|
||||
PSE (Page size extension)
|
||||
TSC (Time stamp counter)
|
||||
MSR (Model specific registers)
|
||||
PAE (Physical address extension)
|
||||
MCE (Machine check exception)
|
||||
CX8 (CMPXCHG8 instruction supported)
|
||||
APIC (On-chip APIC hardware supported)
|
||||
SEP (Fast system call)
|
||||
MTRR (Memory type range registers)
|
||||
PGE (Page global enable)
|
||||
MCA (Machine check architecture)
|
||||
CMOV (Conditional move instruction supported)
|
||||
PAT (Page attribute table)
|
||||
PSE-36 (36-bit page size extension)
|
||||
CLFSH (CLFLUSH instruction supported)
|
||||
DS (Debug store)
|
||||
ACPI (ACPI supported)
|
||||
MMX (MMX technology supported)
|
||||
FXSR (FXSAVE and FXSTOR instructions supported)
|
||||
SSE (Streaming SIMD extensions)
|
||||
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD extensions 2)
|
||||
SS (Self-snoop)
|
||||
HTT (Multi-threading)
|
||||
TM (Thermal monitor supported)
|
||||
PBE (Pending break enabled)
|
||||
Version: Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU P8600 @ 2.40GHz
|
||||
Voltage: 1.2 V
|
||||
External Clock: 266 MHz
|
||||
Max Speed: 2400 MHz
|
||||
Current Speed: 2400 MHz
|
||||
Status: Populated, Enabled
|
||||
Upgrade: None
|
||||
L1 Cache Handle: 0x000A
|
||||
L2 Cache Handle: 0x000C
|
||||
L3 Cache Handle: Not Provided
|
||||
Serial Number: Not Specified
|
||||
Asset Tag: Not Specified
|
||||
Part Number: Not Specified
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0007, DMI type 5, 20 bytes
|
||||
Memory Controller Information
|
||||
Error Detecting Method: None
|
||||
Error Correcting Capabilities:
|
||||
None
|
||||
Supported Interleave: One-way Interleave
|
||||
Current Interleave: One-way Interleave
|
||||
Maximum Memory Module Size: 4096 MB
|
||||
Maximum Total Memory Size: 8192 MB
|
||||
Supported Speeds:
|
||||
Other
|
||||
Supported Memory Types:
|
||||
DIMM
|
||||
SDRAM
|
||||
Memory Module Voltage: 2.9 V
|
||||
Associated Memory Slots: 2
|
||||
0x0008
|
||||
0x0009
|
||||
Enabled Error Correcting Capabilities:
|
||||
Unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0008, DMI type 6, 12 bytes
|
||||
Memory Module Information
|
||||
Socket Designation: DIMM Slot 1
|
||||
Bank Connections: 0 1
|
||||
Current Speed: 42 ns
|
||||
Type: DIMM SDRAM
|
||||
Installed Size: 2048 MB (Double-bank Connection)
|
||||
Enabled Size: 2048 MB (Double-bank Connection)
|
||||
Error Status: OK
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0009, DMI type 6, 12 bytes
|
||||
Memory Module Information
|
||||
Socket Designation: DIMM Slot 2
|
||||
Bank Connections: 2 3
|
||||
Current Speed: 42 ns
|
||||
Type: DIMM SDRAM
|
||||
Installed Size: Not Installed
|
||||
Enabled Size: Not Installed
|
||||
Error Status: OK
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x000A, DMI type 7, 19 bytes
|
||||
Cache Information
|
||||
Socket Designation: Internal L1 Cache
|
||||
Configuration: Enabled, Socketed, Level 1
|
||||
Operational Mode: Write Back
|
||||
Location: Internal
|
||||
Installed Size: 64 kB
|
||||
Maximum Size: 64 kB
|
||||
Supported SRAM Types:
|
||||
Synchronous
|
||||
Installed SRAM Type: Synchronous
|
||||
Speed: Unknown
|
||||
Error Correction Type: Single-bit ECC
|
||||
System Type: Instruction
|
||||
Associativity: 8-way Set-associative
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x000B, DMI type 7, 19 bytes
|
||||
Cache Information
|
||||
Socket Designation: Internal L1 Cache
|
||||
Configuration: Enabled, Socketed, Level 1
|
||||
Operational Mode: Write Back
|
||||
Location: Internal
|
||||
Installed Size: 64 kB
|
||||
Maximum Size: 64 kB
|
||||
Supported SRAM Types:
|
||||
Synchronous
|
||||
Installed SRAM Type: Synchronous
|
||||
Speed: Unknown
|
||||
Error Correction Type: Single-bit ECC
|
||||
System Type: Data
|
||||
Associativity: 8-way Set-associative
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x000C, DMI type 7, 19 bytes
|
||||
Cache Information
|
||||
Socket Designation: Internal L2 Cache
|
||||
Configuration: Enabled, Socketed, Level 2
|
||||
Operational Mode: Write Back
|
||||
Location: Internal
|
||||
Installed Size: 3072 kB
|
||||
Maximum Size: 3072 kB
|
||||
Supported SRAM Types:
|
||||
Burst
|
||||
Installed SRAM Type: Burst
|
||||
Speed: Unknown
|
||||
Error Correction Type: Single-bit ECC
|
||||
System Type: Unified
|
||||
Associativity: 8-way Set-associative
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x000D, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: External Monitor
|
||||
External Connector Type: DB-15 female
|
||||
Port Type: Video Port
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x000E, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: Microphone Jack
|
||||
External Connector Type: Mini Jack (headphones)
|
||||
Port Type: Audio Port
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x000F, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: Headphone Jack
|
||||
External Connector Type: Mini Jack (headphones)
|
||||
Port Type: Audio Port
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0010, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: Modem
|
||||
External Connector Type: RJ-11
|
||||
Port Type: Modem Port
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0011, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: Ethernet
|
||||
External Connector Type: RJ-45
|
||||
Port Type: Network Port
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0012, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: USB 1
|
||||
External Connector Type: Access Bus (USB)
|
||||
Port Type: USB
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0013, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: USB 2
|
||||
External Connector Type: Access Bus (USB)
|
||||
Port Type: USB
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0014, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
|
||||
Port Connector Information
|
||||
Internal Reference Designator: Not Available
|
||||
Internal Connector Type: None
|
||||
External Reference Designator: USB 3
|
||||
External Connector Type: Access Bus (USB)
|
||||
Port Type: USB
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0015, DMI type 126, 9 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0016, DMI type 126, 9 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0017, DMI type 126, 9 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0018, DMI type 126, 9 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0019, DMI type 126, 9 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x001A, DMI type 126, 9 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x001B, DMI type 126, 13 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x001C, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
|
||||
On Board Device Information
|
||||
Type: Other
|
||||
Status: Disabled
|
||||
Description: IBM Embedded Security hardware
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x001D, DMI type 11, 5 bytes
|
||||
OEM Strings
|
||||
String 1: IBM ThinkPad Embedded Controller -[7XHT24WW-1.06 ]-
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x001E, DMI type 13, 22 bytes
|
||||
BIOS Language Information
|
||||
Language Description Format: Abbreviated
|
||||
Installable Languages: 1
|
||||
enUS
|
||||
Currently Installed Language: enUS
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x001F, DMI type 15, 25 bytes
|
||||
System Event Log
|
||||
Area Length: 0 bytes
|
||||
Header Start Offset: 0x0000
|
||||
Header Length: 16 bytes
|
||||
Data Start Offset: 0x0010
|
||||
Access Method: General-purpose non-volatile data functions
|
||||
Access Address: 0x0000
|
||||
Status: Valid, Not Full
|
||||
Change Token: 0x000000FC
|
||||
Header Format: Type 1
|
||||
Supported Log Type Descriptors: 1
|
||||
Descriptor 1: POST error
|
||||
Data Format 1: POST results bitmap
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0020, DMI type 16, 15 bytes
|
||||
Physical Memory Array
|
||||
Location: System Board Or Motherboard
|
||||
Use: System Memory
|
||||
Error Correction Type: None
|
||||
Maximum Capacity: 4 GB
|
||||
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
|
||||
Number Of Devices: 2
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0021, DMI type 17, 27 bytes
|
||||
Memory Device
|
||||
Array Handle: 0x0020
|
||||
Error Information Handle: No Error
|
||||
Total Width: 64 bits
|
||||
Data Width: 64 bits
|
||||
Size: 2048 MB
|
||||
Form Factor: SODIMM
|
||||
Set: None
|
||||
Locator: DIMM 1
|
||||
Bank Locator: Bank 0/1
|
||||
Type: DDR3
|
||||
Type Detail: Synchronous
|
||||
Speed: 1066 MHz
|
||||
Manufacturer: 02FE
|
||||
Serial Number: F4BB7CA2
|
||||
Asset Tag: 0839
|
||||
Part Number: EBJ21UE8BASA-AE-E
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0022, DMI type 17, 27 bytes
|
||||
Memory Device
|
||||
Array Handle: 0x0020
|
||||
Error Information Handle: No Error
|
||||
Total Width: Unknown
|
||||
Data Width: Unknown
|
||||
Size: No Module Installed
|
||||
Form Factor: SODIMM
|
||||
Set: None
|
||||
Locator: DIMM 2
|
||||
Bank Locator: Bank 2/3
|
||||
Type: DDR2
|
||||
Type Detail: Synchronous
|
||||
Speed: 1066 MHz
|
||||
Manufacturer:
|
||||
Serial Number:
|
||||
Asset Tag:
|
||||
Part Number:
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0023, DMI type 18, 23 bytes
|
||||
32-bit Memory Error Information
|
||||
Type: OK
|
||||
Granularity: Unknown
|
||||
Operation: Unknown
|
||||
Vendor Syndrome: Unknown
|
||||
Memory Array Address: Unknown
|
||||
Device Address: Unknown
|
||||
Resolution: Unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0024, DMI type 19, 15 bytes
|
||||
Memory Array Mapped Address
|
||||
Starting Address: 0x00000000000
|
||||
Ending Address: 0x0007FFFFFFF
|
||||
Range Size: 2 GB
|
||||
Physical Array Handle: 0x0020
|
||||
Partition Width: 2
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0025, DMI type 20, 19 bytes
|
||||
Memory Device Mapped Address
|
||||
Starting Address: 0x00000000000
|
||||
Ending Address: 0x0007FFFFFFF
|
||||
Range Size: 2 GB
|
||||
Physical Device Handle: 0x0021
|
||||
Memory Array Mapped Address Handle: 0x0024
|
||||
Partition Row Position: 1
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0026, DMI type 20, 19 bytes
|
||||
Memory Device Mapped Address
|
||||
Starting Address: 0x0007FFFFC00
|
||||
Ending Address: 0x0007FFFFFFF
|
||||
Range Size: 1 kB
|
||||
Physical Device Handle: 0x0022
|
||||
Memory Array Mapped Address Handle: 0x0024
|
||||
Partition Row Position: 1
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0027, DMI type 21, 7 bytes
|
||||
Built-in Pointing Device
|
||||
Type: Track Point
|
||||
Interface: PS/2
|
||||
Buttons: 3
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0028, DMI type 126, 26 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0029, DMI type 126, 26 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x002A, DMI type 24, 5 bytes
|
||||
Hardware Security
|
||||
Power-On Password Status: Disabled
|
||||
Keyboard Password Status: Disabled
|
||||
Administrator Password Status: Disabled
|
||||
Front Panel Reset Status: Unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x002B, DMI type 32, 11 bytes
|
||||
System Boot Information
|
||||
Status: No errors detected
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x002C, DMI type 131, 17 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
83 11 2C 00 01 02 03 FF FF 1F 00 00 00 00 00 02
|
||||
00
|
||||
Strings:
|
||||
BOOTINF 20h
|
||||
BOOTDEV 21h
|
||||
KEYPTRS 23h
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x002D, DMI type 131, 22 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
83 16 2D 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 00 01
|
||||
Strings:
|
||||
TVT-Enablement
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x002E, DMI type 132, 7 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
84 07 2E 00 02 D8 36
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x002F, DMI type 133, 5 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
85 05 2F 00 01
|
||||
Strings:
|
||||
KHOIHGIUCCHHII
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0030, DMI type 134, 13 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
86 0D 30 00 30 10 08 20 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0031, DMI type 134, 16 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
86 10 31 00 00 49 4E 54 43 01 01 00 00 02 01 02
|
||||
Strings:
|
||||
TPM INFO
|
||||
System Reserved
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0032, DMI type 135, 13 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
87 0D 32 00 54 50 07 00 01 00 00 00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0033, DMI type 135, 18 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
87 12 33 00 54 50 07 01 01 B9 05 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0034, DMI type 135, 35 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
87 23 34 00 54 50 07 02 42 41 59 20 49 2F 4F 20
|
||||
01 00 02 00 00 0B 00 48 1C 3E 18 02 00 0B 00 40
|
||||
1C 3A 18
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0035, DMI type 135, 34 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
87 22 35 00 54 50 07 04 01 06 01 01 02 00 02 01
|
||||
02 00 03 01 02 00 04 01 02 00 05 01 02 00 06 01
|
||||
02 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0036, DMI type 135, 10 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
87 0A 36 00 54 50 07 03 01 0A
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0037, DMI type 136, 6 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
88 06 37 00 5A 5A
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0038, DMI type 126, 28 bytes
|
||||
Inactive
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0039, DMI type 138, 40 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8A 28 39 00 14 01 02 01 40 02 01 40 02 01 40 02
|
||||
01 40 01 40 42 49 4F 53 20 50 61 73 73 77 6F 72
|
||||
64 20 46 6F 72 6D 61 74
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x003A, DMI type 139, 37 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8B 25 3A 00 11 01 0A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 50 57 4D 53 20 4B 65 79 20 49 6E 66 6F 72 6D
|
||||
61 74 69 6F 6E
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x003B, DMI type 140, 67 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8C 43 3B 00 4C 45 4E 4F 56 4F 0B 00 01 9A 13 CD
|
||||
C4 7A 2A 8E 76 C3 C4 4E B9 B1 DD 4E 7C 01 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x003C, DMI type 140, 47 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8C 2F 3C 00 4C 45 4E 4F 56 4F 0B 01 01 08 00 BF
|
||||
DA 3C 04 5C 72 D9 7D 0D 79 DE 46 98 23 10 B1 00
|
||||
00 00 00 10 00 10 00 10 01 D0 00 20 01 00 01
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x003D, DMI type 140, 63 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8C 3F 3D 00 4C 45 4E 4F 56 4F 0B 02 01 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x003E, DMI type 140, 17 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8C 11 3E 00 4C 45 4E 4F 56 4F 0B 03 01 00 00 00
|
||||
00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x003F, DMI type 140, 19 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
8C 13 3F 00 4C 45 4E 4F 56 4F 0B 04 01 B2 00 53
|
||||
4D 20 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0040, DMI type 129, 8 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
81 08 40 00 01 01 02 01
|
||||
Strings:
|
||||
Intel_ASF
|
||||
Intel_ASF_001
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0041, DMI type 130, 20 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
82 14 41 00 24 41 4D 54 01 01 01 01 01 A5 0B 04
|
||||
00 00 00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0042, DMI type 131, 64 bytes
|
||||
OEM-specific Type
|
||||
Header and Data:
|
||||
83 40 42 00 14 00 00 00 00 00 40 2A 00 00 00 00
|
||||
F8 00 17 29 00 00 00 00 2D 00 00 00 00 00 04 00
|
||||
64 04 03 00 01 00 01 15 C8 00 F5 10 00 00 00 00
|
||||
00 00 00 00 07 00 00 00 76 50 72 6F 00 00 00 00
|
||||
|
||||
Handle 0x0043, DMI type 127, 4 bytes
|
||||
End Of Table
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
bash: ectool: command not found
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
|
|||
========================================================================
|
||||
WARNING! You seem to be running flashrom on an unsupported laptop.
|
||||
Laptops, notebooks and netbooks are difficult to support and we
|
||||
recommend to use the vendor flashing utility. The embedded controller
|
||||
(EC) in these machines often interacts badly with flashing.
|
||||
See http://www.flashrom.org/Laptops for details.
|
||||
|
||||
If flash is shared with the EC, erase is guaranteed to brick your laptop
|
||||
and write may brick your laptop.
|
||||
Read and probe may irritate your EC and cause fan failure, backlight
|
||||
failure and sudden poweroff.
|
||||
You have been warned.
|
||||
========================================================================
|
||||
Proceeding anyway because user forced us to.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,289 +0,0 @@
|
|||
flashrom v0.9.6.1-r1563 on GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency (x86_64)
|
||||
flashrom is free software, get the source code at http://www.flashrom.org
|
||||
|
||||
flashrom was built with libpci 3.1.9, GCC 4.7.1, little endian
|
||||
Command line (3 args): flashrom -V -p internal:laptop=force_I_want_a_brick
|
||||
Calibrating delay loop... OS timer resolution is 1 usecs, 1578M loops per second, 10 myus = 11 us, 100 myus = 114 us, 1000 myus = 1002 us, 10000 myus = 10004 us, 4 myus = 5 us, OK.
|
||||
Initializing internal programmer
|
||||
No coreboot table found.
|
||||
DMI string system-manufacturer: "LENOVO"
|
||||
DMI string system-product-name: "7459GW4"
|
||||
DMI string system-version: "ThinkPad X200"
|
||||
DMI string baseboard-manufacturer: "LENOVO"
|
||||
DMI string baseboard-product-name: "7459GW4"
|
||||
DMI string baseboard-version: "Not Available"
|
||||
DMI string chassis-type: "Notebook"
|
||||
Laptop detected via DMI.
|
||||
Found chipset "Intel ICH9M-E" with PCI ID 8086:2917. Enabling flash write...
|
||||
0xfff80000/0xffb80000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xfff00000/0xffb00000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffe80000/0xffa80000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffe00000/0xffa00000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffd80000/0xff980000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffd00000/0xff900000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffc80000/0xff880000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffc00000/0xff800000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xff700000/0xff300000 FWH IDSEL: 0x4
|
||||
0xff600000/0xff200000 FWH IDSEL: 0x5
|
||||
0xff500000/0xff100000 FWH IDSEL: 0x6
|
||||
0xff400000/0xff000000 FWH IDSEL: 0x7
|
||||
0xfff80000/0xffb80000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xfff00000/0xffb00000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffe80000/0xffa80000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffe00000/0xffa00000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffd80000/0xff980000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffd00000/0xff900000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffc80000/0xff880000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffc00000/0xff800000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xff700000/0xff300000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
0xff600000/0xff200000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
0xff500000/0xff100000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
0xff400000/0xff000000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
Maximum FWH chip size: 0x400000 bytes
|
||||
BIOS Lock Enable: disabled, BIOS Write Enable: disabled, BIOS_CNTL is 0x0
|
||||
Root Complex Register Block address = 0xfed1c000
|
||||
GCS = 0x7b0461: BIOS Interface Lock-Down: enabled, Boot BIOS Straps: 0x1 (SPI)
|
||||
Top Swap : not enabled
|
||||
SPIBAR = 0xfed1c000 + 0x3800
|
||||
0x04: 0xe008 (HSFS)
|
||||
HSFS: FDONE=0, FCERR=0, AEL=0, BERASE=1, SCIP=0, FDOPSS=1, FDV=1, FLOCKDN=1
|
||||
WARNING: SPI Configuration Lockdown activated.
|
||||
Reading OPCODES... done
|
||||
0x06: 0x3f04 (HSFC)
|
||||
HSFC: FGO=0, FCYCLE=2, FDBC=63, SME=0
|
||||
0x08: 0x00001000 (FADDR)
|
||||
0x50: 0x00001a1b (FRAP)
|
||||
BMWAG 0x00, BMRAG 0x00, BRWA 0x1a, BRRA 0x1b
|
||||
0x54: 0x00000000 FREG0: WARNING: Flash Descriptor region (0x00000000-0x00000fff) is read-only.
|
||||
0x58: 0x07ff0600 FREG1: BIOS region (0x00600000-0x007fffff) is read-write.
|
||||
0x5C: 0x05f50001 FREG2: WARNING: Management Engine region (0x00001000-0x005f5fff) is locked.
|
||||
0x60: 0x05f705f6 FREG3: Gigabit Ethernet region (0x005f6000-0x005f7fff) is read-write.
|
||||
0x64: 0x05ff05f8 FREG4: Platform Data region (0x005f8000-0x005fffff) is read-write.
|
||||
0x74: 0x9fff07e0 PR0: WARNING: 0x007e0000-0x01ffffff is read-only.
|
||||
0x84: 0x85ff85f8 PR4: WARNING: 0x005f8000-0x005fffff is locked.
|
||||
Please send a verbose log to flashrom@flashrom.org if this board is not listed on
|
||||
http://flashrom.org/Supported_hardware#Supported_mainboards yet.
|
||||
Writes have been disabled. You can enforce write support with the
|
||||
ich_spi_force programmer option, but it will most likely harm your hardware!
|
||||
If you force flashrom you will get no support if something breaks.
|
||||
0x90: 0x04 (SSFS)
|
||||
SSFS: SCIP=0, FDONE=1, FCERR=0, AEL=0
|
||||
0x91: 0x000000 (SSFC)
|
||||
SSFC: SCGO=0, ACS=0, SPOP=0, COP=0, DBC=0, SME=0, SCF=0
|
||||
0x94: 0x5006 (PREOP)
|
||||
0x96: 0x143b (OPTYPE)
|
||||
0x98: 0x05200302 (OPMENU)
|
||||
0x9C: 0x0601209f (OPMENU+4)
|
||||
0xA0: 0x00000000 (BBAR)
|
||||
0xC4: 0x00002005 (LVSCC)
|
||||
LVSCC: BES=0x1, WG=1, WSR=0, WEWS=0, EO=0x20, VCL=0
|
||||
0xC8: 0x00002005 (UVSCC)
|
||||
UVSCC: BES=0x1, WG=1, WSR=0, WEWS=0, EO=0x20, VCL=0
|
||||
0xD0: 0x00000000 (FPB)
|
||||
|
||||
SPI Read Configuration: prefetching disabled, caching enabled, OK.
|
||||
The following protocols are supported: FWH, SPI.
