Merge branch 'merge' of shmalebx9/lbwww into master
commit
a8ac49f11d
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Instructions are also on that page for sending patches (via pull requests).
|
|||
IRC chatroom
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
IRC is the main way to contact the Libreboot project. `#libreboot` on Libera
|
||||
IRC is the main way to contact the libreboot project. `#libreboot` on Libera
|
||||
IRC.
|
||||
|
||||
Webchat:
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ In general, you should check the documentation provided by your IRC software.
|
|||
Social media
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot exists officially on many places.
|
||||
libreboot exists officially on many places.
|
||||
|
||||
Twitter and Mastodon
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,42 +10,82 @@ If we forgot to mention you here, let us know and we'll add you. (or if
|
|||
you don't want to be mentioned, let us know and we'll remove your
|
||||
entry)
|
||||
|
||||
Information about who works on Libreboot, and how the project is run, can
|
||||
Information about who works on libreboot, and how the project is run, can
|
||||
be found on this page: [who.md](who.md)
|
||||
|
||||
You can know the history of the Libreboot project, simply by reading this page.
|
||||
You can know the history of the libreboot project, simply by reading this page.
|
||||
It goes into detail about all of the major contributions to the project, and in
|
||||
general how the project was created (and who helped create it).
|
||||
|
||||
Leah Rowe
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
**Founder of the Libreboot project, and currently the lead developer.** Leah
|
||||
works on all aspects of Libreboot, such as:
|
||||
**Founder of the librebootboot project, and currently the lead developer.** Leah
|
||||
works on all aspects of libreboot, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
* General management. Leah handles all outside contributions to Libreboot,
|
||||
* General management. Leah handles all outside contributions to libreboot,
|
||||
reviews pull requests, deals with bug reports, delegates tasks when necessary
|
||||
or desirable. Leah controls the libreboot.org server infrastructure, hosted
|
||||
in her lab (of course it runs Libreboot!)
|
||||
in her lab.
|
||||
* Leah has the final say on all decisions, taking input via discussion with
|
||||
members of the public, mostly on IRC. Leah oversees releases of Libreboot,
|
||||
and generally keeps the project going. Without Leah, there would be no Libreboot!
|
||||
* The build system (lbmk, short for Libreboot Make). This is the automated build
|
||||
system that sits at the heart of Libreboot; it downloads, patches, configures
|
||||
members of the public, mostly on IRC. Leah oversees releases of libreboot,
|
||||
and generally keeps the project going. Without Leah, there would be no Osboot!
|
||||
* The build system (lbmk, short for libreboot Make). This is the automated build
|
||||
system that sits at the heart of libreboot; it downloads, patches, configures
|
||||
and compiles the relevant components like coreboot, GNU GRUB and generates
|
||||
the Libreboot ROM images that you can find in release archives.
|
||||
* Upstream work on coreboot, when necessary (and other projects that Libreboot
|
||||
uses). This means also working with people from outside of the Libreboot
|
||||
the libreboot ROM images that you can find in release archives (as of 23 March
|
||||
2022, there are not yet any binary releases, it's rolling release, built from
|
||||
source. see: <https://libreboot.org/docs/build/>)
|
||||
* Upstream work on coreboot, when necessary (and other projects that libreboot
|
||||
uses). This means also working with people from outside of the libreboot
|
||||
project, to get patches merged (among other things) on the upstream projects
|
||||
that Libreboot uses
|
||||
that libreboot uses
|
||||
* Providing user support on IRC
|
||||
* *Commercial* user support via her company listed
|
||||
on [the suppliers page](/suppliers.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Leah is also responsible for [osboot.org](https://osboot.org/) which is heavily
|
||||
based on Libreboot, but with different project goals.
|
||||
Leah is also responsible for [libreboot.org](https://libreboot.org/) which is heavily
|
||||
based on Osboot, but with different project goals.
|
||||
|
||||
Other people are listed below, in alphabetical order:
|
||||
Caleb La Grange
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
||||
**Secondary developer, number two to Leah.** Caleb is a full time libreboot developer
|
||||
with a narrower focus. Caleb focuses on several areas of development:
|
||||
|
||||
* Build system. Caleb is responsible for improving and fixing the libreboot Make build
|
||||
system. Specifically: binary blob management, automation, and reproducibility.
|
||||
* Hardware modification. Caleb has a passion for hardware alteration; soldering,
|
||||
desoldering, and testing libreboot software on the resulting hardware.
|
||||
* Board porting. Anything supported in Coreboot can be ported to libreboot, Caleb
|
||||
will test and port any board he can get his hands on. Additionally, anyone can
|
||||
contact Caleb to generate libreboot roms for testing on their board.
|
||||
* Documentation. Caleb actively maintains documentation on the above areas of
|
||||
interest. Additionally, Caleb is responsible for disassembly guides with his own
|
||||
pictures and diagrams for several boards.
|
||||
* User support. Caleb is active on irc and willing to help any user interested in
|
||||
using libreboot or in need of help.
|
||||
* Project goals. Caleb collaborates with Leah on determining project goals.
|
||||
Leah has the final say in every decision.