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L05PT, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L05PU, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L10PT, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L10PU, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L20PT, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L20PU, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L40PT, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L40PU, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L80P, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L16PT, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L16PU, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L512, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L010, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L020, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L040, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L080, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L016, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L032, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25LQ032, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF021, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF041A, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF081, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF081A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF161, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF321, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF321A, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF641(A), 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DQ161, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25F512B, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25FS010, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25FS040, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF041, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF081A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF161, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF161A, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26F004, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45CS1282, 16896 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB011D, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB021D, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB041D, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB081D, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB161D, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB321C, 4224 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB321D, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB642D, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for EMST F25L008A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B05, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B05T, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B10T, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B20T, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B40T, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B80T, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B16T, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B32T, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B64T, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F05, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q80(A), 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q32(A/B), 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25QH16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25QH32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L512, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1005, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L2005, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L4005, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L8005, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1605, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1635D, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1635E, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L3205, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L3235D, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L6405, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Chip status register is 00
|
||||
Chip status register: Status Register Write Disable (SRWD) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Bit 6 is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 3 (BP3) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 2 (BP2) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 1 (BP1) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 0 (BP0) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Write Enable Latch (WEL) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Write In Progress (WIP/BUSY) is not set
|
||||
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6405" (8192 kB, SPI) at physical address 0xff800000.
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L12805, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx N25Q064, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV010, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV016B, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV020, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV040, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV080B, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV512, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Sanyo LF25FW203A, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL004A, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL008A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL016A, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL032A, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL064A, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25LF040A, 512 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0xab, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25LF080A, 1024 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0xab, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF010, 128 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF016B, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF032B, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF064C, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF040, 512 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF040B, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF040B.REMS, 512 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF080B, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P05-A, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P05, 64 kB: Ignoring RES in favour of RDID.
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P10-A, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P10, 128 kB: Ignoring RES in favour of RDID.
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P40-old, 512 kB: Ignoring RES in favour of RDID.
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25PX16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25PX32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25PX64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Unknown SFDP-capable chip, 0 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x5a, will not execute.
|
||||
Receiving SFDP signature failed.
|
||||
Probing for AMIC unknown AMIC SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel unknown Atmel SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon unknown Eon SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix unknown Macronix SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC unknown PMC SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST unknown SST SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST unknown ST SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Sanyo unknown Sanyo SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Generic unknown SPI chip (RDID), 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Generic unknown SPI chip (REMS), 0 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT49LH002, 256 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Intel 82802AB, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Intel 82802AC, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm49FL002, 256 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm49FL004, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Sharp LHF00L04, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF002A/B, 256 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF003A/B, 384 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x0a, id2 0xce, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF004A/B, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF004C, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF008A, 1024 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF008C, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF016C, 2048 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x4e, id2 0x41, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW040A, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW040B, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW080A, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW080B, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW002, 256 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW016, 2048 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x4e, id2 0x41, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW040, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW080, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V040FA, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V040FB, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V040FC, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W49V002FA, 256 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V080FA, 1024 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V080FA (dual mode), 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6405" (8192 kB, SPI).
|
||||
No operations were specified.
|
||||
Restoring MMIO space at 0x7f9c951da8a0
|
||||
Restoring PCI config space for 00:1f:0 reg 0xdc
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
|
|||
========================================================================
|
||||
WARNING! You seem to be running flashrom on an unsupported laptop.
|
||||
Laptops, notebooks and netbooks are difficult to support and we
|
||||
recommend to use the vendor flashing utility. The embedded controller
|
||||
(EC) in these machines often interacts badly with flashing.
|
||||
See http://www.flashrom.org/Laptops for details.
|
||||
|
||||
If flash is shared with the EC, erase is guaranteed to brick your laptop
|
||||
and write may brick your laptop.
|
||||
Read and probe may irritate your EC and cause fan failure, backlight
|
||||
failure and sudden poweroff.
|
||||
You have been warned.
|
||||
========================================================================
|
||||
Proceeding anyway because user forced us to.
|
||||
Transaction error!
|
||||
Read operation failed!
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,292 +0,0 @@
|
|||
flashrom v0.9.6.1-r1563 on GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency (x86_64)
|
||||
flashrom is free software, get the source code at http://www.flashrom.org
|
||||
|
||||
flashrom was built with libpci 3.1.9, GCC 4.7.1, little endian
|
||||
Command line (5 args): flashrom -V -p internal:laptop=force_I_want_a_brick -r rom.bin
|
||||
Calibrating delay loop... OS timer resolution is 2 usecs, 1579M loops per second, 10 myus = 10 us, 100 myus = 100 us, 1000 myus = 1004 us, 10000 myus = 10014 us, 8 myus = 9 us, OK.
|
||||
Initializing internal programmer
|
||||
No coreboot table found.
|
||||
DMI string system-manufacturer: "LENOVO"
|
||||
DMI string system-product-name: "7459GW4"
|
||||
DMI string system-version: "ThinkPad X200"
|
||||
DMI string baseboard-manufacturer: "LENOVO"
|
||||
DMI string baseboard-product-name: "7459GW4"
|
||||
DMI string baseboard-version: "Not Available"
|
||||
DMI string chassis-type: "Notebook"
|
||||
Laptop detected via DMI.
|
||||
Found chipset "Intel ICH9M-E" with PCI ID 8086:2917. Enabling flash write...
|
||||
0xfff80000/0xffb80000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xfff00000/0xffb00000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffe80000/0xffa80000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffe00000/0xffa00000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffd80000/0xff980000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffd00000/0xff900000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffc80000/0xff880000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xffc00000/0xff800000 FWH IDSEL: 0x0
|
||||
0xff700000/0xff300000 FWH IDSEL: 0x4
|
||||
0xff600000/0xff200000 FWH IDSEL: 0x5
|
||||
0xff500000/0xff100000 FWH IDSEL: 0x6
|
||||
0xff400000/0xff000000 FWH IDSEL: 0x7
|
||||
0xfff80000/0xffb80000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xfff00000/0xffb00000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffe80000/0xffa80000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffe00000/0xffa00000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffd80000/0xff980000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffd00000/0xff900000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffc80000/0xff880000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xffc00000/0xff800000 FWH decode enabled
|
||||
0xff700000/0xff300000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
0xff600000/0xff200000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
0xff500000/0xff100000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
0xff400000/0xff000000 FWH decode disabled
|
||||
Maximum FWH chip size: 0x400000 bytes
|
||||
BIOS Lock Enable: disabled, BIOS Write Enable: disabled, BIOS_CNTL is 0x0
|
||||
Root Complex Register Block address = 0xfed1c000
|
||||
GCS = 0x7b0461: BIOS Interface Lock-Down: enabled, Boot BIOS Straps: 0x1 (SPI)
|
||||
Top Swap : not enabled
|
||||
SPIBAR = 0xfed1c000 + 0x3800
|
||||
0x04: 0xe008 (HSFS)
|
||||
HSFS: FDONE=0, FCERR=0, AEL=0, BERASE=1, SCIP=0, FDOPSS=1, FDV=1, FLOCKDN=1
|
||||
WARNING: SPI Configuration Lockdown activated.
|
||||
Reading OPCODES... done
|
||||
0x06: 0x3f04 (HSFC)
|
||||
HSFC: FGO=0, FCYCLE=2, FDBC=63, SME=0
|
||||
0x08: 0x00000000 (FADDR)
|
||||
0x50: 0x00001a1b (FRAP)
|
||||
BMWAG 0x00, BMRAG 0x00, BRWA 0x1a, BRRA 0x1b
|
||||
0x54: 0x00000000 FREG0: WARNING: Flash Descriptor region (0x00000000-0x00000fff) is read-only.
|
||||
0x58: 0x07ff0600 FREG1: BIOS region (0x00600000-0x007fffff) is read-write.
|
||||
0x5C: 0x05f50001 FREG2: WARNING: Management Engine region (0x00001000-0x005f5fff) is locked.
|
||||
0x60: 0x05f705f6 FREG3: Gigabit Ethernet region (0x005f6000-0x005f7fff) is read-write.
|
||||
0x64: 0x05ff05f8 FREG4: Platform Data region (0x005f8000-0x005fffff) is read-write.
|
||||
0x74: 0x9fff07e0 PR0: WARNING: 0x007e0000-0x01ffffff is read-only.
|
||||
0x84: 0x85ff85f8 PR4: WARNING: 0x005f8000-0x005fffff is locked.
|
||||
Please send a verbose log to flashrom@flashrom.org if this board is not listed on
|
||||
http://flashrom.org/Supported_hardware#Supported_mainboards yet.
|
||||
Writes have been disabled. You can enforce write support with the
|
||||
ich_spi_force programmer option, but it will most likely harm your hardware!
|
||||
If you force flashrom you will get no support if something breaks.
|
||||
0x90: 0x04 (SSFS)
|
||||
SSFS: SCIP=0, FDONE=1, FCERR=0, AEL=0
|
||||
0x91: 0x004240 (SSFC)
|
||||
SSFC: SCGO=0, ACS=0, SPOP=0, COP=4, DBC=2, SME=0, SCF=0
|
||||
0x94: 0x5006 (PREOP)
|
||||
0x96: 0x143b (OPTYPE)
|
||||
0x98: 0x05200302 (OPMENU)
|
||||
0x9C: 0x0601209f (OPMENU+4)
|
||||
0xA0: 0x00000000 (BBAR)
|
||||
0xC4: 0x00002005 (LVSCC)
|
||||
LVSCC: BES=0x1, WG=1, WSR=0, WEWS=0, EO=0x20, VCL=0
|
||||
0xC8: 0x00002005 (UVSCC)
|
||||
UVSCC: BES=0x1, WG=1, WSR=0, WEWS=0, EO=0x20, VCL=0
|
||||
0xD0: 0x00000000 (FPB)
|
||||
|
||||
SPI Read Configuration: prefetching disabled, caching enabled, OK.
|
||||
The following protocols are supported: FWH, SPI.
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L05PT, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L05PU, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L10PT, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L10PU, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L20PT, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L20PU, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L40PT, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L40PU, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L80P, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L16PT, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L16PU, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L512, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L010, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L020, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L040, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L080, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L016, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25L032, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for AMIC A25LQ032, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF021, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF041A, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF081, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF081A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF161, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF321, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF321A, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DF641(A), 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25DQ161, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25F512B, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25FS010, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT25FS040, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF041, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF081A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF161, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26DF161A, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT26F004, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45CS1282, 16896 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB011D, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB021D, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB041D, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB081D, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB161D, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB321C, 4224 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB321D, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT45DB642D, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for EMST F25L008A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B05, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B05T, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B10T, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B20T, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B40T, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B80T, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B16T, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B32T, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25B64T, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F05, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25F32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q80(A), 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q32(A/B), 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25Q128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25QH16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon EN25QH32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for GigaDevice GD25Q128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L512, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1005, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L2005, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L4005, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L8005, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1605, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1635D, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L1635E, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L3205, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L3235D, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L6405, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Chip status register is 00
|
||||
Chip status register: Status Register Write Disable (SRWD) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Bit 6 is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 3 (BP3) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 2 (BP2) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 1 (BP1) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Block Protect 0 (BP0) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Write Enable Latch (WEL) is not set
|
||||
Chip status register: Write In Progress (WIP/BUSY) is not set
|
||||
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6405" (8192 kB, SPI) at physical address 0xff800000.
|
||||
Probing for Macronix MX25L12805, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx M25PE16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Numonyx N25Q064, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV010, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV016B, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV020, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV040, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV080B, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm25LV512, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Sanyo LF25FW203A, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL004A, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL008A, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL016A, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL032A, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Spansion S25FL064A, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25LF040A, 512 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0xab, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25LF080A, 1024 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0xab, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF010, 128 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF016B, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF032B, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF064C, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF040, 512 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF040B, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF040B.REMS, 512 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for SST SST25VF080B, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P05-A, 64 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P05, 64 kB: Ignoring RES in favour of RDID.
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P10-A, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P10, 128 kB: Ignoring RES in favour of RDID.
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P40-old, 512 kB: Ignoring RES in favour of RDID.
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25P128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25PX16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25PX32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST M25PX64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25Q128, 16384 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X10, 128 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X20, 256 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X40, 512 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X80, 1024 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X16, 2048 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X32, 4096 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W25X64, 8192 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Unknown SFDP-capable chip, 0 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x5a, will not execute.
|
||||
Receiving SFDP signature failed.
|
||||
Probing for AMIC unknown AMIC SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Atmel unknown Atmel SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Eon unknown Eon SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Macronix unknown Macronix SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for PMC unknown PMC SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for SST unknown SST SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for ST unknown ST SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Sanyo unknown Sanyo SPI chip, 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Generic unknown SPI chip (RDID), 0 kB: probe_spi_rdid_generic: id1 0xc2, id2 0x2017
|
||||
Probing for Generic unknown SPI chip (REMS), 0 kB: Invalid OPCODE 0x90, will not execute.
|
||||
Probing for Atmel AT49LH002, 256 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Intel 82802AB, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Intel 82802AC, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm49FL002, 256 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for PMC Pm49FL004, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Sharp LHF00L04, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF002A/B, 256 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF003A/B, 384 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x0a, id2 0xce, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF004A/B, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF004C, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF008A, 1024 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF008C, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for SST SST49LF016C, 2048 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x4e, id2 0x41, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW040A, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW040B, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW080A, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FLW080B, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW002, 256 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW016, 2048 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x4e, id2 0x41, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW040, 512 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for ST M50FW080, 1024 kB: probe_82802ab: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V040FA, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V040FB, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V040FC, 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W49V002FA, 256 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xff, id2 0xff, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V080FA, 1024 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0xba, id2 0x8e, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Probing for Winbond W39V080FA (dual mode), 512 kB: probe_jedec_common: id1 0x50, id2 0x09, id1 parity violation, id1 is normal flash content, id2 is normal flash content
|
||||
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6405" (8192 kB, SPI).
|
||||
Reading flash... SSFS: SCIP=0, FDONE=1, FCERR=1, AEL=0
|
||||
SSFC: SCGO=0, ACS=0, SPOP=0, COP=1, DBC=63, SME=0, SCF=0
|
||||
Running OPCODE 0x03 failed at address 0x001000 (payload length was 64).
|
||||
FAILED.
|
||||
Restoring MMIO space at 0x7f53b721c8a0
|
||||
Restoring PCI config space for 00:1f:0 reg 0xdc
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
|||
0019
|
||||
0000
|
||||
0000
|
||||
0019
|
||||
0019
|
||||
0011
|
||||
0011
|
||||
0019
|
||||
0019
|
||||
0000
|
||||
0000
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
bash: inteltool: command not found
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
|||
0000-0cf7 : PCI Bus 0000:00
|
||||
0000-001f : dma1
|
||||
0020-0021 : pic1
|
||||
0040-0043 : timer0
|
||||
0050-0053 : timer1
|
||||
0060-0060 : keyboard
|
||||
0062-0062 : EC data
|
||||
0064-0064 : keyboard
|
||||
0066-0066 : EC cmd
|
||||
0070-0071 : rtc0
|
||||
0080-008f : dma page reg
|
||||
00a0-00a1 : pic2
|
||||
00c0-00df : dma2
|
||||
00f0-00ff : fpu
|
||||
03c0-03df : vga+
|
||||
0800-080f : pnp 00:01
|
||||
0cf8-0cff : PCI conf1
|
||||
0d00-ffff : PCI Bus 0000:00
|
||||
1000-1003 : ACPI PM1a_EVT_BLK
|
||||
1004-1005 : ACPI PM1a_CNT_BLK
|
||||
1008-100b : ACPI PM_TMR
|
||||
1010-1015 : ACPI CPU throttle
|
||||
1020-102f : ACPI GPE0_BLK
|
||||
1030-1033 : iTCO_wdt
|
||||
1050-1050 : ACPI PM2_CNT_BLK
|
||||
1060-107f : iTCO_wdt
|
||||
1180-11ff : pnp 00:01
|
||||
15e0-15ef : pnp 00:01
|
||||
1600-167f : pnp 00:01
|
||||
1680-169f : pnp 00:01
|
||||
1800-1807 : 0000:00:02.0
|
||||
1830-1837 : 0000:00:03.3
|
||||
1830-1837 : serial
|
||||
1838-183b : 0000:00:1f.2
|
||||
1838-183b : ahci
|
||||
183c-183f : 0000:00:1f.2
|
||||
183c-183f : ahci
|
||||
1840-185f : 0000:00:19.0
|
||||
1860-187f : 0000:00:1a.0
|
||||
1860-187f : uhci_hcd
|
||||
1880-189f : 0000:00:1a.1
|
||||
1880-189f : uhci_hcd
|
||||
18a0-18bf : 0000:00:1a.2
|
||||
18a0-18bf : uhci_hcd
|
||||
18c0-18df : 0000:00:1d.0
|
||||
18c0-18df : uhci_hcd
|
||||
18e0-18ff : 0000:00:1d.1
|
||||
18e0-18ff : uhci_hcd
|
||||
1c00-1c1f : 0000:00:1d.2
|
||||
1c00-1c1f : uhci_hcd
|
||||
1c20-1c3f : 0000:00:1f.2
|
||||
1c20-1c3f : ahci
|
||||
1c40-1c47 : 0000:00:1f.2
|
||||
1c40-1c47 : ahci
|
||||
1c48-1c4f : 0000:00:1f.2
|
||||
1c48-1c4f : ahci
|
||||
1c60-1c7f : 0000:00:1f.3
|
||||
2000-2fff : PCI Bus 0000:05
|
||||
3000-3fff : PCI Bus 0000:02
|
||||
4000-4fff : PCI Bus 0000:03
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
bash: lspnp: command not found
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,820 +0,0 @@
|
|||
|
||||
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 GNU+Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 2.00
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0002 2.0 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency ehci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 EHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1d.7
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0004 1x 4 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 12
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 6
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 10 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x38
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 3: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 4: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 5: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 6: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 008 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 GNU+Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 1.10
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0001 1.1 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency uhci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 UHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1d.2
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0002 1x 2 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 255
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 2
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 1 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x02
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 007 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 GNU+Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 1.10
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0001 1.1 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency uhci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 UHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1d.1
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0002 1x 2 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 255
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 2
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 1 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x06
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 006 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 GNU+Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 1.10
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0001 1.1 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency uhci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 UHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1d.0
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0002 1x 2 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 255
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 2
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 1 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x00
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 GNU+Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 2.00
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0002 2.0 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency ehci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 EHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1a.7
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0004 1x 4 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 12
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 6
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 10 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x58
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 3: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 4: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 5: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 6: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 005 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 GNU+Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 1.10
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0001 1.1 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency uhci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 UHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1a.2
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0002 1x 2 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 255
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 2
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 1 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x04
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 004 Device 002: ID 0a5c:2145 Broadcom Corp. BCM2045B (BDC-2.1) [Bluetooth Controller]
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 2.00
|
||||
bDeviceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x0a5c Broadcom Corp.
|
||||
idProduct 0x2145 BCM2045B (BDC-2.1) [Bluetooth Controller]
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.52
|
||||
iManufacturer 1 Lenovo Computer Corp
|
||||
iProduct 2 ThinkPad Bluetooth with Enhanced Data Rate II
|
||||
iSerial 0
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 216
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 4
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 100mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 3
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x82 EP 2 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 2
|
||||
Transfer Type Bulk
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x02 EP 2 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 2
|
||||
Transfer Type Bulk
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0000 1x 0 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0000 1x 0 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 1
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0009 1x 9 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0009 1x 9 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 2
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0011 1x 17 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0011 1x 17 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 3
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0020 1x 32 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0020 1x 32 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 4
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 5
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 2
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 255 Vendor Specific Class
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 255 Vendor Specific Subclass
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 255 Vendor Specific Protocol
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x84 EP 4 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 2
|
||||
Transfer Type Bulk
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0020 1x 32 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x04 EP 4 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 2
|
||||
Transfer Type Bulk
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0020 1x 32 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 3
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 0
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 254 Application Specific Interface
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Device Firmware Update
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Device Firmware Upgrade Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 33
|
||||
bmAttributes 7
|
||||
Will Not Detach
|
||||
Manifestation Tolerant
|
||||
Upload Supported
|
||||
Download Supported
|
||||
wDetachTimeout 5000 milliseconds
|
||||
wTransferSize 64 bytes
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 GNU+Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 1.10
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0001 1.1 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency uhci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 UHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1a.1
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0002 1x 2 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 255
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 2
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 1 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x06
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0103 power enable connect
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 GNU+Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 1.10
|
||||
bDeviceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x1d6b GNU+Linux Foundation
|
||||
idProduct 0x0001 1.1 root hub
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.13
|
||||
iManufacturer 3 GNU+Linux 3.13.0-39-lowlatency uhci_hcd
|
||||
iProduct 2 UHCI Host Controller
|
||||
iSerial 1 0000:00:1a.0
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 25
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 1
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 1
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 9 Hub
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 0 Full speed (or root) hub
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0x0002 1x 2 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 255
|
||||
Hub Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 41
|
||||
nNbrPorts 2
|
||||
wHubCharacteristic 0x000a
|
||||
No power switching (usb 1.0)
|
||||
Per-port overcurrent protection
|
||||
bPwrOn2PwrGood 1 * 2 milli seconds
|
||||
bHubContrCurrent 0 milli Ampere
|
||||
DeviceRemovable 0x00
|
||||
PortPwrCtrlMask 0xff
|
||||
Hub Port Status:
|
||||
Port 1: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Port 2: 0000.0100 power
|
||||
Device Status: 0x0001
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
bash: msrtool: command not found
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
bash: nvramtool: command not found
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
|||
0x16 0x042140f0
|
||||
0x17 0x61a190f0
|
||||
0x18 0x04a190f0
|
||||
0x19 0x612140f0
|
||||
0x1a 0x901701f0
|
||||
0x1b 0x40f001f0
|
||||
0x1c 0x40f001f0
|
||||
0x1d 0x90a601f0
|
||||
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
bash: superiotool: command not found
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Apple iMac 5,2
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
![iMac5,2]()
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Apple |
|
||||
| **Name** | iMac 17-inch "Core 2 Duo" 1.83 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2006 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Calistoga 945GM |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo T5600 |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 950 |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1440x900 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | 512MB, 1GB (upgradable to 2GB) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | Apple EFI |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Not present. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8 2MiB (Probably upgradable to 16MiB) |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | U |
|
||||
| **Display** | U |
|
||||
| **Audio** | U |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | U |
|
||||
| **External output** | U |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | U |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Information to be written soon, but this board is merged in Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
This board is very similar to the [MacBook2,1](./macbook21.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Just refer back to the [hardware section](./) and [install guides](../install/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Hardware compatibility list
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This sections relates to known hardware compatibility in Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
For installation instructions, refer to [../install/](../install/).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: For T60/R60 thinkpads, make sure that it has an Intel GPU, not an ATI GPU
|
||||
because coreboot lacks native video initialization for the ATI GPUs on these
|
||||
machines.
|
||||
|
||||
(for later machines like T500, T400, ATI GPU doesn't matter, because it also
|
||||
has an Intel GPU, and Canoeboot uses the Intel one)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported hardware
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
Canoeboot currently supports the following systems:
|
||||
|
||||
### Servers (AMD, Intel, x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS KGPE-D16 motherboard](kgpe-d16.md)
|
||||
- [ASUS KFSN4-DRE motherboard](kfsn4-dre.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Desktops (AMD, Intel, x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS KCMA-D8 motherboard](kcma-d8.md)
|
||||
- [Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L motherboard](ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
||||
- [Acer G43T-AM3](acer_g43t-am3.md)
|
||||
- [Intel D510MO and D410PT motherboards](d510mo.md)
|
||||
- [Apple iMac 5,2](imac52.md)
|
||||
- [Intel D945GCLF](d945gclf.md)
|
||||
- Dell OptiPlex 780 USFF and MT variants (no install guide yet)
|
||||
|
||||
### Laptops (Intel, x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Apple MacBook1,1 and MacBook2,1](macbook21.md)
|
||||
- [Dell Latitude E6400, E6400 XFR and E6400 ATG](../install/latitude.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R400](r400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R500](r500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T400 / T400S](t400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T500](t500.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad T60 (with Intel GPU)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad W500](t500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad X200 / X200S / X200 Tablet](x200.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad X301
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R400](r400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T400 / T400S](t400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T500](t500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad W500](t500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R500](r500.md)
|
||||
- [Apple MacBook1,1 and MacBook2,1](macbook21.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Laptops (ARM, with U-Boot payload)
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS Chromebook Flip C101 (gru-bob)](../install/chromebooks.md)
|
||||
- [Samsung Chromebook Plus (v1) (gru-kevin)](../install/chromebooks.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Emulation
|
||||
|
||||
- [Qemu x86](../misc/emulation.md)
|
||||
- [Qemu arm64](../misc/emulation.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: More hardware is supported. See `config/coreboot/` in cbmk. Update
|
||||
the above list!
|
||||
|
||||
'Supported' means that the build scripts know how to build ROM images
|
||||
for these systems, and that the systems have been tested (confirmed
|
||||
working). There may be exceptions; in other words, this is a list of
|
||||
'officially' supported systems.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update on i945 (X60, T60) and GM45 (X200, X301, T400, T500, R400, W500, R500)
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
Canoeboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running Canoeboot is unknown. Canoeboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. better battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
How to find what EC version you have (i945/GM45)
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
In GNU+Linux, you can try this:
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'at EC' /proc/asound/cards
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
ThinkPad Console Audio Control at EC reg 0x30, fw 7WHT19WW-3.6
|
||||
|
||||
7WHT19WW is the version in different notation, use search engine to find
|
||||
out regular version - in this case it's a 1.06 for x200 tablet
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, if `dmidecode` is available, run the following command (as `root`) to
|
||||
find the currently flashed BIOS version:
|
||||
|
||||
dmidecode -s bios-version
|
||||
|
||||
On a T400 running the latest BIOS this would give `7UET94WW (3.24 )` as result.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: 兼容硬件列表
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
这一部分说明了 canoeboot 已知兼容的硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
安装指南,请参看 [../install/](../install/)。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:对 T60/R60 thinkpad 而言,请确认它拥有的是 Intel GPU 而非 ATI GUI,因为 coreboot 对这些机器缺少 ATI GPU 的原生图像初始化。
|
||||
|
||||
(对 T500、T400 等后续机器而言,有 ATI GPU 也没问题,因为它也有 Intel GPU,而 canoeboot 会用 Intel 的)
|
||||
|
||||
已支持的硬件
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
该版本的 canoeboot 目前支持以下机器:
|
||||
|
||||
### 服务器(AMD,x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS KFSN4-DRE 主板](kfsn4-dre.md)
|
||||
- [ASUS KGPE-D16 主板](kgpe-d16.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Desktops (AMD, Intel, x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Acer G43T-AM3](acer_g43t-am3.md)
|
||||
- [Apple iMac 5,2](imac52.md)
|
||||
- [ASUS KCMA-D8 主板](kcma-d8.md)
|
||||
- [Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L 主板](ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
||||
- [Intel D510MO 及 D410PT 主板](d510mo.md)
|
||||
- [Intel D945GCLF](d945gclf.md)
|
||||
- Dell OptiPlex 780 USFF and MT variants (no install guide yet)
|
||||
|
||||
### 笔记本(Intel,x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Apple MacBook1,1 及 MacBook2,1](macbook21.md)
|
||||
- [Dell Latitude E6400, E6400 XFR 及 E6400 ATG](../install/latitude.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R400](r400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R500](r500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T400 / T400S](t400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T500](t500.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad T60(Intel GPU 款)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad W500](t500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad X200 / X200S / X200 Tablet](x200.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad X301
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad X60 / X60S / X60 Tablet
|
||||
|
||||
### 笔记本(ARM,配 U-Boot payload)
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS Chromebook Flip C101 (gru-bob)](../install/chromebooks.md)
|
||||
- [Samsung Chromebook Plus (v1) (gru-kevin)](../install/chromebooks.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### 模拟
|
||||
|
||||
- [Qemu x86](../misc/emulation.md)
|
||||
- [Qemu arm64](../misc/emulation.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
计划:支持更多硬件。见 cbmk 中的 `config/coreboot/`。更新上面的列表!
|
||||
|
||||
所谓“支持”,即指构建脚本知道如何构建这些机器的 ROM 镜像,并且机器经过测试(确认能够工作)。也可能会有例外;换言之,这是“官方”支持的机器列表。
|
||||
|
||||
在 i945(X60、T60)及 GM45(X200、X301、T400、T500、R400、W500、R500)上更新 EC
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
建议更新到最新 EC 固件版本。[EC 固件](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) 与 canoeboot 是独立的,所以我们实际上并不会提供这些固件,但如果你仍还有 Lenovo BIOS,那你可以直接运行 Lenovo BIOS 更新工具,它会同时更新 BIOS 和 EC 版本。见:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
注意:只有在运行 Lenovo BIOS 的时候,你才能这样做。如何在运行 canoeboot 的时候更新 EC 固件尚不清楚。canoeboot 只会替换 BIOS 固件,而不会替换 EC。
|
||||
|
||||
更新的 EC 固件有一些好处,例如电池管理更加好。
|
||||
|
||||
如何得知你的 EC 版本(i945/GM45)
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux,你可以试试这条命令:
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'at EC' /proc/asound/cards
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
ThinkPad Console Audio Control at EC reg 0x30, fw 7WHT19WW-3.6
|
||||
|
||||
7WHT19WW 另一种形式的版本号,使用搜索引擎来找出正常的版本号——这个例子中的 x200 tablet,版本号是 1.06。
|
||||
|
||||
或者,如果能用 `dmidecode`,则(以 `root`)运行以下命令,来得知目前刷入的 BIOS 版本:
|
||||
|
||||
dmidecode -s bios-version
|
||||
|
||||
运行最新 BIOS 的 T400 上,它的输出结果为 `7UET94WW (3.24 )`。
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,215 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ASUS KGPE-D16 server/workstation board
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: OLD page. TODO: check that all the info is still valid.
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This is a server board using AMD hardware (Fam10h *and Fam15h* CPUs
|
||||
available). It can also be used for building a high-powered workstation.
|
||||
Powered by Canoeboot. The coreboot port was done by Timothy Pearson of
|
||||
Raptor Engineering Inc. and, working with them (and sponsoring the
|
||||
work), merged into Libreboot (and inherited by Canoeboot).
|
||||
|
||||
*Memory initialization is still problematic, for some modules. We
|
||||
recommend avoiding Kingston modules.*
|
||||
*For working configurations see <https://www.coreboot.org/Board:asus/kgpe-d16>.*
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog) - note that external
|
||||
flashing is required, if the proprietary (ASUS) firmware is
|
||||
currently installed. If you already have Canoeboot, by default it is
|
||||
possible to re-flash using software running in GNU+Linux on the
|
||||
KGPE-D16, without using external hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
CPU compatibility
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
Opteron 62xx and 63xx CPUs work just fine.
|
||||
|
||||
Board status (compatibility) {#boardstatus}
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
||||
See <https://raptorengineeringinc.com/coreboot/kgpe-d16-status.php>.
|
||||
|
||||
Form factor {#formfactor}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
These boards use the SSI EEB 3.61 form factor; make sure that your case
|
||||
supports this. This form factor is similar to E-ATX in that the size is
|
||||
identical, but the position of the screws are different.
|
||||
|
||||
IPMI iKVM module add-on {#ipmi}
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
Don't use it. It uses proprietary firmware and adds a backdoor (remote
|
||||
out-of-band management chip, similar to the [Intel Management
|
||||
Engine](../../faq.md#intelme). Fortunately, the firmware is
|
||||
unsigned (possibly to replace) and physically separate from the
|
||||
mainboard since it's on the add-on module, which you don't have to
|
||||
install.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash chips {#flashchips}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
2MiB flash chips are included by default, on these boards. It's on a
|
||||
P-DIP 8 slot (SPI chip). The flash chip can be upgraded to higher sizes:
|
||||
4MiB, 8MiB or 16MiB. With at least 8MiB, you could feasibly fit a
|
||||
compressed linux+initramfs image (BusyBox+GNU+Linux system) into CBFS and
|
||||
boot that, loading it into memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Canoeboot has configs for 2, 4, 8 and 16 MiB flash chip sizes (default
|
||||
flash chip is 2MiB).
|
||||
|
||||
*DO NOT hot-swap the chip with your bare hands. Use a P-DIP 8 chip
|
||||
extractor. These can be found online. See
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Developer_Manual/Tools#Chip_removal_tools>*
|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to flash the chip:\
|
||||
[25xx NOR flashing guide](../install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Native graphics initialization {#graphics}
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
Only text-mode is known to work, but linux(kernel) can initialize the
|
||||
framebuffer display (if it has KMS - kernel mode setting).
|
||||
|
||||
Current issues {#issues}
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
- LRDIMM memory modules are currently incompatible
|
||||
(IT MAY WORK NOWADAYS, TODO TEST)
|
||||
- SAS (via PIKE 2008 module) requires non-free option ROM (and
|
||||
SeaBIOS) to boot from it (theoretically possible to replace, but you
|
||||
can put a kernel in CBFS or on SATA and boot from that, which
|
||||
can be on a SAS drive. The linux kernel can use those SAS drives
|
||||
(via PIKE module) without an option ROM).
|
||||
- SeaBIOS lacked serial console support out-of-the-box in GNU Libreboot 20160907
|
||||
and as such a workaround using SGABIOS is necessary. You can find
|
||||
instructions on how to do this on the
|
||||
[Notabug issue tracker](http://web.archive.org/web/20210416011941/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/736)
|
||||
- IPMI iKVM module (optional add-on card) uses proprietary firmware.
|
||||
Since it's for remote out-of-band management, it's theoretically a
|
||||
backdoor similar to the Intel Management Engine. Fortunately, unlike
|
||||
the ME, this firmware is unsigned which means that a free
|
||||
replacement is theoretically possible. For now, the Canoeboot
|
||||
project recommends not installing the module. [This
|
||||
project](https://github.com/facebook/openbmc) might be interesting
|
||||
to derive from, for those who want to work on a free replacement. In
|
||||
practise, out-of-band management isn't very useful anyway (or at
|
||||
the very least, it's not a major inconvenience to not have it).
|
||||
- Graphics: only text-mode works. See [\#graphics](#graphics)
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware specifications {#specifications}
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The information here is adapted, from the ASUS website.
|
||||
|
||||
### Processor / system bus
|
||||
|
||||
- 2 CPU sockets (G34 compatible)
|
||||
- HyperTransport™ Technology 3.0
|
||||
- CPUs supported:
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6100 series (Fam10h. No IOMMU support. *Not*
|
||||
recommended - old. View errata datasheet here:
|
||||
<http://support.amd.com/TechDocs/41322_10h_Rev_Gd.pdf>)
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6200 series (Fam15h, with full IOMMU support in
|
||||
Canoeboot.
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6300 series (Fam15h, with full IOMMU support in
|
||||
Canoeboot.
|
||||
- 6.4 GT/s per link (triple link)
|
||||
|
||||
### Core logic
|
||||
|
||||
- AMD SR5690
|
||||
- AMD SP5100
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory compatibility (with Canoeboot)
|
||||
|
||||
- *Total Slots:* 16 (4-channel per CPU, 8 DIMM per CPU), ECC
|
||||
- *Capacity:* Maximum up to 256GB RDIMM (Tested max 128GB)
|
||||
- *Memory Type that is compatible:*
|
||||
- DDR3 1600/1333/1066/800 UDIMM\*
|
||||
- DDR3 1600/1333/1066/800 RDIMM\*
|
||||
- *Compatible sizes per memory module:*
|
||||
- 16GB, 8GB, 4GB, 3GB, 2GB, 1GB RDIMM
|
||||
- 8GB, 4GB, 2GB, 1GB UDIMM
|
||||
|
||||
### Expansion slots
|
||||
|
||||
- *Total slot:* 6
|
||||
- *Slot Location 1:* PCI 32bit/33MHz
|
||||
- *Slot Location 2:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X8 Link)
|
||||
- *Slot Location 3:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X16 Link), Auto switch to x8
|
||||
link if slot 2 is occupied
|
||||
- *Slot Location 4:* PCI-E x8 (Gen2 X4 Link)
|
||||
- *Slot Location 5:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X16 Link)
|
||||
- *Slot Location 6:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X16 Link), Auto turn off if
|
||||
slot 5 is occupied, For 1U FH/FL Card, MIO supported
|
||||
- *Additional Slot 1:* PIKE slot (for SAS drives. See notes above)
|
||||
- Follow SSI Location\#
|
||||
|
||||
### Form factor {#form-factor}
|
||||
|
||||
- SSI EEB 3.61 (12"x13")
|
||||
|
||||
### ASUS features
|
||||
|
||||
- Fan Speed Control
|
||||
- Rack Ready (Rack and Pedestal dual use)
|
||||
|
||||
### Storage
|
||||
|
||||
- *SATA controller:*
|
||||
- AMD SP5100
|
||||
- 6 x SATA2 300MB/s
|
||||
- *SAS/SATA Controller:*
|
||||
- ASUS PIKE2008 3Gbps 8-port SAS card included
|
||||
|
||||
### Networking
|
||||
|
||||
- 2 x Intel® 82574L + 1 x Mgmt LAN
|
||||
|
||||
### Graphics
|
||||
|
||||
- Aspeed AST2050 with 8MB VRAM
|
||||
|
||||
### On board I/O
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 x PSU Power Connector (24-pin SSI power connector + 8-pin SSI
|
||||
12V + 8-pin SSI 12V power connector)
|
||||
- 1 x Management Connector , Onboard socket for management card
|
||||
- 3 x USB pin header , Up to 6 Devices
|
||||
- 1 x Internal A Type USB Port
|
||||
- 8 x Fan Header , 4pin (3pin/4pin fan dual support)
|
||||
- 2 x SMBus
|
||||
- 1 x Serial Port Header
|
||||
- 1 x TPM header
|
||||
- 1 x PS/2 KB/MS port
|
||||
|
||||
### Back I/O ports
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 x External Serial Port
|
||||
- 2 x External USB Port
|
||||
- 1 x VGA Port
|
||||
- 2 x RJ-45
|
||||
- 1 x PS/2 KB/Mouse
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
- *Operation temperature:* 10C \~ 35C
|
||||
- *Non operation temperature:* -40C \~ 70C
|
||||
- *Non operation humidity:* 20% \~ 90% ( Non condensing)
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
- CPU temperatures
|
||||
- Fan speed (RPM)
|
||||
|
||||
### Note:
|
||||
|
||||
- \* DDR3 1600 can only be supported with AMD Opteron 6300/6200 series
|
||||
processor
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad R400
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
![ThinkPad R400]()
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad R400 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn/Merom family) or
|
||||
Celeron M (Merom L family) |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (and ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3470 or nVIDIA
|
||||
GeForce 9300M on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1440x900 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 8GB |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable to 16MiB) |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an R400 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
It is believed that all or most R400 laptops are compatible. See notes
|
||||
about [CPU
|
||||
compatibility](../install/r400_external.html#cpu_compatibility) for
|
||||
potential incompatibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two possible flash chip sizes for the R400: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
||||
8MiB (64Mbit). This can be identified by the type of flash chip below
|
||||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The R400 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing Canoeboot. Canoeboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update {#ecupdate}
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
Canoeboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running Canoeboot is unknown. Canoeboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
The R400 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: put hardware register logs here like on the [X200](x200.md) and
|
||||
[T400](t400.md) page.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad R500
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
![ThinkPad R500]()
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad R500 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn/Merom family) or
|
||||
Celeron M (Merom L family) |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (or ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3470 on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1680x1050 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | 512MB, 2GB or 4GB (Upgradable to 8GB) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16/WSON-8 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable
|
||||
to 16MiB) |
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an R500 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This board as basically identical to the T500, and has very similar disassembly.
|
||||
You must take it apart and flash the chip externally.
|
||||
|
||||
The chip is 4MiB NOR flash (SPI protocol) is SOIC8 form factory.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following guide:\
|
||||
[Externally rewrite 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol](../install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike other GM45+ICH9M thinkpads in Canoeboot, the R500 doesn't have an Intel
|
||||
PHY (for Gigabit Ethernet). However, Canoeboot still includes an Intel flash
|
||||
descriptor, but with just the descriptor and BIOS region. The `ich9gen` program
|
||||
supports this fully.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, you do not have to worry about the MAC address. The onboard NIC for
|
||||
ethernet is made by Broadcom (and works in linux-libre).
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to T500 disassembly guide. The R500 disassembly procedure is almost
|
||||
identical.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad T400
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 alt="ThinkPad T400" class="p" src="https://av.canoeboot.org/t400/boot1.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.canoeboot.org/t400/boot1.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad T400 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn family). A Quad-core
|
||||
mod exists, replacing the Core 2 Duo with a Core Quad |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (and ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3650 on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1440x900 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | 2 or 4GB (Upgradable to 8GB) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16/WSON-8 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable
|
||||
to 16MiB) |
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an T400 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
It is believed that all or most laptops of the model T400 are compatible. See notes
|
||||
about [CPU
|
||||
compatibility](../install/t400_external.html#cpu_compatibility) for
|
||||
potential incompatibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two possible flash chip sizes for the T400: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
||||
8MiB (64Mbit). This can be identified by the type of flash chip below
|
||||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The T400 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing Canoeboot. Canoeboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update {#ecupdate}
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
Canoeboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running Canoeboot is unknown. Canoeboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
The T400 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad T500
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 alt="ThinkPad T500" class="p" src="https://av.canoeboot.org/t500/0062.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.canoeboot.org/t500/0062.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad T500 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn family). A Quad-core
|
||||
mod exists, replacing the Core 2 Duo with a Core Quad |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (and ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3650 on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1680x1050/1920x1200 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | 2 or 4GB (Upgradable to 8GB) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16/WSON-8 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable
|
||||
to 16MiB) |
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an T500 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
It is believed that all or most T500 laptops are compatible. See notes
|
||||
about [CPU
|
||||
compatibility](../install/t500_external.html#cpu_compatibility) for
|
||||
potential incompatibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
W500 is also compatible, and mostly the same design as T500.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two possible flash chip sizes for the T500: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
||||
8MiB (64Mbit). This can be identified by the type of flash chip below
|
||||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The T500 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing Canoeboot. Canoeboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update {#ecupdate}
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
Canoeboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running Canoeboot is unknown. Canoeboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
The T500 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
|
|
@ -1,196 +0,0 @@
|
|||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7318-g129462d Mon Dec 8 22:08:18 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
WARNING: Ignoring S4-assertion-width violation.
|
||||
Stepping B3
|
||||
2 CPU cores
|
||||
AMT enabled
|
||||
capable of DDR2 of 800 MHz or lower
|
||||
VT-d enabled
|
||||
GMCH: GS45, using low power mode by default
|
||||
TXT enabled
|
||||
Render frequency: 533 MHz
|
||||
IGD enabled
|
||||
PCIe-to-GMCH enabled
|
||||
GMCH supports DDR3 with 1067 MT or less
|
||||
GMCH supports FSB with up to 1067 MHz
|
||||
SMBus controller enabled.
|
||||
0:50:b
|
||||
2:51:b
|
||||
DDR mask 5, DDR 3
|
||||
Bank 0 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: F
|
||||
Row addr bits: 14
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 2
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 15
|
||||
Max clock: 533 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x01c0
|
||||
Bank 1 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: B
|
||||
Row addr bits: 15
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 1
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 12
|
||||
Max clock: 666 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x07e0
|
||||
Trying CAS 7, tCK 15.
|
||||
Found compatible clock / CAS pair: 533 / 7.
|
||||
Timing values:
|
||||
tCLK: 15
|
||||
tRAS: 20
|
||||
tRP: 7
|
||||
tRCD: 7
|
||||
tRFC: 104
|
||||
tWR: 8
|
||||
tRD: 11
|
||||
tRRD: 4
|
||||
tFAW: 20
|
||||
tWL: 6
|
||||
Changing memory frequency: old 3, new 6.
|
||||
Setting IGD memory frequencies for VCO #1.
|
||||
SFF platform unsupported in RCOMP initialization.
|
||||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7318-g129462d Mon Dec 8 22:08:18 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
Interrupted RAM init, reset required.
|
||||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7318-g129462d Mon Dec 8 22:08:18 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
Stepping B3
|
||||
2 CPU cores
|
||||
AMT enabled
|
||||
capable of DDR2 of 800 MHz or lower
|
||||
VT-d enabled
|
||||
GMCH: GS45, using low power mode by default
|
||||
TXT enabled
|
||||
Render frequency: 533 MHz
|
||||
IGD enabled
|
||||
PCIe-to-GMCH enabled
|
||||
GMCH supports DDR3 with 1067 MT or less
|
||||
GMCH supports FSB with up to 1067 MHz
|
||||
SMBus controller enabled.
|
||||
0:50:b
|
||||
2:51:b
|
||||
DDR mask 5, DDR 3
|
||||
Bank 0 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: F
|
||||
Row addr bits: 14
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 2
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 15
|
||||
Max clock: 533 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x01c0
|
||||
Bank 1 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: B
|
||||
Row addr bits: 15
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 1
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 12
|
||||
Max clock: 666 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x07e0
|
||||
Trying CAS 7, tCK 15.
|
||||
Found compatible clock / CAS pair: 533 / 7.
|
||||
Timing values:
|
||||
tCLK: 15
|
||||
tRAS: 20
|
||||
tRP: 7
|
||||
tRCD: 7
|
||||
tRFC: 104
|
||||
tWR: 8
|
||||
tRD: 11
|
||||
tRRD: 4
|
||||
tFAW: 20
|
||||
tWL: 6
|
||||
Changing memory frequency: old 3, new 6.
|
||||
Setting IGD memory frequencies for VCO #1.
|
||||
SFF platform unsupported in RCOMP initialization.
|
||||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7318-g129462d Mon Dec 8 22:08:18 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
Interrupted RAM init, reset required.
|
||||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7318-g129462d Mon Dec 8 22:08:18 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
Stepping B3
|
||||
2 CPU cores
|
||||
AMT enabled
|
||||
capable of DDR2 of 800 MHz or lower
|
||||
VT-d enabled
|
||||
GMCH: GS45, using low power mode by default
|
||||
TXT enabled
|
||||
Render frequency: 533 MHz
|
||||
IGD enabled
|
||||
PCIe-to-GMCH enabled
|
||||
GMCH supports DDR3 with 1067 MT or less
|
||||
GMCH supports FSB with up to 1067 MHz
|
||||
SMBus controller enabled.
|
||||
0:50:b
|
||||
2:51:b
|
||||
DDR mask 5, DDR 3
|
||||
Bank 0 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: F
|
||||
Row addr bits: 14
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 2
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 15
|
||||
Max clock: 533 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x01c0
|
||||
Bank 1 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: B
|
||||
Row addr bits: 15
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 1
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 12
|
||||
Max clock: 666 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x07e0
|
||||
Trying CAS 7, tCK 15.
|
||||
Found compatible clock / CAS pair: 533 / 7.
|
||||
Timing values:
|
||||
tCLK: 15
|
||||
tRAS: 20
|
||||
tRP: 7
|
||||
tRCD: 7
|
||||
tRFC: 104
|
||||
tWR: 8
|
||||
tRD: 11
|
||||
tRRD: 4
|
||||
tFAW: 20
|
||||
tWL: 6
|
||||
Changing memory frequency: old 3, new 6.
|
||||
Setting IGD memory frequencies for VCO #1.
|
||||
SFF platform unsupported in RCOMP initialization.