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot project
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
Without coreboot, the libreboot project simply would not be possible.
|
||||
|
||||
The people and companies that work on coreboot are numerous, and they make the
|
||||
libreboot project what it is. The libreboot project makes heavy use of coreboot, to
|
||||
provide hardware initialization.
|
||||
|
||||
GNU GRUB
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB is the bootloader used by libreboot. It goes without saying that the GRUB
|
||||
developers enable libreboot, through their work.
|
||||
|
||||
SeaBIOS
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot firmware provides SeaBIOS as a payload option. SeaBIOS provides a
|
||||
legacy x86 BIOS implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
Alyssa Rosenzweig
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,8 +5,8 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
|
||||
Guide last updated on 24 August 2022.
|
||||
|
||||
osboot is capable of booting many BSD systems. This section mostly documents
|
||||
the peculiarities of osboot as it pertains to BSD; you can otherwise refer to
|
||||
libreboot is capable of booting many BSD systems. This section mostly documents
|
||||
the peculiarities of libreboot as it pertains to BSD; you can otherwise refer to
|
||||
the official documentation for whatever BSD system you would like to use.
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel Mode Setting
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ you read this article.
|
|||
Boot BSD, using SeaBIOS
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
On x86 platforms, osboot/libreboot both provide the choice of GNU GRUB and/or
|
||||
On x86 platforms, libreboot/libreboot both provide the choice of GNU GRUB and/or
|
||||
SeaBIOS payload. GRUB can technically boot BSD kernels, but the code is
|
||||
poorly maintained and unreliable for this use-case scenario; on BIOS systems,
|
||||
GRUB can chainload BSD bootloaders, but on bare metal (as coreboot payload),
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ probably don't mind running in text mode all the time.
|
|||
Warnings for X11 users
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
One important peculiarity of most libreboot and osboot systems is: VGA mode
|
||||
One important peculiarity of most libreboot and libreboot systems is: VGA mode
|
||||
support exists, if booting with corebootfb (coreboot's own framebuffer) and
|
||||
the SeaVGABIOS option ROM used in the SeaBIOS payload; however, the ability
|
||||
to switch modes is not present, which means you can't switch to text mode
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ on most systems, but not on most coreboot systems with native video
|
|||
initialisation used, due to the quirks already described. If you see any
|
||||
documentation (in BSD land) pertaining to VESA modes, ignore it entirely;
|
||||
unless you're using the proprietary VGA ROM for your device, it won't work,
|
||||
and osboot/libreboot don't distribute these (instead, coreboot's own video
|
||||
and libreboot/libreboot don't distribute these (instead, coreboot's own video
|
||||
initialisation is used where possible, or a headless SeaBIOS payload setup
|
||||
is provided, where you would either run it headless or install a graphics
|
||||
card).
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ Dubious mention: Tianocore
|
|||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Tianocore is extremely bloated, and unauditable, so it is not included
|
||||
in libreboot or osboot, but it is the reference UEFI implementation by
|
||||
in libreboot or libreboot, but it is the reference UEFI implementation by
|
||||
Intel and contributors. It can boot most BSD systems very well.
|
||||
|
||||
More robust ways to provide UEFI services in Libreboot and Osboot are
|
||||
|
|
@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ in any current or future releases of either project.
|
|||
Desktop users
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Desktop users on libreboot/osboot should just install a graphics card,
|
||||
Desktop users on libreboot/libreboot should just install a graphics card,
|
||||
and again boot with SeaBIOS in text mode; however, when you do this,
|
||||
SeaBIOS will execute the VGA option ROM on the card which will provide
|
||||
early video initialisation instead of coreboot's initialisation, and that
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,27 +3,27 @@ title: Build from source
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot's build system is named `lbmk`, short for `Libreboot Make`, and this
|
||||
libreboot's build system is named `lbmk`, short for `Libreboot Make`, and this
|
||||
document describes how to use it. With this guide, you can know how to compile
|
||||
Libreboot from the available source code.
|
||||
libreboot from the available source code.
|
||||
This version, if hosted live on libreboot.org, assumes that you are using
|
||||
the `lbmk` git repository, which
|
||||
you can download using the instructions on [the code review page](../../git.md).