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
|
|
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
|||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7551-ge420139-dirty Wed Dec 10 16:34:05 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
WARNING: Ignoring S4-assertion-width violation.
|
||||
Stepping B3
|
||||
2 CPU cores
|
||||
AMT enabled
|
||||
capable of DDR2 of 800 MHz or lower
|
||||
VT-d enabled
|
||||
GMCH: GS45, using high performance mode by default
|
||||
TXT enabled
|
||||
Render frequency: 533 MHz
|
||||
IGD enabled
|
||||
PCIe-to-GMCH enabled
|
||||
GMCH supports DDR3 with 1067 MT or less
|
||||
GMCH supports FSB with up to 1067 MHz
|
||||
SMBus controller enabled.
|
||||
0:50:b
|
||||
2:51:b
|
||||
DDR mask 5, DDR 3
|
||||
Bank 0 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: F
|
||||
Row addr bits: 14
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 2
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 15
|
||||
Max clock: 533 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x01c0
|
||||
Bank 1 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: B
|
||||
Row addr bits: 15
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 1
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 12
|
||||
Max clock: 666 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x07e0
|
||||
Trying CAS 7, tCK 15.
|
||||
Found compatible clock / CAS pair: 533 / 7.
|
||||
Timing values:
|
||||
tCLK: 15
|
||||
tRAS: 20
|
||||
tRP: 7
|
||||
tRCD: 7
|
||||
tRFC: 104
|
||||
tWR: 8
|
||||
tRD: 11
|
||||
tRRD: 4
|
||||
tFAW: 20
|
||||
tWL: 6
|
||||
Changing memory frequency: old 3, new 6.
|
||||
Setting IGD memory frequencies for VCO #1.
|
||||
Memory configured in dual-channel assymetric mode.
|
||||
Memory map:
|
||||
TOM = 384MB
|
||||
TOLUD = 384MB
|
||||
TOUUD = 384MB
|
||||
REMAP: base = 65535MB
|
||||
limit = 0MB
|
||||
usedMEsize: 0MB
|
||||
Performing Jedec initialization at address 0x00000000.
|
||||
Performing Jedec initialization at address 0x08000000.
|
||||
Performing Jedec initialization at address 0x10000000.
|
||||
Final timings for group 0 on channel 0: 6.1.0.3.2
|
||||
Final timings for group 1 on channel 0: 6.0.2.6.3
|
||||
Final timings for group 2 on channel 0: 6.1.2.0.1
|
||||
Final timings for group 3 on channel 0: 6.1.0.7.3
|
||||
Timing under-/overflow during receive-enable calibration.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,158 +0,0 @@
|
|||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7551-ge420139-dirty Wed Dec 10 16:34:05 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
WARNING: Ignoring S4-assertion-width violation.
|
||||
Stepping B3
|
||||
2 CPU cores
|
||||
AMT enabled
|
||||
capable of DDR2 of 800 MHz or lower
|
||||
VT-d enabled
|
||||
GMCH: GS45, using high performance mode by default
|
||||
TXT enabled
|
||||
Render frequency: 533 MHz
|
||||
IGD enabled
|
||||
PCIe-to-GMCH enabled
|
||||
GMCH supports DDR3 with 1067 MT or less
|
||||
GMCH supports FSB with up to 1067 MHz
|
||||
SMBus controller enabled.
|
||||
0:50:ff
|
||||
2:51:b
|
||||
DDR mask 4, DDR 3
|
||||
Bank 1 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: B
|
||||
Row addr bits: 15
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 1
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 12
|
||||
Max clock: 666 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x07e0
|
||||
DIMMs support 666 MHz, but chipset only runs at up to 533. Limiting...
|
||||
Trying CAS 7, tCK 15.
|
||||
Found compatible clock / CAS pair: 533 / 7.
|
||||
Timing values:
|
||||
tCLK: 15
|
||||
tRAS: 20
|
||||
tRP: 7
|
||||
tRCD: 7
|
||||
tRFC: 104
|
||||
tWR: 8
|
||||
tRD: 11
|
||||
tRRD: 4
|
||||
tFAW: 20
|
||||
tWL: 6
|
||||
Changing memory frequency: old 3, new 6.
|
||||
Setting IGD memory frequencies for VCO #1.
|
||||
Memory configured in single-channel mode.
|
||||
Memory map:
|
||||
TOM = 128MB
|
||||
TOLUD = 128MB
|
||||
TOUUD = 128MB
|
||||
REMAP: base = 65535MB
|
||||
limit = 0MB
|
||||
usedMEsize: 0MB
|
||||
Performing Jedec initialization at address 0x00000000.
|
||||
Final timings for group 0 on channel 1: 6.0.2.6.4
|
||||
Final timings for group 1 on channel 1: 6.0.2.6.4
|
||||
Final timings for group 2 on channel 1: 6.0.2.8.3
|
||||
Final timings for group 3 on channel 1: 6.0.2.8.6
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 0 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 0 on channel 1: 10.4
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 0 on channel 1: 5.2
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 1 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 1 on channel 1: 11.2
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 1 on channel 1: 5.5
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 2 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 2 on channel 1: 10.5
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 2 on channel 1: 5.2
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 3 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 3 on channel 1: 9.7
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 3 on channel 1: 4.7
|
||||
Timing overflow during read training.
|
||||
Read training failure: lower bound.
|
||||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7551-ge420139-dirty Wed Dec 10 16:34:05 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
Interrupted RAM init, reset required.
|
||||
USB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot-4.0-7551-ge420139-dirty Wed Dec 10 16:34:05 GMT 2014 starting...
|
||||
running main(bist = 0)
|
||||
Stepping B3
|
||||
2 CPU cores
|
||||
AMT enabled
|
||||
capable of DDR2 of 800 MHz or lower
|
||||
VT-d enabled
|
||||
GMCH: GS45, using high performance mode by default
|
||||
TXT enabled
|
||||
Render frequency: 533 MHz
|
||||
IGD enabled
|
||||
PCIe-to-GMCH enabled
|
||||
GMCH supports DDR3 with 1067 MT or less
|
||||
GMCH supports FSB with up to 1067 MHz
|
||||
SMBus controller enabled.
|
||||
0:50:ff
|
||||
2:51:b
|
||||
DDR mask 4, DDR 3
|
||||
Bank 1 populated:
|
||||
Raw card type: B
|
||||
Row addr bits: 15
|
||||
Col addr bits: 10
|
||||
byte width: 1
|
||||
page size: 1024
|
||||
banks: 8
|
||||
ranks: 1
|
||||
tAAmin: 105
|
||||
tCKmin: 12
|
||||
Max clock: 666 MHz
|
||||
CAS: 0x07e0
|
||||
DIMMs support 666 MHz, but chipset only runs at up to 533. Limiting...
|
||||
Trying CAS 7, tCK 15.
|
||||
Found compatible clock / CAS pair: 533 / 7.
|
||||
Timing values:
|
||||
tCLK: 15
|
||||
tRAS: 20
|
||||
tRP: 7
|
||||
tRCD: 7
|
||||
tRFC: 104
|
||||
tWR: 8
|
||||
tRD: 11
|
||||
tRRD: 4
|
||||
tFAW: 20
|
||||
tWL: 6
|
||||
Setting IGD memory frequencies for VCO #1.
|
||||
Memory configured in single-channel mode.
|
||||
Memory map:
|
||||
TOM = 128MB
|
||||
TOLUD = 128MB
|
||||
TOUUD = 128MB
|
||||
REMAP: base = 65535MB
|
||||
limit = 0MB
|
||||
usedMEsize: 0MB
|
||||
Performing Jedec initialization at address 0x00000000.
|
||||
Final timings for group 0 on channel 1: 6.0.2.7.6
|
||||
Final timings for group 1 on channel 1: 6.0.2.6.6
|
||||
Final timings for group 2 on channel 1: 6.0.2.8.7
|
||||
Final timings for group 3 on channel 1: 6.1.0.2.5
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 0 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 0 on channel 1: 10.3
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 0 on channel 1: 5.1
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 1 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 1 on channel 1: 11.3
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 1 on channel 1: 5.5
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 2 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 2 on channel 1: 10.5
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 2 on channel 1: 5.2
|
||||
Lower bound for byte lane 3 on channel 1: 0.0
|
||||
Upper bound for byte lane 3 on channel 1: 9.6
|
||||
Final timings for byte lane 3 on channel 1: 4.7
|
||||
Timing overflow during read training.
|
||||
Read training failure: lower bound.
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@ article titled [What is Canoeboot?](../about.md).
|
|||
Installing Canoeboot
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
- [What systems can I use Canoeboot on?](hardware/)
|
||||
- [How to install Canoeboot](install/)
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation related to operating systems
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,10 +11,9 @@ Canoeboot. Новини, включаючи оголошення про випу
|
|||
What is Canoeboot? An article is available for that; please read the
|
||||
article titled [What is Canoeboot?](../about.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Встановлення Canoeboot
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
Встановлення libreboot
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
- [На яких системах я можу встановлювати Canoeboot?](hardware/)
|
||||
- [Як встановити Canoeboot](install/)
|
||||
|
||||
Документація, яка має відношення до операційних систем
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,8 +12,7 @@ article titled [What is Canoeboot?](../about.md).
|
|||
安装 canoeboot
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
- [哪些机器上可以使用 canoeboot?](hardware/)
|
||||
- [如何安装 canoeboot](install/)
|
||||
- [如何安装 Canoeboot](install/)
|
||||
|
||||
操作系统相关文档
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: D510MO flashing tutorial
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their Intel D510MO
|
||||
motherboard while they still have the original BIOS present.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: D410PT is another designation and it's the same board. Flash the same ROM.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash chip size {#flashchips}
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Use this to find out:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions {#clip}
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [spi.md](spi.md) for how to re-flash externally.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,14 +1,103 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Intel D945GCLF flashing tutorial
|
||||
title: Intel D945GCLF desktop board
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their Intel D945GCLF
|
||||
motherboard while they still have the original BIOS present.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 alt="D945GCLF" class="p" src="https://av.canoeboot.org/d945gclf/d945gclf.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.canoeboot.org/d945gclf/d945gclf.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Intel |
|
||||
| **Name** | D945GCLF/D945GCLF2D |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2008 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Calistoga 945GC |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Atom |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | ? |
|
||||
| **Display** | None. |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 2GB |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | Intel BIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Not present. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8 512KiB |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works without blobs;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
W*: Works with blobs;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
P*: Partially works with blobs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | | Notes |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|-------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N | |
|
||||
| **Display** | - | |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ | |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ | |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ | |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | - | |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|--------------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Doesn't work |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Doesn't work |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
If you just want flashing instructions, go to
|
||||
[../install/d945gclf.md](../install/d945gclf.md)
|
||||
>>>>>>> 09844d62 (simplify docs/install and merge docs/hardware)
|
||||
|
||||
D945GCLF2D also reported working by a user.
|
||||
|
||||
For information about this board, go to
|
||||
[../hardware/d945gclf.md](../hardware/d945gclf.md)
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This board is a mini-itx desktop board for 2008. It uses an atom 230,
|
||||
which is a singe core CPU but it is hyperthreaded so it appears to have
|
||||
2 thread to the OS. The flash chip is very small, 512KiB, so grub2 does
|
||||
not fit, which is why Canoeboot has to use seabios on this target. Full
|
||||
disk encryption like on other supported targets will not be possible, so
|
||||
plan accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
This board has a 945gc chipset which is the desktop equivalent of 945gm
|
||||
which can be found in the Lenovo x60/t60 or macbook2,1. This chipset
|
||||
features an ICH7 southbridge. It has 1 DIMM slot that can accommodate up
|
||||
to 2G of DDR2 RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
Connectivity-wise it has 1 PCI slot, a 10/100 ethernet port, 4 usb slot
|
||||
and 4 usb ports, with one internal header and 2 SATA ports.
|
||||
|
||||
The D945GCLF2 is an upgraded version of this board. The differences are:
|
||||
1 more USB header, 10/100/1000 ethernet and a dual core cpu (also
|
||||
hyperthreaded). Since the board is almost identical (and coreboot code
|
||||
seem to indicate that it works, since MAX\_CPU=4 is set), it is believed
|
||||
that it should also work but this is untested.
|
||||
|
||||
Remarks about vendor bios:
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Without Canoeboot or Libreboot this board is completely useless, since the
|
||||
vendor bios is very bad. It cannot boot from any HDD whether it is
|
||||
connected to the SATA port or USB. With Canoeboot it works just
|
||||
fine.
|
||||
|
||||
- The vendor bios write protects the flash so it requires external
|
||||
flashing to install Canoeboot on this device. Once Canoeboot is
|
||||
flashed there is no problem to update the firmware internally
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an image of the board:\
|
||||
\
|
||||
Here is an image of the D945GCLF2 board:\
|
||||
{width="80%" height="80%"}\
|
||||
And SPI SOIC8 flash chip\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions {#clip}
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,3 +106,31 @@ Refer to [spi.md](spi.md) for how to re-flash externally.
|
|||
|
||||
Here is an image of the flash chip:\
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
How to replace thermal paste and fan
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This board comes with very crappy disposable loud fan, that one has no
|
||||
bearings, which can not be repaired or oiled properly, do not waste your
|
||||
time trying to fix it, just buy one chinese same size fan\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Make sure that new one has same wiring\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
This is a new one, with bearing and maintenable\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Now remove the both coolers rotating them a bit, slowly, then clean both
|
||||
silicons and both coolers (removing cmos battery first is recommended)\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Put a little bit of non conductive thermal paste on both silicons (only
|
||||
cpu silicon iis shown on that image)\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
|
||||
Before assembling new fan, some need new longer screws, make sure having
|
||||
these (on the left is original one, too short for new fan)\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
After that, assemble your new fan into CPU cooler\
|
||||
{width="50%" height="50%"}\
|
||||
Finally assemle both coolers on both chips, do not forget put in the CPU
|
||||
fan connector back, and you are done.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,10 +1,109 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: GA-G41M-ES2L flashing tutorial
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
title: Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L desktop board
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<<<<<<< HEAD
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their Intel GA-G41M-ES2L
|
||||
motherboard while they still have the original BIOS present.
|
||||
=======
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
GA-G41M-ES2L
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Gigabyte |
|
||||
| **Name** | GA-G41M-ES2L |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel G41 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Extreme/Quad/Duo,
|
||||
Pentium Extreme/D/4 Extreme/4/Celeron |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Integrated |
|
||||
| **Display** | None. |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 8GB (2x4GB DDR2-800) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | AWARD BIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be disabled |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | 2x8Mbit |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works without blobs;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
W*: Works with blobs;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
P*: Partially works with blobs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display** | - |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | P+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | P+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | - |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Slow! |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This is a desktop board using intel hardware (circa \~2009, ICH7
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the ThinkPad X200. It can make
|
||||
for quite a nifty desktop. Powered by Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
IDE on the board is untested, but it might be possible to use a SATA HDD
|
||||
using an IDE SATA adapter. The SATA ports do work, but it's IDE emulation. The
|
||||
emulation is slow in DMA mode sia SeaBIOS, so SeaBIOS is configured to use PIO
|
||||
mode on this board. This SeaBIOS configuration does not affect the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
You need to set a custom MAC address in Linux for the NIC to work.
|
||||
In /etc/network/interfaces on debian-based systems like Debian or
|
||||
Devuan, this would be in the entry for your NIC:\
|
||||
hwaddress ether macaddressgoeshere
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively:
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool canoeboot.rom extract -n rt8168-macaddress -f rt8168-macaddress
|
||||
|
||||
Modify the MAC address in the file `rt8168-macaddress` and then:
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool canoeboot.rom remove -n rt8168-macaddress
|
||||
cbfstool canoeboot.rom add -f rt8168-macaddress -n rt8168-macaddress -t raw
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have a different MAC address hardcoded. In the above example, the ROM
|
||||
image is named `canoeboot.rom` for your board. You can find cbfstool
|
||||
under `cbutils/` after running the following command
|
||||
in the build system:
|
||||
|
||||
./mk -d coreboot TREENAME
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about using the build system, cbmk, here:\
|
||||
[Canoeboot build instructions](../build/)
|
||||
|
||||
RAM
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
**This board is very picky with RAM. If it doesn't boot, try an EHCI debug
|
||||
dongle, serial usb adapter and null modem cable, or spkmodem, to get a
|
||||
coreboot log to see if it passed raminit.**
|
||||
|
||||
Kingston 8 GiB Kit KVR800D2N6/8G with Elpida Chips E2108ABSE-8G-E
|
||||
|
||||
this is a 2x4GB setup and these work quite well, according to a user on IRC.
|
||||
|
||||
Nanya NT2GT64U8HD0BY-AD with 2 GiB of NT5TU128M8DE-AD chips works too.
|
||||
|
||||
Many other modules will probably work just fine, but raminit is very picky on
|
||||
this board. Your mileage *will* fluctuate, wildly.
|
||||
>>>>>>> 09844d62 (simplify docs/install and merge docs/hardware)
|
||||
|
||||
MAC ADDRESS
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,16 +1,85 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Installation instructions
|
||||
title: Canoeboot installation guides
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Flashprog
|
||||
=========
|
||||
This article will teach you how to install Canoeboot, on any of the supported
|
||||
laptop, desktop and server motherboards.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.**
|
||||
**ALWAYS remember to make a backup of the current flash, when overwriting it,
|
||||
regardless of what firmware you currently have and what firmware you're
|
||||
re-flashing it with; this includes updates between Canoeboot releases. Use
|
||||
the `-r` option in flashprog instead `-w`, to read from the flash.**
|
||||
|
||||
Install Canoeboot via external flashing
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Externally rewrite 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol](spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
You are strongly advised to *have* an external flashing setup, and make sure
|
||||
it works, before attempting internal flashing. This, in addition to making
|
||||
a backup of the current flash contents, prior to flashing, whether you dump
|
||||
externally or internally - if only external flashing is available, then it's
|
||||
usually the case that only external dumping is available too.
|
||||
|
||||
This section relates to installing canoeboot on supported targets.
|
||||
|
||||
Which systems are supported by Canoeboot?
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
|
||||
Before actually reading the installation guides, please ensure that your
|
||||
system is fully supported by Canoeboot. More information about the Canoeboot
|
||||
build system can be found in the [cbmk maintenance manual](../maintain/).
|
||||
|
||||
With x86 machines, you can use the SeaBIOS or GNU GRUB payloads. On ARM
|
||||
systems, you can use the U-Boot payload (coreboot still initialises hardware).
|
||||
|
||||
Canoeboot currently supports the following systems:
|
||||
|
||||
Servers (AMD, x86)
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS KFSN4-DRE motherboard](kfsn4-dre.md)
|
||||
- [ASUS KGPE-D16 motherboard](kgpe-d16.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Desktops (AMD, Intel, x86)
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [Acer G43T-AM3](acer_g43t-am3.md)
|
||||
- Apple iMac 5,2
|
||||
- [ASUS KCMA-D8 motherboard](kcma-d8.md)
|
||||
- Dell OptiPlex 7010 **MT** (known to work, using the T1650 ROM, but more
|
||||
research is needed) - 9010 also known to work. No GPIO changes, so it should
|
||||
be safe to flash.
|
||||
- [Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L motherboard](ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
||||
- Intel D510MO and D410PT motherboards
|
||||
- [Intel D945GCLF](d945gclf.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Laptops (Intel, x86)
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [Apple MacBook1,1 and MacBook2,1](macbook21.md)
|
||||
- [Dell Latitude E6400, E6400 XFR and E6400 ATG](latitude.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R400](r400.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad R500
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T400 / T400S](t400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T500 / W500](t500.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad T520 / W520 / T530 / W530
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad T60, X60, X60S, X60 Tablet (with Intel GPU)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad X200 / X200S / X200 Tablet](x200.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Laptops (ARM, with U-Boot payload)
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS Chromebook Flip C101 (gru-bob)](chromebooks.md)
|
||||
- [Samsung Chromebook Plus (v1) (gru-kevin)](chromebooks.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Emulation
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
- [Qemu x86 and arm64](../misc/emulation.md)
|
||||
|
||||
**Disable security before flashing**
|
||||
================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,144 +88,106 @@ sure to re-enable them after you're finished.**
|
|||
|
||||
**See: [Disabling /dev/mem protection](devmem.md)**
|
||||
|
||||
PRECAUTIONS
|
||||
===========
|
||||
ROM image file names
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
Canoeboot flashing can be risky business. Please ensure that you have external
|
||||
flashing equipment, in case anything goes wrong. The general rule of thumb with
|
||||
firmware is this: if it's non-free, replace it, but if you're already running
|
||||
free firmware and it works nicely for you, you do not need to update it.
|
||||
However, you might want to tweak it or try out newer releases of Canoeboot if
|
||||
they have bug fixes for your board, and/or new security fixes.
|
||||
Canoeboot ROM images are named like
|
||||
this: `payload_board_inittype_displaytype_keymap.rom`
|
||||
|
||||
If you're already running libre firmware on your board, you should decide for
|
||||
sure whether you wish to risk it. See changelogs on
|
||||
the [release announcements via the news page](/news/) and decide for yourself.
|
||||
The `payload` option can be SeaBIOS, SeaGRUB or U-Boot. If GRUB is available
|
||||
on a given board, in flash, both SeaBIOS and SeaGRUB are provided; SeaBIOS
|
||||
images still have GRUB available via the SeaBIOS menu, and SeaGRUB means that
|
||||
SeaBIOS automatically loads GRUB from flash first (but you can still choose
|
||||
something else, by pressing ESC in SeaBIOS when prompted).
|
||||
|
||||
About ROM image file names
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
Inittype can be `libgfxinit`, `vgarom` or `normal`. The `libgfxinit` option
|
||||
means coreboot provides native video initialisation, for onboard graphics.
|
||||
The `vgarom` option means coreboot executes a VGA option ROM for video
|
||||
initialisation. The `normal` option means coreboot provides no video
|
||||
initialisation, via VGA ROM or native code.
|
||||
|
||||
Init types and display mode
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
Displaytype can be `txtmode` or `corebootfb` - if inittype is `normal`, this
|
||||
is ignored because `txtmode` is assumed.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: regardless of init type, on desktops, an external/add-on GPU can always
|
||||
be used. On laptop hardware in Canoeboot, libgfxinit will always be used. On
|
||||
desktop/server hardware, if available, libgfxinit will also always be used by
|
||||
default (but in that setup, SeaBIOS can be used if you want to use an add-on
|
||||
graphics card, e.g. on KCMA-D8, KGPE-D16, GA-G41M-ES2L)
|
||||
If `payload` is `seabios` instead of `seagrub`, no keymaps are inserted into
|
||||
flash and only US QWERTY is assumed, otherwise the keymap refers to what is used
|
||||
in GRUB on `seagrub` payload setups.
|
||||
|
||||
**This means that on desktop hardware such as KCMA-D8, KGPE-D16, G43T-AM3,
|
||||
GA-G41M-ES2L and others, you can use either the internal GPU or an add-on
|
||||
PCI-E graphics card. Simply use a ROM image that starts with SeaBIOS, and you
|
||||
can use both. On desktop/server hardware, libgfxinit simply means that you
|
||||
CAN use the internal graphics chip, but you don't have to; external add-on
|
||||
GPUs will also still work! However, if libgfxinit is enabled, that disables
|
||||
coreboot from loading/executing PCI option ROMs which means you MUST use SeaBIOS
|
||||
if you wish to use the add-on cards!**
|
||||
If you use a libgfxinit image on a desktop machine, you can still insert a
|
||||
graphics card and it'll work just fine; its own VGA option ROM will be
|
||||
executed instead, if the primary payload is SeaBIOS, whether that be pure
|
||||
SeaBIOS or a SeaGRUB setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### libgfxinit
|
||||
EC firmware updates
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
In this setup, on supported systems, coreboot's own native video initialization
|
||||
code is used. This is referred to generically as libgfxinit, which is coreboot's
|
||||
library in `3rdparty/libgfxinit` but not all boards with native video
|
||||
initialization use libgfxinit; some of them are using coreboot's older style
|
||||
of video initialization method, written purely in C.
|
||||
Obviously, free EC firmware would be preferable, but it is not the case on
|
||||
all machine. We would like to have free EC firmware on more machines, but for
|
||||
now, we must rely on the vendor in a lot of cases. The EC is usually on a
|
||||
separate flash, so you wouldn't think about it unless you knew it was there;
|
||||
this is exactly why it's mentioned, so that you think about it,
|
||||
[because proprietary software is bad](../../news/policy.md).
|
||||
|
||||
#### corebootfb (libgfxinit)
|
||||
In many cases, the EC firmware must be updated on a separate IC to the main
|
||||
boot flash, and this can usually only be done with the vendor's own tool,
|
||||
running from the vendor boot firmware, and usually only on Windows, because
|
||||
they provide EC and BIOS/UEFI updates in the same utility. Find out what you
|
||||
need to do for your machine before installing Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
high resolution coreboot framebuffer used on startup
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware)
|
||||
|
||||
#### txtmode (libgfxinit)
|
||||
Updating the EC can sometimes provide benefit depending on the vendor. For
|
||||
example, they might fix power issues that could then enhance battery life.
|
||||
|
||||
int10h text mode is used on startup.
|
||||
ThinkPads
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
### vgarom
|
||||
See: <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: no configs in Canoeboot are currently available that use this method.
|
||||
Otherwise, check the Lenovo website to find the update utility for your
|
||||
mainboard.
|
||||
|
||||
With this method, coreboot is finding, loading and executing a VGA option ROM
|
||||
for your graphics hardware. This would not be done on laptops, because that
|
||||
implies supplying non-free binary blobs in Canoeboot, so this setup would only
|
||||
ever be provided on desktop hardware where no GPU exists or where it is
|
||||
desirable for you to use an external/add-on graphics card
|
||||
Other
|
||||
-----
|
||||
|
||||
#### vesafb (vgarom)
|
||||
The same wisdom applies to other laptop vendors.
|
||||
|
||||
high resolution VESA framebuffer used on startup. This is equivalent
|
||||
to `corebootfb` (high resolution framebuffer), but for setups where a VGA
|
||||
Option ROM is used.
|
||||
Non-laptops typically do not have embedded controllers in them.
|
||||
|
||||
#### txtmode (vgarom)
|
||||
Canoeboot installation instructions
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
int10h text mode is used on startup
|
||||
In general, if Canoeboot is already running, you can skip
|
||||
towards the final section on this page, which provides general internal
|
||||
flashing instructions. Internal flashing is when you flash the target machine
|
||||
from the target machine, inside an operating system running on it.
|
||||
|
||||
### normal
|
||||
Some boards require special steps, even if Canoeboot is already running,
|
||||
for example if you [locked down the flash](../linux/grub_hardening.md).
|
||||
|
||||
int10h text mode startup is implied here. The `vesafb` mode is unavailable here.
|
||||
For `vesafb` mode, please use init type `vgarom`; most useful for GRUB payloads
|
||||
or perhaps Tianocore.
|
||||
|
||||
In this setup, coreboot is neither implementing libgfxinit / native graphics
|
||||
initialization nor is it finding/loading/executing VGA option ROMs. In this
|
||||
setup, SeaBIOS would most likely be used for that.
|
||||
|
||||
The `normal` setup is supported in the Canoeboot build system, but not
|
||||
currently used. It is there for desktop hardware that will be added in the
|
||||
future, where those desktop boards do not have an onboard GPU and therefore an
|
||||
add-on GPU is always used..
|
||||
|
||||
Payload names
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
### grub
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images with just `grub` in the file name will start first with the GRUB
|
||||
payload. They may or may not also provide other payloads in the menu, such as
|
||||
memtest86+, SeaBIOS, Tianacore and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
### seabios
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images with just `seabios` in the file name will start first with the
|
||||
SeaBIOS payload. They will only contain SeaBIOS, but may also contain memtest as
|
||||
an option in the boot menu.
|
||||
|
||||
### seabios\_withgrub
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images that have `seabios_withgrub` in the file name start with SeaBIOS
|
||||
first, but also have GRUB available in the boot menu when you press ESC.
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images with this and `grubonly` in the image start SeaBIOS, but only load
|
||||
GRUB from SeaBIOS and the SeaBIOS menu is disabled. Use these images if you
|
||||
only want GRUB; they are provided on systems that only have VGA ROM-based
|
||||
initialisation, usually discrete graphics cards on desktop machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Which systems are supported?
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
||||
[Refer to the hardware compatibility page](../hardware/)
|
||||
Therefore, before following generic guides, make sure to check first whether
|
||||
your board has special instructions, otherwise use the generic guide at the
|
||||
end of this article.
|
||||
|
||||
Intel GbE MAC address (IFD-based systems)
|
||||
=====================================================================
|
||||
---------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the MAC address in flash, on these machines. See:
|
||||
[nvmutil documentation](nvmutil.md)
|
||||
On all Intel platforms except X4X (e.g. Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L) and i945
|
||||
ones (e.g. ThinkPad X60, ThinkPad T60, MacBook2,1), an Intel Flash Descriptor is
|
||||
used. If the board has Intel gigabit ethernet, the MAC address is included in
|
||||
flash, and can (must) be changed prior to installation.
|
||||
|
||||
The MAC address is stored in a region of the boot flashed called *GbE NVM*
|
||||
which is short for *gigabit ethernet non-volatile memory*. Refer to the
|
||||
following article:
|
||||
You can use [nvmutil](nvmutil.md) to change the MAC address. You will perform
|
||||
this modification to the ROM image, before flashing it.
|
||||
|
||||
For GM45/ICH9M systems (e.g. ThinkPad X200/T400, Dell Latitude E6400), see:
|
||||
[ich9utils documentation](ich9utils.md) (you can also use nvmutil, see link
|
||||
above)
|
||||
Flash lockdown / boot security
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Canoeboot puts a default MAC address in the available ROM images, but this is
|
||||
a generic MAC address and it's identical on every ROM image. Technically, you
|
||||
can use it but if you encounter other Canoeboot users on the same ethernet
|
||||
switch, using the same physical network as you, you will encounter a MAC
|
||||
address conflict.
|
||||
This is referred to informally as *Secure libreBoot*.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: R500 thinkpads do not have an Intel gigabit ethernet NIC, so on that
|
||||
laptop you can just flash the default ROM and you do not have to worry.
|
||||
Full flash lockdown is possible, with cryptographic verification of your
|
||||
Linux kernel and other files, using special features in the GRUB payload.
|
||||
|
||||
There are also some Intel X4X platforms that use an ICH10 southbridge,
|
||||
supported in Canoeboot, but these are flashed in a *descriptorless* setup,
|
||||
|
|
@ -167,248 +198,158 @@ an Intel PHY module and the onboard NIC is usable).
|
|||
Install via host CPU (internal flashing)
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
|
||||
On all mainboards is a built-in programmer, which can read, erase and rewrite
|
||||
the boot flash. However, it is not always usable by default. For example, it
|
||||
may be configured to restrict write privileges by the host CPU.
|
||||
See: [GRUB hardening / Secure libreBoot](../linux/grub_hardening.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In some situations, the host CPU can rewrite/erase/dump the boot flash.
|
||||
This is called *internal flashing*. This means that you will run software,
|
||||
namely `flashprog`, to read/erase/write the contents of the boot flash from a
|
||||
running operating system on the target device.
|
||||
If you already did this, it's possible that you may no longer be able to
|
||||
flash internally. If that is the case, you must [flash externally](spi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: please also read the sections further down this page. On some systems,
|
||||
external flashing is required. This means that you power the system down and
|
||||
use a special tool that connects to and reprograms the boot flash.
|
||||
Updating an existing installation
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: in some cases, external flashing is possible but special steps are
|
||||
required. This depends on your mainboard. Again, please read this page
|
||||
carefully.
|
||||
Unless otherwise stated, in sections pertaining to each mainboard below,
|
||||
an existing Canoeboot installation can be updated via internal flashing,
|
||||
without any special steps; simply follow the general internal flashing
|
||||
guide, in the final section further down this page.
|
||||
|
||||
Run flashprog on host CPU
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
If you have an existing Canoeboot installation but you *locked down the flash*,
|
||||
updating it will require external flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
You can simply take any ROM image from the canoeboot project, and flash it.
|
||||
Boot a GNU+Linux distribution on the target device, and install flashprog.
|
||||
If you currently have the factory firmware, you probably need to flash
|
||||
externally; on *some* machines, internal flashing is possible, usually with
|
||||
special steps required that differ from updating an existing installation.
|
||||
>>>>>>> 09844d62 (simplify docs/install and merge docs/hardware)
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, this is not possible or there are other considerations. Please
|
||||
read this section *carefully*.
|
||||
The next sections will pertain to specific mainboards, where indicated,
|
||||
followed by general internal flashing instructions where applicable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Flash chip size
|
||||
|
||||
Use this to find out:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
In the output will be information pertaining to your boot flash.
|
||||
|
||||
### Howto: read/write/erase the boot flash
|
||||
|
||||
How to read the current chip contents:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo flashprog -p internal:laptop=force_I_want_a_brick,boardmismatch=force -r dump.bin
|
||||
|
||||
You should still make several dumps, even if you're flashing internally, to
|
||||
ensure that you get the same checksums. Check each dump using `sha1sum`
|
||||
|
||||
How to erase and rewrite the chip contents:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo flashprog -p internal:laptop=force_I_want_a_brick,boardmismatch=force -w canoeboot.rom
|
||||
|
||||
If you are re-flashing a GM45+ICH9M laptop (e.g. ThinkPad X200/X200S/X200T,
|
||||
T400, T500, R400, W500 etc - but not R500), you should run the ich9gen utility
|
||||
to preserve your mac address.
|
||||
Please read the ich9utils documentation:
|
||||
[/docs/install/ich9utils.html](/docs/install/ich9utils.html)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: `force_I_want_a_brick` is not scary. Do not be scared! This merely disables
|
||||
the safety checks in flashprog. Flashrom and coreboot change a lot, over the years,
|
||||
and sometimes it's necessary to use this option. If you're scared, then just
|
||||
follow the above instructions, but remove that option. So, just use `-p internal`.
|
||||
If that doesn't work, next try `-p internal:boardmismatch=force`. If that doesn't
|
||||
work, try `-p internal:boardmismatch=force,laptop=force_I_want_a_brick`. So long
|
||||
as you *ensure* you're using the correct ROM for your machine, it will be safe
|
||||
to run flashprog. These extra options just disable the safetyl checks in flashprog.
|
||||
There is nothing to worry about.
|
||||
|
||||
If successful, it will either say `VERIFIED` or it will say that the chip
|
||||
contents are identical to the requested image.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: there are exceptions where the above is not possible. Read about them in
|
||||
the sections below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Exceptions
|
||||
|
||||
#### If your boot flash is currently write-protected
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### DELL Latitude laptops
|
||||
Dell Latitude laptops (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See: [Dell Latitude flashing guide](latitude.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### ThinkPad X200/T400/T500/W500/R400/R500 vendor BIOS
|
||||
This applies to all supported Dell Latitude models. Remember to [update the
|
||||
MAC address with nvmutil](nvmutil.md), before flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're running one of these, it cannot be flashed internally if you're still
|
||||
running the non-free Lenovo BIOS firmware.
|
||||
ThinkPad X200/T400/T500/W500/R400/R500
|
||||
--------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
If you're running one of these with Lenovo BIOS, you must externally flash
|
||||
Canoeboot, because the original firmware restricts writes to the flash.
|
||||
|
||||
See notes further down on this page. We have guides for specific thinkpads,
|
||||
related to disassembly and reassembly so that you can access the flash.
|
||||
There machines all use SOIC8/SOIC16 flash ICs. Refer to pages specifically for
|
||||
each machine:
|
||||
|
||||
Please also see notes about the built-in MAC address inside the boot flash, for
|
||||
the onboard NIC (ethernet one); not relevant on R500, which doesn't use an
|
||||
Intel NIC.
|
||||
* [ThinkPad X200](x200.md)
|
||||
* [ThinkPad T400](t400.md)
|
||||
* [ThinkPad R400](r400.md)
|
||||
* [ThinkPad T500/W500](t500.md) (R500 is similar)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Intel D510MO and D410PT running non-free Intel BIOS
|
||||
NOTE: T400S, X200S and X200 Tablet require different steps, because these have
|
||||
WSON8 flash ICs on them, which will require some soldering. Please read
|
||||
the [external flashing guide](spi.md) in the section pertaining to WSON.
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
You can find WSON8 probes online, that are similar to a SOIC8/SOIC16 clip. Your
|
||||
mileage may very, but WSON8 has the same pinout as SOIC8 so you might have some
|
||||
luck with that.
|
||||
|
||||
D410PT is more or less the same board as D510MO, but we would like more info
|
||||
about this board. If you have a D410PT mainboard, please contact the Canoeboot
|
||||
project via IRC and ping `leah` before you flash it. When you do so, please
|
||||
reference this paragraph on this web page.
|
||||
Intel D510MO/D410PT (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
#### Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2l (any firmware)
|
||||
See: [External flashing guide](spi.md) - both boards are compatible with
|
||||
the same image.
|
||||
|
||||
Ignore this section. Internal flashing *is* possible, but there are two chips
|
||||
and you must flash both chips. Refer to the guide:\
|
||||
[Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L installation guide](ga-g41m-es2l.html)
|
||||
Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
#### Macbook1,1 running non-free Apple EFI firmware
|
||||
Internal flashing is possible, from factory BIOS to Canoeboot, but special
|
||||
steps are required.
|
||||
|
||||
This laptop requires external flashing. Remove the mainboard and refer to
|
||||
the [external flashing guide](spi.md); if Canoeboot is already running, you
|
||||
can flash internally.
|
||||
See: [Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L installation guide](ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
||||
|
||||
MacBook2,1 can be flashed internally.
|
||||
Acer G43T-AM3 (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
#### ASUS KFSN4-DRE?
|
||||
See: [Acer G43T-AM3](acer_g43t-am3.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Simply boot GNU+Linux with the default vendor firmware, and flash it internally,
|
||||
but before you do: take a push pin, remove the metal pin, and superglue the
|
||||
plastic part to the chip. Then remove the chip after you booting your
|
||||
GNU+Linux system. Install a new chip, and flash *that*.
|
||||
MacBook 1,1 / 2,1 / iMac 5,2 (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
MacBook *1,1* requires [external flashing](spi.md). MacBook *2,1* can always
|
||||
be flashed internally. iMac 5,2 can be flashed internally.
|
||||
|
||||
Also check the [Macbook2,1 hardware page](macbook21.md)
|
||||
|
||||
ASUS KCMA-D8 / KGPE-D16 (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md) (DIP-8 section) - also look at
|
||||
the [KGPE-D16 hardware page](kgpe-d16.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Further information is available on the [KCMA-D8 page](kcma-d8.md).
|
||||
|
||||
KGPE-D16 installation is essentially the same, with the same type of flash
|
||||
IC (DIP-8). Refer to the external flashing guide.
|
||||
|
||||
ASUS KFSN4-DRE (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This board uses LPC flash in a PLCC32 socket. This coreboot page shows an
|
||||
example of the push pin as a proof of concept:
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Developer_Manual/Tools#Chip_removal_tools>
|
||||
|
||||
#### ASUS KGPE-D16 running non-free ASUS BIOS
|
||||
See: [ASUS KFSN4-DRE guide](kfsn4-dre.md)
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
Hot-swap the flash IC with another one while it's running, and flash it
|
||||
internally.
|
||||
|
||||
#### ASUS KCMA-D8 running non-free ASUS BIOS
|
||||
Intel D945GCLF (vendor BIOS)
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
See: [Intel D945GCLF flashing guide](d945gclf.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### ASUS D945GCLF running non-free Intel BIOS
|
||||
ThinkPad T60/X60/X60Tablet/X60S
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
Only the Intel GPU is compatible. Do not flash the ATI GPU models.
|
||||
|
||||
#### ThinkPad X60/X60S/X60T/T60 with Lenovo BIOS {#flashrom_lenovobios}
|
||||
External flashing guides:
|
||||
|
||||
The sections below will tell you to use staticly linked executables built from
|
||||
Libreboot 20160907 sources, because no Libreboot or Libreboot-based release since
|
||||
then (at least as of 8 May 2024) has provided these, but the ones in
|
||||
Libreboot 20160907 will still work just fine. Libreboot 20160907 is GNU FSDG
|
||||
compliant (it was even one of the three *GNU Libreboot* releases), so FSF fans
|
||||
needn't worry. There won't be any magic numbers. Though, gdb symbols were
|
||||
accidentally not turned off during build so those binaries are quite huge. That's
|
||||
just about the only idiosyncrasy.
|
||||
* [ThinkPad X60](x60_unbrick.md)
|
||||
* [ThinkPad X60 Tablet](x60tablet_unbrick.md)
|
||||
* [ThinkPad T60](t60_unbrick.md)
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE: the section below pertaining to Libreboot 20160907 static binaries references
|
||||
flashrom. Canoeboot recommends flashprog nowadays, but if you're using that
|
||||
utils archive, please note that it is from a time when Canoeboot used
|
||||
flashrom. Use flashrom there as that's what included in those binaries.
|
||||
Canoeboot does not currently document how to patch flashprog for sst/macronix
|
||||
on X60/T60, when going (in software) from lenovobios to canoeboot.**
|
||||
These machines can also be flashed internally, by exploiting a bug
|
||||
in the original Lenovo BIOS. If there's a BIOS password at boot, you should
|
||||
just flash externally.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: If BIOS password auth is enabled, you can clear it by shorting pins on
|
||||
an EEPROM and then resetting the password in Lenovo BIOS, prior to flashing
|
||||
Canoeboot. For T60, see:
|
||||
<https://ounapuu.ee/posts/2022/10/13/recovering-password-locked-thinkpad-t60/>
|
||||
(TODO: link something here for X60)
|
||||
Internal flashing instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
X60 BIOS password (Lenovo): you might find info here:
|
||||
<https://bios-pw.org/>
|
||||
First, please ensure that your CR2032/CMOS battery is working. This is what
|
||||
powers the SRAM containing BIOS settings, and it powers the real-time clock.
|
||||
It also holds the BUC.TS value - this is what we need.
|
||||
|
||||
You can just get bucts from the libreboot project, same thing for the patched
|
||||
flashrom. In the Libreboot 20160907 release, there is a *utility* archive, which
|
||||
has statically compiled executables. They still work just fine on modern
|
||||
systems, and they can be used for this purpose.
|
||||
BUC (Backup Control) register contains a bit called Top Swap (TS). The 64KB
|
||||
bootblock at the top of flash is complemented by a backup Top Swap just above
|
||||
it. The one at the end can't be flashed internally while Lenovo BIOS is running,
|
||||
but the rest of it can be flashed (everything above the main bootblock).