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using a release archive of Libreboot, please refer to the
|
||||
documentation included with *that* release. Libreboot releases are only intended
|
||||
If you're using a release archive of libreboot, please refer to the
|
||||
documentation included with *that* release. libreboot releases are only intended
|
||||
as *snapshots*, not for development. For proper development, you should always
|
||||
be working directly in the Libreboot git repository.
|
||||
be working directly in the libreboot git repository.
|
||||
|
||||
The following document describes how `lbmk` works, and how you can make changes
|
||||
to it: [Libreboot maintenance manual](../maintain/)
|
||||
to it: [libreboot maintenance manual](../maintain/)
|
||||
|
||||
GNU Make
|
||||
========
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot Make includes a file called `Makefile`. You can still use
|
||||
libreboot Make includes a file called `Makefile`. You can still use
|
||||
the `lbmk` build system directly, or you can use GNU Make. The `Makefile`
|
||||
simply runs `lbmk` commands. However, using `lbmk` directly will offer you
|
||||
simply runs `lbmk` commands. However, using `osbmk` directly will offer you
|
||||
much more flexibility; for example, the Makefile currently cannot build single
|
||||
ROM images (it just builds all of them, for all boards).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Now, simply build the coreboot images like so:
|
|||
make
|
||||
|
||||
This single command will build ROM images for *every* board integrated in
|
||||
Libreboot. If you only wish to build a limited set, you can use `lbmk` directly:
|
||||
libreboot. If you only wish to build a limited set, you can use `lbmk` directly:
|
||||
|
||||
./build boot roms x200_8mb
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ started:
|
|||
First, install build dependencies
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot includes a script that automatically installs apt-get dependencies
|
||||
libreboot includes a script that automatically installs apt-get dependencies
|
||||
in Ubuntu 20.04. It works well in other apt-get distros (such as Trisquel and
|
||||
Debian):
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,11 +98,11 @@ Separate scripts also exist:
|
|||
|
||||
sudo ./build dependencies void
|
||||
|
||||
Technically, any GNU+Linux distribution can be used to build Libreboot.
|
||||
Technically, any GNU+Linux distribution can be used to build libreboot.
|
||||
However, you will have to write your own script for installing build
|
||||
dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot Make (lbmk) automatically runs all necessary commands; for example
|
||||
libreboot Make (lbmk) automatically runs all necessary commands; for example
|
||||
`./build payload grub` will automatically run `./build module grub` if the
|
||||
required utilities for GRUB are not built, to produce payloads.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -129,13 +129,29 @@ lbmk.
|
|||
Therefore, if you only want to build ROM images, just do the above. Otherwise,
|
||||
please continue reading!
|
||||
|
||||
Optional: extract binary blobs
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Some boards, including all sandy/ivybridge boards require nonfree blobs which cannot be included in libreboot.
|
||||
For boards requiring these blobs, libreboot will attempt to download the blobs itself.
|
||||
If your board does not have blob sources available, then you must extract them from a backup of you vendor rom.
|
||||
You must point libreboot to the backup rom and tell the build system which board you want to extract blobs for.
|
||||
For example, to extract blobs for the t440p you must run:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil extract t440p_12mb /path/to/12mb_backup.rom
|
||||
|
||||
You can then build the rom for this board as normal:
|
||||
|
||||
./build boot roms t440p_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Second, download all of the required software components
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
If you didn't simply run `./build boot roms` (with or without extra
|
||||
arguments), you can still perform the rest of the build process manually. Read
|
||||
on! You can read about all available scripts in `lbmk` by reading
|
||||
the [Libreboot maintenance manual](../maintain/); lbmk is designed to be modular
|
||||
the [libreboot maintenance manual](../maintain/); lbmk is designed to be modular
|
||||
which means that each script *can* be used on its own (if that's not true, for
|
||||
any script, it's a bug that should be fixed).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -143,7 +159,7 @@ It's as simple as that:
|
|||
|
||||
./download all
|
||||
|
||||
The above command downloads all modules defined in the Libreboot build system.
|
||||
The above command downloads all modules defined in the libreboot build system.
|
||||
However, you can download modules individually.
|
||||
|
||||
This command shows you the list of available modules:
|
||||
|
|
@ -171,7 +187,7 @@ Again, very simple:
|
|||
|
||||
./build module all
|
||||
|
||||
This builds every module defined in the Libreboot build system, but you can
|
||||
This builds every module defined in the libreboot build system, but you can
|
||||
build modules individually.
|
||||
|
||||
The following command lists available modules:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,180 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Depthcharge payload
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
**This documentation is retained from Libreboot 20160907, but it may also be
|
||||
prudent to check documentation from Libreboot 20160907 itself. It is included
|
||||
in the source code archive, for that release.**
|
||||
|
||||
This section relates to the depthcharge payload used in libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
CrOS security model
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
CrOS (Chromium OS/Chrome OS) devices such as Chromebooks implement a strict
|
||||
security model to ensure that these devices do not become compromised, that is
|
||||
implemented as the verified boot (vboot) reference, most of which is executed
|
||||
within depthcharge. A detailed overview of the CrOS security model is available
|
||||
on the dedicated page.
|
||||
|
||||
In spite of the CrOS security model, depthcharge won't allow booting kernels
|
||||
without verifying their signature and booting from external media or legacy
|
||||
payload unless explicitly allowed: see [configuring verified boot
|
||||
parameters](#configuring_verified_boot_parameters).
|
||||
|
||||
Developer mode screen
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
The developer mode screen can be accessed in depthcharge when developer mode is
|
||||
enabled. Developer mode can be enabled from the recovery mode screen.
|
||||
|
||||
It allows booting normally, booting from internal storage, booting from
|
||||
external media (when enabled), booting from legacy payload (when enabled),
|
||||
showing information about the device and disabling developer mode.
|
||||
|
||||
Holding the developer mode screen
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
As instructed on the developer mode screen, the screen can be held by pressing
|
||||
*Ctrl + H* in the first 3 seconds after the screen is shown. After that delay,
|
||||
depthcharge will resume booting normally.
|
||||
|
||||
Booting normally
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
As instructed on the developer mode screen, a regular boot will happen after *3
|
||||
seconds* (if developer mode screen is not held).
|
||||
|
||||
The default boot medium (internal storage, external media, legacy payload) is
|
||||
shown on screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Booting from different mediums
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Depthcharge allows booting from different mediums, when they are allowed (see
|
||||
[configuring verified boot parameters](#configuring_verified_boot_parameters)
|
||||
to enable or disable boot mediums).
|
||||
|
||||
As instructed on the developer mode screen, booting from various mediums can be
|
||||
triggered by pressing various key combinations:
|
||||
|
||||
- Internal storage: *Ctrl + D*
|
||||
- External media: *Ctrl + U* (when enabled)
|
||||
- Legacy payload: *Ctrl + L* (when enabled)
|
||||
|
||||
Showing device information
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
As instructed on the developer mode screen, showing device information can be
|
||||
triggered by pressing *Ctrl + I* or *Tab*. Various information is shown,
|
||||
including vboot non-volatile data, TPM status, GBB flags and key hashes.
|
||||
|
||||
Warnings
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
The developer mode screen will show warnings when:
|
||||
|
||||
- Booting kernels without verifying their signature is enabled
|
||||
- Booting from external media is enabled
|
||||
- Booting legacy payloads is enabled
|
||||
|
||||
Recovery mode screen
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
The recovery mode screen can be accessed in depthcharge, by pressing *Escape +
|
||||
Refresh + Power* when the device is off.
|
||||
|
||||
It allows recovering the device from a bad state by booting from a trusted
|
||||
recovery media. When accessed with the device in a good state, it also allows
|
||||
enabling developer mode.
|
||||
|
||||
Recovering from a bad state
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
When the device fails to verify the signature of a piece of the boot software
|
||||
or when an error occurs, it is considered to be in a bad state and will
|
||||
instruct the user to reboot to recovery mode.
|
||||
|
||||
Recovery mode boots using only software located in write-protected memory, that
|
||||
is considered to be trusted and safe.
|
||||
|
||||
Recovery mode then allows recovering the device by booting from a trusted
|
||||
recovery media, that is automatically detected when recovery mode starts. When
|
||||
no external media is found or when the recovery media is invalid, instructions
|
||||
are shown on screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Trusted recovery media are external media (USB drives, SD cards, etc) that hold
|
||||
a kernel signed with the recovery key.
|
||||
|
||||
Google provides images of such recovery media for Chrome OS (which are not
|
||||
advised to users as they contain proprietary software).
|
||||
|
||||
They are signed with Google's recovery keys, that are pre-installed on the
|
||||
device when it ships.
|
||||
|
||||
When replacing the full flash of the device, the pre-installed keys are
|
||||
replaced. When the recovery private key is available (e.g. when using
|
||||
self-generated keys), it can be used to sign a kernel for recovery purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling developer mode
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
As instructed on the recovery mode screen, developer mode can be enabled by
|
||||
pressing *Ctrl + D*. Instructions to confirm enabling developer mode are then
|
||||
shown on screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuring verified boot parameters
|
||||
====================================
|
||||
|
||||
Depthcharge's behavior relies on the verified boot (vboot) reference
|
||||
implementation, that can be configured with parameters stored in the verified
|
||||
boot non-volatile storage.
|
||||
|
||||
These parameters can be modified with the `crossystem` tool, that requires
|
||||
sufficient privileges to access the verified boot non-volatile storage.