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a list of targets:
|
||||
By setting the TS bit, you can make the machine boot from the backup bootblock.
|
||||
|
||||
* ThinkPad X60/X60S/X60T: flash the X60 ROM
|
||||
* ThinkPad T60 with Intel GPU: flash the T60 ROM
|
||||
* ThinkPad T60 with ATI GPU: flash the Headless T60 ROM (no video init, but you
|
||||
can get a serial console on the RS232 port if you use the Advanced Dock or
|
||||
Advanced Mini Dock. Connect to it from another machine, using null modem
|
||||
cable and USB serial adapter; *Screen* can connect to the serial console
|
||||
and you will run it at 115200 baud rate. agetty/fgetty in GNU+Linux can give
|
||||
you a serial console in your OS)
|
||||
|
||||
Download and build flashprog, using the instructions
|
||||
on [the Git page](../../git.md), and download the `bucts` software using the
|
||||
notes on that very same page.
|
||||
|
||||
You can replace Lenovo BIOS with Canoeboot, using flashprog running on the host
|
||||
CPU. However, there are some considerations.
|
||||
|
||||
Firstly, make sure that the yellow CMOS battery is installed, and functioning
|
||||
correctly. You could check the voltage. The battery is a CR2032
|
||||
coin cell and it *should* be providing a 3V signal. You should check this while
|
||||
it is connected to the board, because this will give a more accurate reading
|
||||
(if the battery is weak, it will have severe voltage drop when there is any
|
||||
load on it, which there will be. This coincell powers the real-time clock and
|
||||
CMOS memory).
|
||||
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS restricts write access, but there is a weakness in it. With a
|
||||
specially patched flashprog binary, you can easily flash it but the top 64KiB
|
||||
region of the boot flash, containing your bootblock, cannot be flashed just
|
||||
yet. However, there is a register called the *Backup Control* or *BUC* register
|
||||
and in that register is a status bit called *Top Swap* or *TS*.
|
||||
|
||||
There are *2* bootblocks possible. The *other* bootblock is below the upper
|
||||
64KiB one, which can't be flashed, but the lower one can. By using bucts, you
|
||||
can set the machine to boot using that lower 64KiB bootblock, which is
|
||||
read-write. You do this by setting the BUC.TS register to 1, using the `bucts`
|
||||
program referenced below.
|
||||
|
||||
The Canoeboot ROM images already have the upper 64KiB bootblock copied to the lower
|
||||
one, so you don't have to worry about copying it yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
If you build flashprog using the Canoeboot build system, there will be three
|
||||
binaries:
|
||||
Download the Libreboot 20160907 utils archive, and in there you will find
|
||||
these binaries:
|
||||
|
||||
* `flashprog`
|
||||
* `flashprog_i945_sst`
|
||||
* `flashprog_i945_mx`
|
||||
|
||||
It's these last two binaries that you should use. Now compile bucts (just
|
||||
run `make` in the bucts source directory).
|
||||
You'll also find the bucts tool. Run it as root:
|
||||
|
||||
Run the bucts tool:
|
||||
./bucts 1
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./bucts 1
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure that your CMOS battery is connected too. Now you must determine whether
|
||||
you have Macronix or SST. An X60/T60 thinkpad will have either an SST or a
|
||||
Macronix chip. The Macronix chip will have "MX" written on the chip. You will
|
||||
use `flashprog_i945_sst` for the SST chip, and `flashprog_i945_mx` for the
|
||||
Macronix chip.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run flashprog (for SST):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./flashprog_i945_sst -p internal -w coreboot.rom
|
||||
|
||||
Or Macronix:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./flashprog_i945_mx -p internal -w coreboot.rom
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: you *can* just run both. One of them will succeed. It is perfectly
|
||||
harmless to run both versions of flashprog. In fact, you should do so!
|
||||
Now run both of these as root:
|
||||
|
||||
./flashrom_i945_sst -p internal -w coreboot.rom
|
||||
./flashrom_i945_mx -p internal -w coreboot.rom
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see a lot of errors. This is normal. You should see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -436,190 +377,103 @@ Your flash chip is in an unknown state.
|
|||
If you see this, rejoice! It means that the flash was successful. Please do not
|
||||
panic. Shut down now, and wait a few seconds, then turn back on again.
|
||||
|
||||
If you *did* run flashrom and it failed to flash, but you set bucts to 1 and
|
||||
shut down, don't worry. Just remove the yellow coin-cell battery (it's underneath
|
||||
the keyboard, connected to the mainboard), wait a minute or two, reconnect the
|
||||
coin-cell and try again from scratch. In this instance, if flashprog didn't do
|
||||
anything, and didn't flash anything, it means you still have Lenovo BIOS but
|
||||
if bucts is set to 1, you can flush it and set it back to 0. BUC.TS is stored in
|
||||
volatile memory, powered by that CR2032 coin-cell battery.
|
||||
The main bootblock still isn't flashed, but you can shut down, wait a few
|
||||
seconds and boot up again. When you do, you'll have Canoeboot. Please make
|
||||
sure to flash a second time, like so:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal -w coreboot.rom
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that everything went well:
|
||||
Canoeboot recommends `flashprog` now, which is a fork of flashrom, but we used
|
||||
flashrom in the 2016 release. The macronix/ssh flashrom binaries there are
|
||||
specifically patched; check the Libreboot 20160907 source code for the actual
|
||||
patches. The patches modify some flash chip definitions in flashrom, to exploit
|
||||
the bug in Lenovo BIOS enabling internal flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash the ROM for a second time. For this second flashing attempt, the upper
|
||||
64KiB bootblock is now read-write. Use the *unpatched* flashprog binary:
|
||||
You must ensure that the second flash is performed, upon reboot, because
|
||||
otherwise if the CR2032 battery dies, bucts will be reset and it will no
|
||||
longer boot.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./flashprog -p internal -w canoeboot.rom
|
||||
When you've done the second flash, which includes overwriting the main
|
||||
bootblock, set bucts back to zero:
|
||||
|
||||
To reset bucts, do this:
|
||||
./bucts 0
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./bucts 0
|
||||
The second flash can be done by simply following the general internal flashing
|
||||
guide further down on this page.
|
||||
|
||||
ONLY set bucts back to 0 if you're sure that the upper 64KiB bootblock is
|
||||
flashed. It is flashed if flashprog said VERIFIED when running the above
|
||||
command.
|
||||
ARM-based Chromebooks
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
If it said VERIFIED, shut down. If it didn't say VERIFIED, make sure bucts is
|
||||
still set to 1, and consult the Canoeboot project on IRC for advice, and avoid
|
||||
shutting down your system until you get help.
|
||||
See: [Chromebook flashing instructions](chromebooks.md)
|
||||
|
||||
If all went well, Canoeboot should now be booting and you should be able to
|
||||
boot into your operating system.
|
||||
NOTE: The generic flashing instructions (later on this page) apply only to
|
||||
the x86 machines, because the Chromebooks still use flashrom with
|
||||
the `-p host` argument instead of `-p internal` when flashing, and you typically
|
||||
need to flash externally, due to Google's security model.
|
||||
|
||||
If you messed up, there are external flashing instructions. See main navigation
|
||||
menu on this page. These "external" instructions teach you how to flash
|
||||
externally, using special equipment (requires disassembling your laptop and
|
||||
removing the mainboard).
|
||||
QEMU (arm64 and x86)
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Install using external flashing equipment
|
||||
=========================================
|
||||
Canoeboot can be used on QEMU (virtual machine), which is useful for debugging
|
||||
payloads and generally trying out Canoeboot, without requiring real hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
In many situations, the host CPU is restricted from rewriting/erasing/dumping
|
||||
the boot flash. In this situations, you must re-flash the chip (containing the
|
||||
boot firmware) externally. This is called *external flashing*.
|
||||
See: [Canoeboot QEMU guide](../misc/emulation.md)
|
||||
|
||||
DO NOT buy CH341A! Read the above link, which explains why you shouldn't use it.
|
||||
CH341A will damage your flash chip, and other components on your mainboard.
|
||||
Install via host CPU (internal flashing)
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
|
||||
How to use external flashing equipment
|
||||
--------------------------------------
|
||||
NOTE: This mainly applies to the x86 machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Externally rewrite 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol](spi.md)
|
||||
Please check other sections listed above, to see if there is anything
|
||||
pertaining to your mainboard. Internal flashing means that you boot GNU+Linux or
|
||||
BSD on the target machine, and run `flashprog` there, flashing the machine
|
||||
directly.
|
||||
|
||||
DELL Latitude laptops
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
**If you can't flash internally, you must [flash externally](spi.md).**
|
||||
|
||||
See: [Dell Latitude flashing guide](latitude.md)
|
||||
Internal flashing is often unavailable with the factory firmware, but it is
|
||||
usually possible when Canoeboot is running (barring special circumstances).
|
||||
|
||||
ASUS KFSN4-DRE
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
Run flashprog on host CPU
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The KFSN4-DRE has an LPC chip. Most people have been flashing these
|
||||
internally, hot-swapping the chip out after boot, preserving the original chip,
|
||||
and using flashprog on a new chip as described above.
|
||||
**Always remember to [insert vendor files](ivy_has_common.md), when using
|
||||
release images. Otherwise, these files are added automatically at build
|
||||
time, when building from source (but they are not present in release images).**
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: Document PLCC32 (LPC) flashing.
|
||||
The [FlexyICE](https://www.coreboot.org/FlexyICE) has been used to flash these
|
||||
chips, but it is hard to find now. A custom flasher may be made such as
|
||||
[flashprog serprog stm32](https://github.com/wosk/stm32-vserprog-lpc) or
|
||||
[teensy flasher](https://www.flashprog.org/Teensy_3.1_SPI_%2B_LPC/FWH_Flasher)
|
||||
### Flash chip size
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Apple Macbook2,1, Macbook1,1 and iMac5,2 (i945 platform)
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Use this to find out:
|
||||
|
||||
iMac5,2 is essentially the same board as Macbook2,1, and it is compatible with
|
||||
Canoeboot.
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Macbook2,1 and MacBook1,1 installation guide](../hardware/macbook21.md)
|
||||
In the output will be information pertaining to your boot flash.
|
||||
|
||||
iMac5,2 isn't documented but you can find the flash chip on that board quite
|
||||
easily. See the generic flashing guide:\
|
||||
[Externally rewrite 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol](spi.md)
|
||||
### Howto: read/write/erase the boot flash
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L mainboard
|
||||
---------------------------------------
|
||||
How to read the current chip contents:
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L](ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
||||
sudo flashprog -p internal:laptop=force_I_want_a_brick,boardmismatch=force -r dump.bin
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Intel D510MO and D410PT mainboards
|
||||
------------------------------------------
|
||||
You should still make several dumps, even if you're flashing internally, to
|
||||
ensure that you get the same checksums. Check each dump using `sha1sum`
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Intel D510MO and D410PT boards](d510mo.md)
|
||||
How to erase and rewrite the chip contents:
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Intel D945GCLF mainboard
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
sudo flashprog -p internal:laptop=force_I_want_a_brick,boardmismatch=force -w canoeboot.rom
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Intel D945GCLF](d945gclf.md)
|
||||
NOTE: `force_I_want_a_brick` is not scary. Do not be scared! This merely disables
|
||||
the safety checks in flashprog. Flashrom and coreboot change a lot, over the years,
|
||||
and sometimes it's necessary to use this option. If you're scared, then just
|
||||
follow the above instructions, but remove that option. So, just use `-p internal`.
|
||||
If that doesn't work, next try `-p internal:boardmismatch=force`. If that doesn't
|
||||
work, try `-p internal:boardmismatch=force,laptop=force_I_want_a_brick`. So long
|
||||
as you *ensure* you're using the correct ROM for your machine, it will be safe
|
||||
to run flashprog. These extra options just disable the safetyl checks in flashprog.
|
||||
There is nothing to worry about.
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: ASUS KGPE-D16 mainboard
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
If successful, it will either say `VERIFIED` or it will say that the chip
|
||||
contents are identical to the requested image.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ASUS KGPE-D16](kgpe-d16.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: ASUS KCMA-D8 mainboard
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ASUS KCMA-D8](../hardware/kcma-d8.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: ASUS Chromebook C201 laptop
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ASUS Chromebook C201](c201.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad X60 laptop
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad X60](x60_unbrick.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad X60 Tablet laptop
|
||||
-----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad X60 Tablet](x60tablet_unbrick.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad T60 laptop
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad T60](t60_unbrick.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad X200 laptop
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad X200](x200_external.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad X200S or X200 Tablet laptop
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Software-wise, identical to regular X200 but SMD rework skills are required.
|
||||
You must de-solder the default flash chip, and replace it with another one.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[25xx NOR flashing guide](spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
That guide, linked above, has instructions for how to deal with these machines.
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad T400 laptop
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad T400](t400_external.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad T400S laptop
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Software-wise, identical to regular T400 but SMD rework skills are required.
|
||||
You must de-solder the default flash chip, and replace it with another one.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[25xx NOR flashing guide](spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad R400 laptop
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad R400](r400_external.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad T500 or W500 laptop
|
||||
-------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
These two laptops have identical mainboard, except for a few minor changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad T500/W500](t500_external.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad R500 laptop
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following laptop:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad R500](../hardware/r500.md)
|
||||
NOTE: there are exceptions where the above is not possible. Read about them in
|
||||
the sections below:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,32 +1,215 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: KGPE-D16 external flashing instructions
|
||||
title: ASUS KGPE-D16 server/workstation board
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
These will be re-added to Canoeboot at a later date, once proper testing
|
||||
has been done.
|
||||
TODO: OLD page. TODO: check that all the info is still valid.
|
||||
|
||||
Initial flashing instructions for KGPE-D16.
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their ASUS KGPE-D16
|
||||
motherboard, while they still have the proprietary ASUS BIOS present.
|
||||
This guide can also be followed (adapted) if you brick you board, to
|
||||
know how to recover.
|
||||
This is a server board using AMD hardware (Fam10h *and Fam15h* CPUs
|
||||
available). It can also be used for building a high-powered workstation.
|
||||
Powered by libreboot. The coreboot port was done by Timothy Pearson of
|
||||
Raptor Engineering Inc. and, working with them (and sponsoring the
|
||||
work), merged into libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
*Memory initialization is still problematic, for some modules. We
|
||||
recommend avoiding Kingston modules.*
|
||||
*For working configurations see <https://www.coreboot.org/Board:asus/kgpe-d16>.*
|
||||
|
||||
For more general information about this board, refer to
|
||||
[../hardware/kgpe-d16.md](../hardware/kgpe-d16.md).
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog) - note that external
|
||||
flashing is required, if the proprietary (ASUS) firmware is
|
||||
currently installed. If you already have libreboot, by default it is
|
||||
possible to re-flash using software running in Linux on the
|
||||
KGPE-D16, without using external hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: show photos here, and other info.
|
||||
CPU compatibility
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
External programmer
|
||||
===================
|
||||
Opteron 62xx and 63xx CPUs work just fine.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [spi.md](spi.md) for a guide on how to re-flash externally.
|
||||
Board status (compatibility) {#boardstatus}
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
||||
The flash chip is in a PDIP 8 socket (SPI flash chip) on the
|
||||
motherboard, which you take out and then re-flash with Canoeboot, using
|
||||
the programmer. *DO NOT* remove the chip with your hands. Use a chip
|
||||
extractor tool.
|
||||
See <https://raptorengineeringinc.com/coreboot/kgpe-d16-status.php>.
|
||||
|
||||
Form factor {#formfactor}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
These boards use the SSI EEB 3.61 form factor; make sure that your case
|
||||
supports this. This form factor is similar to E-ATX in that the size is
|
||||
identical, but the position of the screws are different.
|
||||
|
||||
IPMI iKVM module add-on {#ipmi}
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
Don't use it. It uses proprietary firmware and adds a backdoor (remote
|
||||
out-of-band management chip, similar to the [Intel Management
|
||||
Engine](../../faq.md#intelme). Fortunately, the firmware is
|
||||
unsigned (possibly to replace) and physically separate from the
|
||||
mainboard since it's on the add-on module, which you don't have to
|
||||
install.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash chips {#flashchips}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
2MiB flash chips are included by default, on these boards. It's on a
|
||||
P-DIP 8 slot (SPI chip). The flash chip can be upgraded to higher sizes:
|
||||
4MiB, 8MiB or 16MiB. With at least 8MiB, you could feasibly fit a
|
||||
compressed linux+initramfs image (BusyBox+Linux system) into CBFS and
|
||||
boot that, loading it into memory.
|
||||
|
||||
libreboot has configs for 2, 4, 8 and 16 MiB flash chip sizes (default
|
||||
flash chip is 2MiB).
|
||||
|
||||
*DO NOT hot-swap the chip with your bare hands. Use a P-DIP 8 chip
|
||||
extractor. These can be found online. See
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Developer_Manual/Tools#Chip_removal_tools>*
|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to flash the chip:\
|
||||
[25xx NOR flashing guide](../install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Native graphics initialization {#graphics}
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
Only text-mode is known to work, but linux(kernel) can initialize the
|
||||
framebuffer display (if it has KMS - kernel mode setting).
|
||||
|
||||
Current issues {#issues}
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
- LRDIMM memory modules are currently incompatible
|
||||
(IT MAY WORK NOWADAYS, TODO TEST)
|
||||
- SAS (via PIKE 2008 module) requires a vendor option ROM (and
|
||||
SeaBIOS) to boot from it (theoretically possible to replace, but you
|
||||
can put a kernel in CBFS or on SATA and boot from that, which
|
||||
can be on a SAS drive. The linux kernel can use those SAS drives
|
||||
(via PIKE module) without an option ROM).
|
||||
- SeaBIOS lacked serial console support out-of-the-box in release 20160907
|
||||
and as such a workaround using SGABIOS is necessary. You can find
|
||||
instructions on how to do this on the
|
||||
[Notabug issue tracker](http://web.archive.org/web/20210416011941/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/736)
|
||||
- IPMI iKVM module (optional add-on card) uses proprietary firmware.
|
||||
Since it's for remote out-of-band management, it's theoretically a
|
||||
backdoor similar to the Intel Management Engine. Fortunately, unlike
|
||||
the ME, this firmware is unsigned which means that a free
|
||||
replacement is theoretically possible. For now, the libreboot
|
||||
project recommends not installing the module. [This
|
||||
project](https://github.com/facebook/openbmc) might be interesting
|
||||
to derive from, for those who want to work on a free replacement. In
|
||||
practise, out-of-band management isn't very useful anyway (or at
|
||||
the very least, it's not a major inconvenience to not have it).
|
||||
- Graphics: only text-mode works. See [\#graphics](#graphics)
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware specifications {#specifications}
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The information here is adapted, from the ASUS website.
|
||||
|
||||
### Processor / system bus
|
||||
|
||||
- 2 CPU sockets (G34 compatible)
|
||||
- HyperTransport™ Technology 3.0
|
||||
- CPUs supported:
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6100 series (Fam10h. No IOMMU support. *Not*
|
||||
recommended - old. View errata datasheet here:
|
||||
<http://support.amd.com/TechDocs/41322_10h_Rev_Gd.pdf>)
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6200 series (Fam15h, with full IOMMU support in
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6300 series (Fam15h, with full IOMMU support in
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
- 6.4 GT/s per link (triple link)
|
||||
|
||||
### Core logic
|
||||
|
||||
- AMD SR5690
|
||||
- AMD SP5100
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory compatibility (with libreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
- *Total Slots:* 16 (4-channel per CPU, 8 DIMM per CPU), ECC
|
||||
- *Capacity:* Maximum up to 256GB RDIMM (Tested max 128GB)
|
||||
- *Memory Type that is compatible:*
|
||||
- DDR3 1600/1333/1066/800 UDIMM\*
|
||||
- DDR3 1600/1333/1066/800 RDIMM\*
|
||||
- *Compatible sizes per memory module:*
|
||||
- 16GB, 8GB, 4GB, 3GB, 2GB, 1GB RDIMM
|
||||
- 8GB, 4GB, 2GB, 1GB UDIMM
|
||||
|
||||
### Expansion slots
|
||||
|
||||
- *Total slot:* 6
|
||||
- *Slot Location 1:* PCI 32bit/33MHz
|
||||
- *Slot Location 2:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X8 Link)
|
||||
- *Slot Location 3:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X16 Link), Auto switch to x8
|
||||
link if slot 2 is occupied
|
||||
- *Slot Location 4:* PCI-E x8 (Gen2 X4 Link)
|
||||
- *Slot Location 5:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X16 Link)
|
||||
- *Slot Location 6:* PCI-E x16 (Gen2 X16 Link), Auto turn off if
|
||||
slot 5 is occupied, For 1U FH/FL Card, MIO supported
|
||||
- *Additional Slot 1:* PIKE slot (for SAS drives. See notes above)
|
||||
- Follow SSI Location\#
|
||||
|
||||
### Form factor {#form-factor}
|
||||
|
||||
- SSI EEB 3.61 (12"x13")
|
||||
|
||||
### ASUS features
|
||||
|
||||
- Fan Speed Control
|
||||
- Rack Ready (Rack and Pedestal dual use)
|
||||
|
||||
### Storage
|
||||
|
||||
- *SATA controller:*
|
||||
- AMD SP5100
|
||||
- 6 x SATA2 300MB/s
|
||||
- *SAS/SATA Controller:*
|
||||
- ASUS PIKE2008 3Gbps 8-port SAS card included
|
||||
|
||||
### Networking
|
||||
|
||||
- 2 x Intel® 82574L + 1 x Mgmt LAN
|
||||
|
||||
### Graphics
|
||||
|
||||
- Aspeed AST2050 with 8MB VRAM
|
||||
|
||||
### On board I/O
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 x PSU Power Connector (24-pin SSI power connector + 8-pin SSI
|
||||
12V + 8-pin SSI 12V power connector)
|
||||
- 1 x Management Connector , Onboard socket for management card
|
||||
- 3 x USB pin header , Up to 6 Devices
|
||||
- 1 x Internal A Type USB Port
|
||||
- 8 x Fan Header , 4pin (3pin/4pin fan dual support)
|
||||
- 2 x SMBus
|
||||
- 1 x Serial Port Header
|
||||
- 1 x TPM header
|
||||
- 1 x PS/2 KB/MS port
|
||||
|
||||
### Back I/O ports
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 x External Serial Port
|
||||
- 2 x External USB Port
|
||||
- 1 x VGA Port
|
||||
- 2 x RJ-45
|
||||
- 1 x PS/2 KB/Mouse
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
- *Operation temperature:* 10C \~ 35C
|
||||
- *Non operation temperature:* -40C \~ 70C
|
||||
- *Non operation humidity:* 20% \~ 90% ( Non condensing)
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
- CPU temperatures
|
||||
- Fan speed (RPM)
|
||||
|
||||
### Note:
|
||||
|
||||
- \* DDR3 1600 can only be supported with AMD Opteron 6300/6200 series
|
||||
processor
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ Thermal safety
|
|||
**Thermal safety**: this machine shuts down very quickly, when the machine
|
||||
exceeds 80c CPU temperature, which is far more conservative than on most
|
||||
laptops (non-Dell ones), so you should make sure that your thermals are
|
||||
excellent. More info available [here](../hardware/dell_thermal.md). This is a
|
||||
excellent. More info available [here](../install/dell_thermal.md). This is a
|
||||
known bug, but otherwise the machine will be mostly stable.