|
||||
|
||||
`crossystem` relies on `mosys`, that is used to access the verified boot
|
||||
non-volatile storage on some devices. `crossystem` and `mosys` are both free
|
||||
software and their source code is made available by Google:
|
||||
[crossystem](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromiumos/platform/vboot_reference/).
|
||||
[mosys](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromiumos/platform/mosys/).
|
||||
|
||||
These tools are not distributed along with Libreboot yet. However, they are
|
||||
preinstalled on the device, with ChromeOS.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of these parameters have the potential of *weakening the security of the
|
||||
device*. In particular, disabling kernels signature verification, external
|
||||
media boot and legacy payload boot can weaken the security of the device.
|
||||
|
||||
The following parameters can be configured:
|
||||
|
||||
Kernels signature verification:
|
||||
|
||||
crossystem dev_boot_signed_only=1 # enable
|
||||
crossystem dev_boot_signed_only=0 # disable
|
||||
|
||||
External media boot:
|
||||
|
||||
crossystem dev_boot_usb=1 # enable
|
||||
crossystem dev_boot_usb=0 # disable
|
||||
|
||||
Legacy payload boot:
|
||||
|
||||
crossystem dev_boot_legacy=1 # enable
|
||||
crossystem dev_boot_legacy=0 # disable
|
||||
|
||||
Default boot medium:
|
||||
|
||||
crossystem dev_default_boot=disk # internal storage
|
||||
crossystem dev_default_boot=usb # external media
|
||||
crossystem dev_default_boot=legacy # legacy payload
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright © 2015 Paul Kocialkowski <contact@paulk.fr>\
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document
|
||||
under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License Version 1.3 or any later
|
||||
version published by the Free Software Foundation
|
||||
with no Invariant Sections, no Front Cover Texts, and no Back Cover Texts.
|
||||
A copy of this license is found in [../fdl-1.3.md](../fdl-1.3.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,13 +18,13 @@ and no other coreboot payload provides this functionality.
|
|||
If booting in text mode
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot ROM images are provided, which will either boot the system in classic
|
||||
libreboot ROM images are provided, which will either boot the system in classic
|
||||
text mode, or with a framebuffer implemented by coreboot for video display
|
||||
initialization (not to be confused with int10h VGA modes).
|
||||
|
||||
*Text mode* is the default video mode on *most* x86 platforms, using `INT 10H`
|
||||
functions. It's an interrupt service that text-mode applications use, a hangover
|
||||
from the days of CS/M and DOS. In this mode, no framebuffer exists and Libreboot
|
||||
from the days of CS/M and DOS. In this mode, no framebuffer exists and onboot
|
||||
currently does not implement VGA modes. The Debian net installer will attempt
|
||||
to use VGA modes that most implementations of INT 10H provide. Therefore, you
|
||||
must force Debian's installation program to operate in text mode.
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,10 +44,10 @@ would presumably handle INT10H VGA modes.
|
|||
Boot the installer
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot on x86 can use the GNU GRUB bootloader as a bare metal coreboot
|
||||
libreboot on x86 can use the GNU GRUB bootloader as a bare metal coreboot
|
||||
[payload](http://www.coreboot.org/Payloads#GRUB_2) if you wish, which
|
||||
means that the GRUB configuration file (where your GRUB menu comes from)
|
||||
is stored directly alongside Libreboot and its GRUB payload executable,
|
||||
is stored directly alongside libreboot and its GRUB payload executable,
|
||||
inside the flash chip. In context, this means that installing
|
||||
distributions and managing them is handled slightly differently compared
|
||||
to traditional BIOS or UEFI systems.
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ to traditional BIOS or UEFI systems.
|
|||
On most systems, the `/boot/` partition has to be left unencrypted while
|
||||
the others are encrypted. This is so that GRUB, and therefore the
|
||||
kernel, can be loaded and executed since the firmware can't open a LUKS
|
||||
volume. Not so with Libreboot! Since GRUB is already included directly
|
||||
volume. Not so with libreboot! Since GRUB is already included directly
|
||||
as a payload, even `/boot/` can be encrypted. This protects /boot from
|
||||
tampering by someone with physical access to the system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ Tasksel
|
|||
=======
|
||||
|
||||
For Debian, use the *MATE* option, or one of the others if you want. The
|
||||
Libreboot project recommends MATE, unless you're saavy enough to choose
|
||||
libreboot project recommends MATE, unless you're saavy enough to choose
|
||||
something else.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want debian-testing, then you should only select barebones
|
||||
|
|
@ -208,7 +208,7 @@ Booting your system
|
|||
|
||||
If you didn't install GRUB during the net installation process, don't worry.
|
||||
You can boot your installed system manually, using the *terminal* in GRUB on
|
||||
your boot flash (the version that Libreboot gives you).
|
||||
your boot flash (the version that libreboot gives you).
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you will have finished the installation. At your GRUB
|
||||
payload, press C to get to reach the GRUB terminal and enter these commands:
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,16 +245,14 @@ somewhere secret. Ideally, you should memorize it and then burn the note
|
|||
LUKSv2
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
LUKSv2 is fully supported nowadays, in recent Libreboot releases. The old
|
||||
Libreboot release, version 20160907 (and earlier releases), did not support
|
||||
LUKSv2 in GNU GRUB. By default, modern Debian distributions will use LUKSv2.
|
||||
|
||||
You do not need to downgrade LUKSv2 to v1, but you shouldn't use any of the special features that LUKSv2 offers. Basically, the partitioning should be done exactly the same way as with LUKSv1 (but with newer encryption/hashing algorithms used by LUKSv2 partitions). This is because of limitations in the implementation of LUKSv2 in GNU GRUB. GRUB uses its own custom implementation, instead of directly adapting the Linux kernel implementation. At the moment it is [only the PBKDF2](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub/grub.html#cryptomount) key derivation function supported. Argon2i, is not yet supported. That's the point, you must convert it from Argon2i to PBKDF2, if you wish to use LUKSv2. Therefor you can use any live distribution with the package, that include dm-crypt.
|
||||
|
||||
If the installation is finished, boot with a live CD and change it with:
|
||||
|
||||
cryptsetup luksConvertKey --pbkdf pbkdf2 /dev/sdX
|
||||
|
||||
If you do find that LUKSv2 is broken, just downgrade to LUKSv1.
|
||||
|
||||
Generate distro's grub.cfg
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ This guide assumes that you are using the GNU GRUB bootloader directly.
|
|||
If you're using SeaBIOS, it's quite intuitive and works similarly to other BIOS
|
||||
software; refer to the documentation on <https://seabios.org/SeaBIOS>.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide explains how to prepare a bootable USB for Libreboot systems that
|
||||
This guide explains how to prepare a bootable USB for libreboot systems that
|
||||
can be used to install several GNU+Linux distributions. For this guide, you
|
||||
will only need a USB flash drive and the `dd` utility (it's installed into all
|
||||
GNU+Linux distributions, by default).
|
||||
|
|
@ -156,7 +156,7 @@ to distro. If you did all of that correctly, then it should now be booting your
|
|||
USB drive in the way that you specified.
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
Most of these issues occur when using Libreboot with coreboot's `text-mode`
|
||||
Most of these issues occur when using libreboot with coreboot's `text-mode`
|
||||
with libgfxinit for video initialization. This mode is useful for text mode
|
||||
payloads, like `MemTest86+`, which expect `text-mode`, but for GNU+Linux
|
||||
distributions it can be problematic when they are trying to switch to a
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ on *bare metal* as a native coreboot payload and does *not* use BIOS or UEFI
|
|||
services (but it *can* load and execute SeaBIOS, in addition to any other
|
||||
coreboot payload, by chainloading it).
|
||||
|
||||
In most circumstances, this guide will not benefit you. Libreboot's default
|
||||
In most circumstances, this guide will not benefit you. libreboot's default
|
||||
GRUB configuration file contains scripting logic within it that intelligently
|
||||
searches for GRUB partitions installed onto a partition on your SSD, HDD or
|
||||
USB drive installed on your computer. If such a file is found, libreboot's
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ a known state.
|
|||
Compile flashrom and cbfstool
|
||||
=============================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot does not currently distribute utilities pre-compiled. It only
|
||||
libreboot does not currently distribute utilities pre-compiled. It only
|
||||
provides ROM images pre-compiled, where feasible. Therefore, you have to build
|
||||
the utilities from source.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ image:
|
|||
how to do this are covered in the following article:
|
||||
[How to build libreboot from source](../build/)
|
||||
|
||||
In either case, you will use the `cbfstool` supplied in the Libreboot build
|
||||
In either case, you will use the `cbfstool` supplied in the libreboot build
|
||||
system.
|
||||
This can be found under `coreboot/*/util/cbfstool/` as source code,
|
||||
where `*` can be any coreboot source code directory for a given mainboard.
|
||||
|
|
@ -117,7 +117,7 @@ machine powered down) and read the contents of the boot flash.