|
||||
|
||||
Machine-specific notes
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,6 +3,116 @@ title: Flashing the ThinkPad R400
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
![ThinkPad R400]()
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad R400 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn/Merom family) or
|
||||
Celeron M (Merom L family) |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (and ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3470 or nVIDIA
|
||||
GeForce 9300M on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1440x900 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | Up to 8GB |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable to 16MiB) |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works without blobs;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
W*: Works with blobs;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
P*: Partially works with blobs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an R400 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Libreboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
It is believed that all or most R400 laptops are compatible. See notes
|
||||
about [CPU
|
||||
compatibility](#cpu_compatibility) for
|
||||
potential incompatibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two possible flash chip sizes for the R400: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
||||
8MiB (64Mbit). This can be identified by the type of flash chip below
|
||||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The R400 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Libreboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 27 January 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update {#ecupdate}
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
libreboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
The R400 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: put hardware register logs here like on the [X200](x200.md) and
|
||||
[T400](t400.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
Installation notes
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
[External flashing](spi.md) required, if Lenovo BIOS is running.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an R400 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +182,7 @@ now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
|||
MAC address {#macaddress}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](../hardware/mac_address.md).
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](../install/mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
External flashing
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,21 +3,111 @@ title: Flashing the ThinkPad T400 externally
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 alt="ThinkPad T400" class="p" src="https://av.libreboot.org/t400/boot1.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.libreboot.org/t400/boot1.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad T400 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn family). A Quad-core
|
||||
mod exists, replacing the Core 2 Duo with a Core Quad |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (and ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3650 on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1440x900 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | 2 or 4GB (Upgradable to 8GB) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16/WSON-8 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable
|
||||
to 16MiB) |
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works without blobs;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
W*: Works with blobs;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
P*: Partially works with blobs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an T400 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
Initial flashing instructions for T400.
|
||||
It is believed that all or most laptops of the model T400 are compatible. See notes
|
||||
about [CPU
|
||||
compatibility](#cpu_compatibility) for
|
||||
potential incompatibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two possible flash chip sizes for the T400: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
||||
8MiB (64Mbit). This can be identified by the type of flash chip below
|
||||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The T400 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing canoeboot. Canoeboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Libreboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 27 January 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update {#ecupdate}
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
libreboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
The T400 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Installation notes
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
[External flashing](spi.md) required, if Lenovo BIOS is running.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their ThinkPad T400 while
|
||||
they still have the original Lenovo BIOS present. This guide can also be
|
||||
|
|
@ -85,7 +175,7 @@ Use this to find out:
|
|||
MAC address {#macaddress}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](../hardware/mac_address.md).
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
How to flash externally
|
||||
=========================
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,15 +3,113 @@ title: ThinkPad T500 external flashing
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
<div class="specs">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 alt="ThinkPad T500" class="p" src="https://av.libreboot.org/t500/0062.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.libreboot.org/t500/0062.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought a T500 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
| ***Specifications*** | |
|
||||
|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Manufacturer** | Lenovo |
|
||||
| **Name** | ThinkPad T500 |
|
||||
| **Released** | 2009 |
|
||||
| **Chipset** | Intel Cantiga GM45 |
|
||||
| **CPU** | Intel Core 2 Duo (Penryn family). A Quad-core
|
||||
mod exists, replacing the Core 2 Duo with a Core Quad |
|
||||
| **Graphics** | Intel GMA 4500MHD (and ATI Mobility Radeon HD
|
||||
3650 on some models) |
|
||||
| **Display** | 1280x800/1680x1050/1920x1200 TFT |
|
||||
| **Memory** | 2 or 4GB (Upgradable to 8GB) |
|
||||
| **Architecture** | x86_64 |
|
||||
| **EC** | Proprietary |
|
||||
| **Original boot firmware** | LenovoBIOS |
|
||||
| **Intel ME/AMD PSP** | Present. Can be completly disabled. |
|
||||
| **Flash chip** | SOIC-8/SOIC-16/WSON-8 4MiB/8MiB (Upgradable
|
||||
to 16MiB) |
|
||||
```
|
||||
W+: Works without blobs;
|
||||
N: Doesn't work;
|
||||
W*: Works with blobs;
|
||||
U: Untested;
|
||||
P+: Partially works;
|
||||
P*: Partially works with blobs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Features*** | |
|
||||
|----------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **Internal flashing with original boot firmware** | N |
|
||||
| **Display** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Audio** | W+ |
|
||||
| **RAM Init** | W+ |
|
||||
| **External output** | W+ |
|
||||
| **Display brightness** | P+ |
|
||||
|
||||
| ***Payloads supported*** | |
|
||||
|---------------------------|-----------|
|
||||
| **GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an T500 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](../install/latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Initial flashing instructions for T500.
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
It is believed that all or most T500 laptops are compatible. See notes
|
||||
about [CPU
|
||||
compatibility](#cpu_compatibility) for
|
||||
potential incompatibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
W500 is also compatible, and mostly the same design as T500.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two possible flash chip sizes for the T500: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
||||
8MiB (64Mbit). This can be identified by the type of flash chip below
|
||||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The T500 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing canoeboot. Canoeboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 27 January 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
EC update {#ecupdate}
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you update to the latest EC firmware version. The
|
||||
[EC firmware](../../faq.md#ec-embedded-controller-firmware) is separate from
|
||||
Canoeboot, so we don't actually provide that, but if you still have
|
||||
Lenovo BIOS then you can just run the Lenovo BIOS update utility, which
|
||||
will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
||||
|
||||
- [../install/#flashprog](../install/#flashprog)
|
||||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running Canoeboot is unknown. Canoeboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
The T500 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Installation notes
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
[External flashing](spi.md) required, if Lenovo BIOS is running.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their ThinkPad T500 while
|
||||
they still have the original Lenovo BIOS present. This guide can also be
|
||||
|
|
@ -81,7 +179,7 @@ Use this to find out:
|
|||
MAC address {#macaddress}
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](../hardware/mac_address.md).
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Clip wiring
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
|
@ -211,14 +309,6 @@ the proper application procedure.
|
|||
Wifi
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
The T500 typically comes with an Intel wifi chipset, which does not work
|
||||
without proprietary software. For a list of wifi chipsets that work
|
||||
without proprietary software, see
|
||||
[../hardware/\#recommended\_wifi](../hardware/#recommended_wifi).
|
||||
|
||||
Some T500 laptops might come with an Atheros chipset, but this is
|
||||
802.11g only.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you install a new wifi chipset. This can only be
|
||||
done after installing Canoeboot, because the original firmware has a
|
||||
whitelist of approved chips, and it will refuse to boot if you use an
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad X200
|
||||
title: First-time ThinkPad X200 flashing
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,6 +46,7 @@ P+: Partially works;
|
|||
| **SeaBIOS** | Works |
|
||||
| **SeaBIOS with GRUB** | Works |
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Dell Latitude E6400
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -180,14 +181,159 @@ the following: *"This product contains Lithium Ion Battery, Lithium Battery and
|
|||
a lamp which contains mercury; dispose according to local, state or federal
|
||||
laws"* (one with an LED backlit panel will say something different).
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware register dumps {#regdumps}
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
Installation notes
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
The coreboot wiki
|
||||
[shows](http://www.coreboot.org/Motherboard_Porting_Guide) how to
|
||||
collect various logs useful in porting to new boards. Following are
|
||||
outputs from the X200:
|
||||
[External flashing](spi.md) required, if running Lenovo BIOS.
|
||||
|
||||
- BIOS 3.15, EC 1.06
|
||||
- [hwdumps/x200/](hwdumps/x200/)
|
||||
This guide is for those who want libreboot on their ThinkPad X200 while
|
||||
they still have the original Lenovo BIOS present. This guide can also be
|
||||
followed (adapted) if you brick your X200, to know how to recover.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have the original Lenovo firmware running, you will need to take the
|
||||
keyboard and palmrest off so that you can access the flash chip, which is just
|
||||
underneath the palm rest. You will then connect an external SPI programmer, to
|
||||
re-flash the chip externally while it is powered off with the battery removed.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This guide only applies to the regular X200. For X200S and X200 Tablet
|
||||
flashing, please read other guides available on libreboot.org.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash chip size
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Run this command on x200 to find out flash chip model and its size:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
MAC address
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
The procedure
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
This section is for the X200. This does not apply to the X200S or X200
|
||||
Tablet (for those systems, you have to remove the motherboard
|
||||
completely, since the flash chip is on the other side of the board).
|
||||
|
||||
Remove these screws:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gently push the keyboard towards the screen, then lift it off, and optionally
|
||||
disconnect it from the board:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Disconnect the cable of the fingerpring reader, and then pull up the palm rest,
|
||||
lifting up the left and right side of it:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This shows the location of the flash chip, for both SOIC-8 and SOIC-16:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lift back the tape that covers a part of the flash chip, and then
|
||||
connect the clip:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, you should be ready to install libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [SPI programming instructions](spi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
When you're done, put the system back together. If it doesn't boot, try other
|
||||
RAM modules because raminit is very unreliable on this platform (in coreboot).
|
||||
|
||||
Memory
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
In DDR3 machines with Cantiga (GM45/GS45/PM45), northbridge requires sticks
|
||||
that will work as PC3-8500 (faster PC3/PC3L sticks can work as PC3-8500).
|
||||
Non-matching pairs may not work. Single module (meaning, one of the slots
|
||||
will be empty) will currently only work in slot 0.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: according to users reports, non matching pairs (e.g. 1+2 GiB) might
|
||||
work in some cases.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that the RAM you buy is the 2Rx8 configuration when buying 4GiB sticks
|
||||
(In other words: maximum of 2GiB per rank, 2 ranks per card).
|
||||
|
||||
In this photo, 8GiB of RAM (2x4GiB) is installed:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Boot it!
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
You should see something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now [install Linux](../linux/).
|
||||
|
||||
X200S and X200 Tablet users: GPIO33 trick will not work.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
sgsit found out about a pin called GPIO33, which can be grounded to
|
||||
disable the flashing protections by the descriptor and stop the ME from
|
||||
starting (which itself interferes with flashing attempts). The theory
|
||||
was proven correct; however, it is still useless in practise.
|
||||
|
||||
Look just above the 7 in TP37 (that's GPIO33):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
By default we would see this in lenovobios, when trying flashprog -p
|
||||
internal -w rom.rom:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FREG0: Warning: Flash Descriptor region (0x00000000-0x00000fff) is read-only.
|
||||
FREG2: Warning: Management Engine region (0x00001000-0x005f5fff) is locked.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With GPIO33 grounded during boot, this disabled the flash protections as
|
||||
set by descriptor, and stopped the ME from starting. The output changed
|
||||
to:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
The Flash Descriptor Override Strap-Pin is set. Restrictions implied by
|
||||
the Master Section of the flash descriptor are NOT in effect. Please note
|
||||
that Protected Range (PR) restrictions still apply.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The part in bold is what got us. This was still observed:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
PR0: Warning: 0x007e0000-0x01ffffff is read-only.
|
||||
PR4: Warning: 0x005f8000-0x005fffff is locked.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is actually possible to disable these protections. Lenovobios does,
|
||||
when updating the BIOS (proprietary one). One possible way to go about
|
||||
this would be to debug the BIOS update utility from Lenovo, to find out
|
||||
how it's disabling these protections. Some more research is available
|
||||
here:
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Board:lenovo/x200/internal_flashing_research>
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, it's likely that the Lenovo BIOS is checking for some bit in memory
|
||||
that tells it not to disable flashing, and then it won't set PRx registers. The
|
||||
way the Lenovo BIOS updater works is, it is executed in Windows first and then
|
||||
a reboot happens, triggering the re-flashing to happen during early boot. It is
|
||||
probably setting something in memory and loading the ROM, plus a payload program
|
||||
that does the flashing; Lenovo BIOS then probably sees that and runs that, instead
|
||||
of setting PRx and going for normal boot. It is theoretically possible that we
|
||||
could discover how this works, by debugging the Lenovo BIOS update utility (in
|
||||
Windows), and then replicate what it is doing, with some tool for Linux,
|
||||
then load a flashprog binary into memory and the ROM to flash (for the BIOS
|
||||
region). You would do this with GPIO33 grounded, and the payload program would
|
||||
actually flash the entire chip, with just a normal libreboot image.
|
||||
|
||||
It's possible. The above is likely the only way that the Lenovo BIOS updater
|
||||
program works. So if we discover precisely how to do that, then you could
|
||||
just connect some pogo pins to ground GPIO33, then boot up, run some software
|
||||
(which would have to be written) that does the above.
|
||||
|
||||
On a related note, libreboot has a utility that could help with
|
||||
investigating this:
|
||||
[ich9utils.md#demefactory](ich9utils.md#demefactory)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad X200
|
||||
title: Прошивка ThinkPad X200 вперше
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -173,14 +173,153 @@ CCFL містять меркурій. На X200 з CCFL підсвіткою (я
|
|||
яка містить ртуть; утилізуйте відповідно до місцевих, державних або федеральних
|
||||
законів"* (на тому, що має світлодіодне підсвічування, буде написано щось інше).
|
||||
|
||||
Дампи апаратного регістру {#regdumps}
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
Installation notes
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
Вікі coreboot
|
||||
[показує](http://www.coreboot.org/Motherboard_Porting_Guide) як
|
||||
збирати різноманітні логи, корисні для портування на нові плати. Нижче наведено
|
||||
вихідні дані X200:
|
||||
[External flashing](spi.md) required, if running Lenovo BIOS.
|
||||
|
||||
- BIOS 3.15, EC 1.06
|
||||
- [hwdumps/x200/](hwdumps/x200/)
|
||||
Цей посібник призначений для тих, хто бажає libreboot на своєму ThinkPad X200,
|
||||
поки у нього все ще є оригінальний Lenovo BIOS в наявності. Цього керівництва також можна
|
||||
дотримуватися (адаптувати), якщо ви перетворили ваш X200 на цеглину, щоб знати, як його відновити.
|
||||
|
||||
Якщо у вас виконується оригінальна мікропрограма Lenovo, вам потрібно буде зняти
|
||||
клавіатуру та підставку для рук, щоб мати доступ до мікросхеми флеш-пам'яті, яка знаходиться прямо
|
||||
під підставкою для рук. Потім ви підключите зовнішній програматор SPI, щоб
|
||||
повторно прошити мікросхему зовні, коли вона вимкнена та акумулятор висунуто.
|
||||
|
||||
ПРИМІТКА: Цей посібник стосується лише звичайного X200. Для перепрошивки X200S та X200 Tablet,
|
||||
будь-ласка прочитайте інші посібники, доступні на libreboot.org.
|
||||
|
||||
Розмір флеш-чіпа
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Виконайте цю команду на x200, щоб дізнатися модель флеш-чіпа та його розмір:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
MAC адреса
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Зверніться до [mac\_address.md](mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Процедура
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Цей розділ стосується X200. Цей не стосується X200S або X200
|
||||
Tablet (для цих систем потрібно повністю видалити материнську плату,
|
||||
оскільки мікросхема флеш-пам'яті знаходиться з іншого боку плати).
|
||||
|
||||
Викрутіть ці гвинти:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Обережно притисніть клавіатуру до екрана, потім підніміть її та за бажанням
|
||||
від'єднайте від плати:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Від'єднайте кабель пристрою для зчитування відбитків пальців, а потім потягніть упор для рук,
|
||||
піднявши його ліву та праву сторону:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Тут показано розташування мікросхеми флеш-пам'яті, для обох SOIC-8 та SOIC-16:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Підніміть стрічку, яка закриває частину флеш-пам'яті, а потім
|
||||
приєднайте затискач:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Тепер ви повинні бути готові до встановлення libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Зверніться до [інструкцій програмування SPI](spi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Закінчивши, знову зберіть систему. Якщо вона не завантажується, спробуйте інші
|
||||
модулі оперативної пам'яті, тому що raminit дуже ненадійний на цій платформі (в coreboot).
|
||||
|
||||
Пам'ять
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
У машинах DDR3 з Cantiga (GM45/GS45/PM45), північний міст потребує стіків,
|
||||
які працюватимуть як PC3-8500 (швидші стіки PC3/PC3L можуть працювати як PC3-8500).
|
||||
Пари, що не збігаються, можуть не працювати. Один модуль (тобто один із слотів
|
||||
буде порожнім) наразі працюватиме лише в слоті 0.
|
||||
|
||||
ПРИМІТКА: згідно зі звітами користувачів, у деяких випадках невідповідні пари ( 1+2 ГБ) можуть
|
||||
працювати в деяких випадках.
|
||||
|
||||
Переконайтесь, що оперативна пам'ять, яку ви купуєте, має конфігурацію 2Rx8, купуючи стіки по 4 ГБ
|
||||
(Іншими словами: максимально 2 ГБ на ранг, 2 ранга на картку).
|
||||
|
||||
На цьому фото встановлено 8 ГБ оперативної пам'яті (2x4ГБ):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Завантажуйтесь!