|
|||
Extract grub.cfg
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot images that use the GNU GRUB bootloader will have *two* configuration
|
||||
libreboot images that use the GNU GRUB bootloader will have *two* configuration
|
||||
files in CBFS:
|
||||
|
||||
* `grub.cfg`
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,21 +5,21 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
|
||||
This article only applies to those people who use the GNU GRUB bootloader as
|
||||
their default payload (options besides GNU GRUB are also available in
|
||||
Libreboot). Whenever this article refers to GNU GRUB, or configuration files
|
||||
libreboot). Whenever this article refers to GNU GRUB, or configuration files
|
||||
used in GNU GRUB, it is referring exclusively to those files hosted in CBFS
|
||||
(coreboot file system) in the Libreboot ROM image. In this configuration, GNU
|
||||
(coreboot file system) in the libreboot ROM image. In this configuration, GNU
|
||||
GRUB is running on *bare metal* as a coreboot payload (instead of relying on
|
||||
BIOS or UEFI services, like it does on *most* x86 based configurations).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide deals with various ways in which you can harden your GNU GRUB
|
||||
configuration, for security purposes. These steps are optional, but *strongly*
|
||||
recommended by the Libreboot project.
|
||||
recommended by the libreboot project.
|
||||
|
||||
GNU GRUB provides *many* advanced security features, which most people don't
|
||||
know about but are fully documented on the Libreboot website. Read on!
|
||||
know about but are fully documented on the libreboot website. Read on!
|
||||
|
||||
This article doesn't cover how to dump your ROM, or flash a new one. Please
|
||||
read other sections in the Libreboot documentation if you don't know how to do
|
||||
read other sections in the libreboot documentation if you don't know how to do
|
||||
that. As such, this is an *expert only* guide. There is a great possibility for
|
||||
bricking your system if you follow this guide incorrectly, or otherwise don't
|
||||
know what you're doing.
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ PGP signatures on *any* type of file, on any storage medium supported by
|
|||
GNU GRUB (it supports basically everything, including CBFS which is short
|
||||
for coreboot file system and it is what we will focus on in this article).
|
||||
We will be using this functionality to verify the signature of a Linux kernel,
|
||||
at boot time. In conjunction with reproducible builds (both Libreboot and your
|
||||
at boot time. In conjunction with reproducible builds (both libreboot and your
|
||||
Linux kernel), this can greatly improve system security; Debian is an excellent
|
||||
example of a GNU+Linux distribution that is fully reproducible nowadays (in
|
||||
stable releases).
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,9 +49,9 @@ repository). More information about reproducible builds can be found here:
|
|||
|
||||
<https://reproducible-builds.org/>
|
||||
|
||||
Reproducibility is a key goal of the Libreboot project, though it has not yet
|
||||
Reproducibility is a key goal of the libreboot project, though it has not yet
|
||||
achieved that goal. However, it is an important part of any secure system. We
|
||||
suggest that, when securing your Libreboot system as instructed by this guide,
|
||||
suggest that, when securing your libreboot system as instructed by this guide,
|
||||
you should also use a reproducible GNU+Linux distribution (because checking GPG
|
||||
signatures on a non-reproducible binary, such as a Linux kernel, is meaningless
|
||||
if that binary can be compromised as a result of literally not being able to
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ they gave you. Based on these facts, we can observe that checking GPG
|
|||
signatures will improve your *operational* security, but only in specific
|
||||
circumstances under *controlled conditions*.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial assumes you have a Libreboot image (ROM) that you wish to modify,
|
||||
This tutorial assumes you have a libreboot image (ROM) that you wish to modify,
|
||||
which from now on we will refer to simply as *`my.rom`*. It should go without
|
||||
saying that this ROM uses the GNU GRUB bootloader as payload. This page shows
|
||||
how to modify grubtest.cfg, which means that signing and password protection
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,13 +72,13 @@ incorrect configuration will be impossible. After you are satisfied with the
|
|||
new setup, you should transfer the new settings to grub.cfg to make your
|
||||
machine truly secure.
|
||||
|
||||
First, extract the old grubtest.cfg and remove it from the Libreboot
|
||||
First, extract the old grubtest.cfg and remove it from the libreboot
|
||||
image:
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool my.rom extract -n grubtest.cfg -f my.grubtest.cfg
|
||||
cbfstool my.rom remove -n grubtest.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
You can build `cbfstool` in the Libreboot build system. Run this command:
|
||||
You can build `cbfstool` in the libreboot build system. Run this command:
|
||||
|
||||
./build module cbutils
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,13 +87,13 @@ This assumes that you already downloaded coreboot:
|
|||
./download coreboot
|
||||
|
||||
This, in turn, assumes that you have installed the build dependencies for
|
||||
Libreboot. On Ubuntu 20.04 and other apt-get distros, you can do this:
|
||||
libreboot. On Ubuntu 20.04 and other apt-get distros, you can do this:
|
||||
|
||||
./build dependencies ubuntu2004
|
||||
|
||||
The `cbfstool` executables will be under each coreboot directory, under
|
||||
each `coreboot/boardname/` directory for each board. Just pick one, presumably
|
||||
from the coreboot directory for your board. Libreboot creates multiple coreboot
|
||||
from the coreboot directory for your board. libreboot creates multiple coreboot
|
||||
archives for different board revisions, on different boards.
|
||||
|
||||
References:
|
||||
|
|
@ -152,9 +152,9 @@ done using the `grub-mkpasswd-pbkdf2` utility. You can get it by
|
|||
installing GRUB version 2. Generate a key by giving it a password:
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This utility is included under the `grub/` directory, when you build
|
||||
GRUB using the Libreboot build system. Run the following commands (assuming
|
||||
GRUB using the libreboot build system. Run the following commands (assuming
|
||||
you have the correct build dependencies installed) to build GNU GRUB, from the
|
||||
Libreboot Git repository:
|
||||
libreboot Git repository:
|
||||
|
||||
./download grub
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -208,9 +208,9 @@ function try\_user\_config:
|
|||
|
||||
The `unset superusers` command disables password authentication, which will
|
||||
allow the attacker to boot an arbitrary operating system, regardless of
|
||||
signature checking. The default Libreboot configuration is tweaked for *easy of
|
||||
signature checking. The default libreboot configuration is tweaked for *easy of
|
||||
use* by end users, and it is *not* done with security in mind (though security
|
||||
is preferred). Thus, Libreboot is less restrictive by default. What you are
|
||||
is preferred). Thus, libreboot is less restrictive by default. What you are
|
||||
doing, per this article, is making your system *more secure* but at the expense
|
||||
of user-friendliness.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -255,7 +255,7 @@ entries):
|
|||
trust (cbfsdisk)/boot.key
|
||||
set check_signatures=enforce
|
||||
|
||||
What remains now is to include the modifications into the Libreboot image
|
||||
What remains now is to include the modifications into the libreboot image
|
||||
(ROM):
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool my.rom add -n boot.key -f boot.key -t raw
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ Objective
|
|||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
To provide step-by-step guide for setting up guix system (stand-alone guix) with
|
||||
full disk encryption (including /boot) on devices powered by Libreboot.
|
||||
full disk encryption (including /boot) on devices powered by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Scope
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ Reboot the device.
|
|||
Pre-Installation
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
On reboot, as soon as you see the Libreboot Graphic Art, press arrow keys to
|
||||
On reboot, as soon as you see the GNU GRUB menu, press arrow keys to
|
||||
change the menu entry.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose “Search for GRUB2 configuration on external media [s]” and wait for the
|
||||
|
|
@ -314,10 +314,10 @@ Reboot the device.
|
|||
Post-Installation
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
On reboot, as soon as you see the Libreboot Graphic Art, choose the option
|
||||
On reboot, as soon as you see the GNU GRUB menu, choose the option
|
||||
'Load Operating System [o]'
|
||||
|
||||
Enter LUKS Key, for Libreboot's grub, as prompted.
|
||||
Enter LUKS Key, for libreboot's grub, as prompted.
|
||||
|
||||
You may have to go through warning prompts by repeatedly pressing the
|
||||
"enter/return" key.
|
||||
|
|
@ -362,7 +362,7 @@ update/upgrade part of post-installation section, to keep your guix distribution
|
|||
and guix system updated.
|
||||
|
||||
That is it! You have now setup guix system with full-disk encryption on your
|
||||
device powered by Libreboot. Enjoy!
|
||||
device powered by libreboot. Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
References
|
||||
==========
|
||||
|
|
@ -374,3 +374,26 @@ Acknowledgements
|
|||
|
||||
[1] Thanks to Guix Developer, Clement Lassieur (clement@lassieur.org),
|
||||
for helping me with the Guile Scheme Code for the Bootloader Configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide was originally written for the Libreboot project, and later adapted
|
||||
for the libreboot project. This fact is clearly stated, out of respect to the
|
||||
Guix project; it is a GNU project, and therefore probably does not agree with
|
||||
the policies of the libreboot project. Rather, they most likely agree with the
|
||||
Libreboot policies instead. This paragraph is written simply to provide such
|
||||
clarification, so that people do not think the GNU project (or FSF) endorse or
|
||||
condone libreboot in any way; they do not.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot project respects GNU, and it is itself a project that aims to bring
|
||||
as much free software as possible to everyone, on as much hardware as possible.
|
||||
Without the GNU project, it is unlikely that we would have much Free Software
|
||||
today; there were others that started around the same time, but GNU was the
|
||||
project that provided the most momentum in the very early days of the movement.
|
||||
Today, GNU is still a driving force in the Free Software movement.
|
||||
|
||||
Respect the GNU project. Cherish it.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot policies are written here: [binary blob reduction
|
||||
policy](../../news/policy.md)
|
||||