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
Ви маєте побачити щось подібне цьому:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Тепер [встановлюйте Linux](../linux/).
|
||||
|
||||
Користувачі X200S та X200 Tablet: трюк GPIO33 не спрацює.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
sgsit дізнався про контакт під назвою GPIO33, який можна заземлити,
|
||||
щоб вимкнути захист прошивки за допомогою дескриптора та зупинити ME від
|
||||
запуску (який сам по собі перешкоджає спробам прошивки). Теорія була
|
||||
доведена правильною; однак на практиці це все одно марно.
|
||||
|
||||
Подивіться трохи вище 7 у TP37 (це GPIO33):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Це замовчуванням ми побачимо це в lenovobios, під час спроби flashprog -p
|
||||
internal -w rom.rom:
|
||||
|
||||
FREG0: Warning: Flash Descriptor region (0x00000000-0x00000fff) is read-only.
|
||||
FREG2: Warning: Management Engine region (0x00001000-0x005f5fff) is locked.
|
||||
|
||||
Коли GPIO33 було заземлено під час завантаження, це вимкнуло захист флеш-пам'яті,
|
||||
встановлений дескриптором, і зупинило запуск ME. Результат змінився
|
||||
на:
|
||||
|
||||
The Flash Descriptor Override Strap-Pin is set. Restrictions implied by
|
||||
the Master Section of the flash descriptor are NOT in effect. Please note
|
||||
that Protected Range (PR) restrictions still apply.
|
||||
|
||||
Частина, виділена жирним шрифтом, - це те, що нас дістало. Це все ж спостерігалось:
|
||||
|
||||
PR0: Warning: 0x007e0000-0x01ffffff is read-only.
|
||||
PR4: Warning: 0x005f8000-0x005fffff is locked.
|
||||
|
||||
Насправді ці засоби захисту можна відключити. Lenovobios робить це,
|
||||
під час оновлення BIOS (пропрієтарного). Одним із можливих способів вирішити цю проблему
|
||||
було б відлагодити утиліту оновлення BIOS від Lenovo, для віднаходження,
|
||||
як вона вимикає ці засоби захисту. Додаткові дослідження доступні
|
||||
тут:
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Board:lenovo/x200/internal_flashing_research>
|
||||
|
||||
Звичайно, ймовірно, що Lenovo BIOS перевіряє якийсь біт в пам'яті,
|
||||
який говорить йому не вимикати перепрошивку, а потім він не встановлює регістри PRx. Принцип
|
||||
роботи програми оновлення BIOS Lenovo полягає в тому, що вона спочатку виконується в Windows,
|
||||
а потім відбувається перезавантаження, ініціюючи перепрошивку під час раннього завантаження. Ймовірно,
|
||||
це встановлює щось у пам'яті та завантажує ROM, плюс програму корисного навантаження,
|
||||
яка виконує перепрошивання; тоді Lenovo BIOS, ймовірно, бачить це та запускає це замість
|
||||
встановлення PRx і переходу до нормального завантаження. Теоретично можливо, що ми
|
||||
зможемо дізнатися, як це працює, налагодивши утиліту оновлення BIOS Lenovo (у
|
||||
Windows), а потім відтворивши її дії за допомогою якогось інструменту для Linux,
|
||||
а потім завантаживши двійковий файл flashprog в пам'ять та ROM для прошивки (для BIOS
|
||||
регіона). Ви б зробили це з заземленням GPIO33, і програма корисного навантаження
|
||||
фактично прошиє весь чіп, лише звичайним образом libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Це можливо. Ймовірно, це єдиний спосіб роботи програми оновлення BIOS Lenovo.
|
||||
Отже, якщо ми дізнаємося, як саме це зробити, тоді ви можете просто підключити кілька
|
||||
контактів pogo для заземлення GPIO33, потім завантажитися, запустити програмне забезпечення
|
||||
(яке потрібно було б написати), яке виконує вищезазначене.
|
||||
|
||||
У зв'язку з цим у libreboot є утиліта, яка може допомогти
|
||||
розслідувати це:
|
||||
[ich9utils.md#demefactory](ich9utils.md#demefactory)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,164 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: First-time ThinkPad X200 flashing
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an X200 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is for those who want Canoeboot on their ThinkPad X200 while
|
||||
they still have the original Lenovo BIOS present. This guide can also be
|
||||
followed (adapted) if you brick your X200, to know how to recover.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have the original Lenovo firmware running, you will need to take the
|
||||
keyboard and palmrest off so that you can access the flash chip, which is just
|
||||
underneath the palm rest. You will then connect an external SPI programmer, to
|
||||
re-flash the chip externally while it is powered off with the battery removed.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This guide only applies to the regular X200. For X200S and X200 Tablet
|
||||
flashing, please read other guides available on the Canoeboot website.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash chip size
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Run this command on x200 to find out flash chip model and its size:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
MAC address
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [mac\_address.md](../hardware/mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
The procedure
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
This section is for the X200. This does not apply to the X200S or X200
|
||||
Tablet (for those systems, you have to remove the motherboard
|
||||
completely, since the flash chip is on the other side of the board).
|
||||
|
||||
Remove these screws:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gently push the keyboard towards the screen, then lift it off, and optionally
|
||||
disconnect it from the board:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Disconnect the cable of the fingerpring reader, and then pull up the palm rest,
|
||||
lifting up the left and right side of it:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This shows the location of the flash chip, for both SOIC-8 and SOIC-16:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lift back the tape that covers a part of the flash chip, and then
|
||||
connect the clip:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, you should be ready to install Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [SPI programming instructions](spi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
When you're done, put the system back together. If it doesn't boot, try other
|
||||
RAM modules because raminit is very unreliable on this platform (in coreboot).
|
||||
|
||||
Memory
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
In DDR3 machines with Cantiga (GM45/GS45/PM45), northbridge requires sticks
|
||||
that will work as PC3-8500 (faster PC3/PC3L sticks can work as PC3-8500).
|
||||
Non-matching pairs may not work. Single module (meaning, one of the slots
|
||||
will be empty) will currently only work in slot 0.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: according to users reports, non matching pairs (e.g. 1+2 GiB) might
|
||||
work in some cases.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that the RAM you buy is the 2Rx8 configuration when buying 4GiB sticks
|
||||
(In other words: maximum of 2GiB per rank, 2 ranks per card).
|
||||
|
||||
In this photo, 8GiB of RAM (2x4GiB) is installed:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Boot it!
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
You should see something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now [install GNU+Linux](../gnulinux/).
|
||||
|
||||
X200S and X200 Tablet users: GPIO33 trick will not work.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
sgsit found out about a pin called GPIO33, which can be grounded to
|
||||
disable the flashing protections by the descriptor and stop the ME from
|
||||
starting (which itself interferes with flashing attempts). The theory
|
||||
was proven correct; however, it is still useless in practise.
|
||||
|
||||
Look just above the 7 in TP37 (that's GPIO33):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
By default we would see this in lenovobios, when trying flashprog -p
|
||||
internal -w rom.rom:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FREG0: Warning: Flash Descriptor region (0x00000000-0x00000fff) is read-only.
|
||||
FREG2: Warning: Management Engine region (0x00001000-0x005f5fff) is locked.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With GPIO33 grounded during boot, this disabled the flash protections as
|
||||
set by descriptor, and stopped the ME from starting. The output changed
|
||||
to:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
The Flash Descriptor Override Strap-Pin is set. Restrictions implied by
|
||||
the Master Section of the flash descriptor are NOT in effect. Please note
|
||||
that Protected Range (PR) restrictions still apply.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The part in bold is what got us. This was still observed:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
PR0: Warning: 0x007e0000-0x01ffffff is read-only.
|
||||
PR4: Warning: 0x005f8000-0x005fffff is locked.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is actually possible to disable these protections. Lenovobios does,
|
||||
when updating the BIOS (proprietary one). One possible way to go about
|
||||
this would be to debug the BIOS update utility from Lenovo, to find out
|
||||
how it's disabling these protections. Some more research is available
|
||||
here:
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Board:lenovo/x200/internal_flashing_research>
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, it's likely that the Lenovo BIOS is checking for some bit in memory
|
||||
that tells it not to disable flashing, and then it won't set PRx registers. The
|
||||
way the Lenovo BIOS updater works is, it is executed in Windows first and then
|
||||
a reboot happens, triggering the re-flashing to happen during early boot. It is
|
||||
probably setting something in memory and loading the ROM, plus a payload program
|
||||
that does the flashing; Lenovo BIOS then probably sees that and runs that, instead
|
||||
of setting PRx and going for normal boot. It is theoretically possible that we
|
||||
could discover how this works, by debugging the Lenovo BIOS update utility (in
|
||||
Windows), and then replicate what it is doing, with some tool for GNU+Linux,
|
||||
then load a flashprog binary into memory and the ROM to flash (for the BIOS
|
||||
region). You would do this with GPIO33 grounded, and the payload program would
|
||||
actually flash the entire chip, with just a normal Canoeboot image.
|
||||
|
||||
It's possible. The above is likely the only way that the Lenovo BIOS updater
|
||||
program works. So if we discover precisely how to do that, then you could
|
||||
just connect some pogo pins to ground GPIO33, then boot up, run some software
|
||||
(which would have to be written) that does the above.
|
||||
|
||||
On a related note, Canoeboot has a utility that could help with
|
||||
investigating this:
|
||||
[ich9utils.md#demefactory](ich9utils.md#demefactory)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,158 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Прошивка ThinkPad X200 вперше
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Canoeboot standardises on [flashprog](https://flashprog.org/wiki/Flashprog)
|
||||
now, as of 3 May 2024, which is a fork of flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you haven't bought an X200 yet: the [Dell Latitude
|
||||
E6400](latitude.md) is much easier to flash; no disassembly required,
|
||||
it can be flashed entirely in software from Dell BIOS to Canoeboot. It is the
|
||||
same hardware generation (GM45), with same CPUs, video processor, etc.**
|
||||
|
||||
Цей посібник призначений для тих, хто бажає Canoeboot на своєму ThinkPad X200,
|
||||
поки у нього все ще є оригінальний Lenovo BIOS в наявності. Цього керівництва також можна
|
||||
дотримуватися (адаптувати), якщо ви перетворили ваш X200 на цеглину, щоб знати, як його відновити.
|
||||
|
||||
Якщо у вас виконується оригінальна мікропрограма Lenovo, вам потрібно буде зняти
|
||||
клавіатуру та підставку для рук, щоб мати доступ до мікросхеми флеш-пам'яті, яка знаходиться прямо
|
||||
під підставкою для рук. Потім ви підключите зовнішній програматор SPI, щоб
|
||||
повторно прошити мікросхему зовні, коли вона вимкнена та акумулятор висунуто.
|
||||
|
||||
ПРИМІТКА: Цей посібник стосується лише звичайного X200. Для перепрошивки X200S та X200 Tablet,
|
||||
будь-ласка прочитайте інші посібники, доступні на Canoeboot
|
||||
|
||||
Розмір флеш-чіпа
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Виконайте цю команду на x200, щоб дізнатися модель флеш-чіпа та його розмір:
|
||||
|
||||
flashprog -p internal
|
||||
|
||||
MAC адреса
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
Зверніться до [mac\_address.md](../hardware/mac_address.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Процедура
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Цей розділ стосується X200. Цей не стосується X200S або X200
|
||||
Tablet (для цих систем потрібно повністю видалити материнську плату,
|
||||
оскільки мікросхема флеш-пам'яті знаходиться з іншого боку плати).
|
||||
|
||||
Викрутіть ці гвинти:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Обережно притисніть клавіатуру до екрана, потім підніміть її та за бажанням
|
||||
від'єднайте від плати:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Від'єднайте кабель пристрою для зчитування відбитків пальців, а потім потягніть упор для рук,
|
||||
піднявши його ліву та праву сторону:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Тут показано розташування мікросхеми флеш-пам'яті, для обох SOIC-8 та SOIC-16:\
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Підніміть стрічку, яка закриває частину флеш-пам'яті, а потім
|
||||
приєднайте затискач:\
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Тепер ви повинні бути готові до встановлення Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Зверніться до [інструкцій програмування SPI](spi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Закінчивши, знову зберіть систему. Якщо вона не завантажується, спробуйте інші
|
||||
модулі оперативної пам'яті, тому що raminit дуже ненадійний на цій платформі (в coreboot).
|
||||
|
||||
Пам'ять
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
У машинах DDR3 з Cantiga (GM45/GS45/PM45), північний міст потребує стіків,
|
||||
які працюватимуть як PC3-8500 (швидші стіки PC3/PC3L можуть працювати як PC3-8500).
|
||||
Пари, що не збігаються, можуть не працювати. Один модуль (тобто один із слотів
|
||||
буде порожнім) наразі працюватиме лише в слоті 0.
|
||||
|
||||
ПРИМІТКА: згідно зі звітами користувачів, у деяких випадках невідповідні пари ( 1+2 ГБ) можуть
|
||||
працювати в деяких випадках.
|
||||
|
||||
Переконайтесь, що оперативна пам'ять, яку ви купуєте, має конфігурацію 2Rx8, купуючи стіки по 4 ГБ
|
||||
(Іншими словами: максимально 2 ГБ на ранг, 2 ранга на картку).
|
||||
|
||||
На цьому фото встановлено 8 ГБ оперативної пам'яті (2x4ГБ):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Завантажуйтесь!
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
Ви маєте побачити щось подібне цьому:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Тепер [встановлюйте GNU+Linux](../gnulinux/).
|
||||
|
||||
Користувачі X200S та X200 Tablet: трюк GPIO33 не спрацює.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
sgsit дізнався про контакт під назвою GPIO33, який можна заземлити,
|
||||
щоб вимкнути захист прошивки за допомогою дескриптора та зупинити ME від
|
||||
запуску (який сам по собі перешкоджає спробам прошивки). Теорія була
|
||||
доведена правильною; однак на практиці це все одно марно.
|
||||
|
||||
Подивіться трохи вище 7 у TP37 (це GPIO33):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Це замовчуванням ми побачимо це в lenovobios, під час спроби flashprog -p
|
||||
internal -w rom.rom:
|
||||
|
||||
FREG0: Warning: Flash Descriptor region (0x00000000-0x00000fff) is read-only.
|
||||
FREG2: Warning: Management Engine region (0x00001000-0x005f5fff) is locked.
|
||||
|
||||
Коли GPIO33 було заземлено під час завантаження, це вимкнуло захист флеш-пам'яті,
|
||||
встановлений дескриптором, і зупинило запуск ME. Результат змінився
|
||||
на:
|
||||
|
||||
The Flash Descriptor Override Strap-Pin is set. Restrictions implied by
|
||||
the Master Section of the flash descriptor are NOT in effect. Please note
|
||||
that Protected Range (PR) restrictions still apply.
|
||||
|
||||
Частина, виділена жирним шрифтом, - це те, що нас дістало. Це все ж спостерігалось:
|
||||
|
||||
PR0: Warning: 0x007e0000-0x01ffffff is read-only.
|
||||
PR4: Warning: 0x005f8000-0x005fffff is locked.
|
||||
|
||||
Насправді ці засоби захисту можна відключити. Lenovobios робить це,
|
||||
під час оновлення BIOS (пропрієтарного). Одним із можливих способів вирішити цю проблему
|
||||
було б відлагодити утиліту оновлення BIOS від Lenovo, для віднаходження,
|
||||
як вона вимикає ці засоби захисту. Додаткові дослідження доступні
|
||||
тут:
|
||||
<http://www.coreboot.org/Board:lenovo/x200/internal_flashing_research>
|
||||
|
||||
Звичайно, ймовірно, що Lenovo BIOS перевіряє якийсь біт в пам'яті,
|
||||
який говорить йому не вимикати перепрошивку, а потім він не встановлює регістри PRx. Принцип
|
||||
роботи програми оновлення BIOS Lenovo полягає в тому, що вона спочатку виконується в Windows,
|
||||
а потім відбувається перезавантаження, ініціюючи перепрошивку під час раннього завантаження. Ймовірно,
|
||||
це встановлює щось у пам'яті та завантажує ROM, плюс програму корисного навантаження,
|
||||
яка виконує перепрошивання; тоді Lenovo BIOS, ймовірно, бачить це та запускає це замість
|
||||
встановлення PRx і переходу до нормального завантаження. Теоретично можливо, що ми
|
||||
зможемо дізнатися, як це працює, налагодивши утиліту оновлення BIOS Lenovo (у
|
||||
Windows), а потім відтворивши її дії за допомогою якогось інструменту для GNU+Linux,
|
||||
а потім завантаживши двійковий файл flashprog в пам'ять та ROM для прошивки (для BIOS
|
||||
регіона). Ви б зробили це з заземленням GPIO33, і програма корисного навантаження
|
||||
фактично прошиє весь чіп, лише звичайним образом Canoeboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Це можливо. Ймовірно, це єдиний спосіб роботи програми оновлення BIOS Lenovo.
|
||||
Отже, якщо ми дізнаємося, як саме це зробити, тоді ви можете просто підключити кілька
|
||||
контактів pogo для заземлення GPIO33, потім завантажитися, запустити програмне забезпечення
|
||||
(яке потрібно було б написати), яке виконує вищезазначене.
|
||||
|
||||
У зв'язку з цим у Canoeboot є утиліта, яка може допомогти
|
||||
розслідувати це:
|
||||
[ich9utils.md#demefactory](ich9utils.md#demefactory)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
|||
From 34270811fce1ecf0bcf3b1363b0dc3dbf284ab09 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
|
||||
From: Leah Rowe <info@minifree.org>
|
||||
Date: Wed, 10 Jun 2015 22:53:28 +0000
|
||||
Subject: flash script: fix a really really really dumb mistake
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
diff --git a/flash b/flash
|
||||
index c96b915..04fd274 100755
|
||||
--- a/flash
|
||||
+++ b/flash
|
||||
@@ -95,12 +95,12 @@ if [ "$mode" = "i945lenovo_firstflash" ] || [ "$mode" = "i945lenovo_secondflash"
|
||||
# git or libreboot_src
|
||||
bucts="./bucts/bucts"
|
||||
flashrom_lenovobios_sst="./flashrom/flashrom_lenovobios_sst"
|
||||
- flashrom_lenovobios_macronix="./flashrom/flashrom_lenovobios_sst"
|
||||
+ flashrom_lenovobios_macronix="./flashrom/flashrom_lenovobios_macronix"
|
||||
else
|
||||
# libreboot_util
|
||||
bucts="./bucts/$arch/bucts"
|
||||
flashrom_lenovobios_sst="./flashrom/$arch/flashrom_lenovobios_sst"
|
||||
- flashrom_lenovobios_macronix="./flashrom/$arch/flashrom_lenovobios_sst"
|
||||
+ flashrom_lenovobios_macronix="./flashrom/$arch/flashrom_lenovobios_macronix"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# anti-bricking precaution
|
||||
--
|
||||
cgit v0.9.0.2
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,9 +3,8 @@ title: U-Boot payload
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Canoeboot has experimental support for using U-Boot as a coreboot payload.
|
||||
Refer to [docs/hardware/](../hardware/) for a complete list of U-Boot
|
||||
targets in Libreboot. Canoeboot inherited U-Boot support from Libreboot.
|
||||
Canoeboot has experimental support for using U-Boot as a coreboot
|
||||
payload.
|
||||
|
||||
U-Boot integration in Canoeboot is currently at a proof-of-concept
|
||||
stage, with most boards completely untested and most likely not working.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -155,7 +155,7 @@ What systems are compatible with Canoeboot?
|
|||
Any system can easily be added, so *compatibility* merely refers to whatever
|
||||
boards are integrated in the `cbmk` build system, which Canoeboot uses.
|
||||
|
||||
Please read the [hardware compatibility list](docs/hardware/).
|
||||
The [installation page](docs/install/) lists compatible machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Freedom pitfalls with modern Intel hardware {#intel}
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -286,8 +286,8 @@ ME can be disabled by setting a couple of values in the SPI flash
|
|||
memory. The ME firmware can then be removed entirely from the flash
|
||||
memory space. The Canoeboot project [does this](docs/install/ich9utils.md) on
|
||||
the Intel 4 Series systems that it supports, such as the [ThinkPad
|
||||
X200](../docs/install/x200_external.md) and [ThinkPad
|
||||
T400](../docs/install/t400_external.md). ME firmware versions 6.0 and
|
||||
X200](../docs/install/x200.md) and [ThinkPad
|
||||
T400](../docs/install/t400.md). ME firmware versions 6.0 and
|
||||
later, which are found on all systems with an Intel Core i3/i5/i7 CPU
|
||||
and a PCH, include "ME Ignition" firmware that performs some hardware
|
||||
initialization and power management. If the ME's boot ROM does not find
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ Ethernet не працює на моєму X200/T400/X60/T60, коли я йог
|
|||
Будь-яку систему можна легко додати, тому *сумісність* посилається до будь-якої
|
||||
інтегрованої до системи побудови `cbmk` плати, яку Canoeboot використовує.
|
||||
|
||||
Прочитайте [список сумісного обладнання](docs/hardware/).
|
||||
The [installation page](docs/install/) lists compatible machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Пастки свободи з сучасним обладнанням Intel {#intel}
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -290,8 +290,8 @@ ME можна вимкнути, встановивши пару значень
|
|||
Прошивку ME потім можна повністю видалити з простору флеш-
|
||||
пам'яті. Проект Canoeboot [робить це](docs/install/ich9utils.md) на
|
||||
системах Intel серії 4, які він підтримує, наприклад [ThinkPad
|
||||
X200](../docs/install/x200_external.uk.md) та [ThinkPad
|
||||
T400](../docs/install/t400_external.md). Прошивка ME версії 6.0 та
|
||||
X200](../docs/install/x200.uk.md) та [ThinkPad
|
||||
T400](../docs/install/t400.md). Прошивка ME версії 6.0 та
|
||||
пізніше, яка є на всіх системах з процесорами Intel Core i3/i5/i7
|
||||
PCH, включає мікропрограму "ME Ignition", яка виконує деяку апаратну
|
||||
ініціалізацію та контроль живленням. Якщо завантажувальний ROM ME не знаходить
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
|
||||
Das *Canoeboot* Projekt bietet
|
||||
eine [freie](https://writefreesoftware.org/learn) *Boot
|
||||
Firmware* welche auf [bestimmten Intel/AMD x86 und ARM Geräten](docs/hardware/)
|
||||
Firmware* welche auf [bestimmten Intel/AMD x86 und ARM Geräten](docs/install/)
|
||||
die Hardware initialisiert (z.b. Speicher-Controller, CPU, Peripherie),
|
||||
und dann einen Bootloader für dein Betriebssystem startet. [GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/)
|
||||
sowie [BSD](docs/bsd/) werden gut unterstützt. Es ersetzt proprietäre BIOS/UEFI
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
|
||||
Canoeboot est un micrologiciel de démarrage [libéré](https://writefreesoftware.org/learn)
|
||||
qui initialise le matériel (càd le contrôleur mémoire, CPU,
|
||||
périphériques) sur [des ordinateurs x86/ARM spécifiques](docs/hardware/)
|
||||
périphériques) sur [des ordinateurs x86/ARM spécifiques](docs/install/)
|
||||
et lance un chargeur d'amorçage pour votre système d'exploitation. [GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/) et [BSD](docs/bsd/) sont bien supportés. C'est un
|
||||
remplacement pour le micrologiciel UEFI/BIOS propriétaire.
|
||||
Des canaux d'aide sont disponibles
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
|
||||
Il progetto *Canoeboot* fornisce avvio [libero](https://writefreesoftware.org/learn)
|
||||
grazie al firmware basato su coreboot, sostituendo cosi', firmware BIOS/UEFI proprietario
|
||||
su [alcune schede madri basate su Intel/AMD x86 o ARM](docs/hardware/),
|
||||
su [alcune schede madri basate su Intel/AMD x86 o ARM](docs/install/),
|
||||
in computer fissi e portatili. Inizializza l'hardware (controller di
|
||||
memoria, CPU, periferiche) e avvia un bootloader per il tuo sistema operativo.
|
||||
[GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/) e [BSD](docs/bsd/) sono ben supportati.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
The *Canoeboot* project provides
|
||||
[free](https://writefreesoftware.org/learn) (*libre*) boot
|
||||
firmware based on coreboot, replacing proprietary BIOS/UEFI firmware
|
||||
on [specific Intel/AMD x86 and ARM based motherboards](docs/hardware/),
|
||||
on [specific Intel/AMD x86 and ARM based motherboards](docs/install/),
|
||||
including laptop and desktop computers. It initialises the hardware (e.g. memory
|
||||
controller, CPU, peripherals) and starts a bootloader for your operating
|
||||
system. [GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/) and [BSD](docs/bsd/) are well-supported. Help is
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
Проект *Canoeboot* надає
|
||||
[вільну](https://writefreesoftware.org/learn) *завантажувальну
|
||||
прошивку*, яка ініціалізує апаратне забезпечення (наприклад, контролер пам'яті, ЦП,
|
||||
периферію) на [конкретних цілях Intel/AMD x86 та ARM](docs/hardware/), що
|
||||
периферію) на [конкретних цілях Intel/AMD x86 та ARM](docs/install/), що
|
||||
потім розпочинає завантажувач для вашої операційної системи. [GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/)
|
||||
та [BSD](docs/bsd/) добре підтримуються. Це заміняє пропрієтарну BIOS/UEFI
|
||||
прошивку. Допомога доступна
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue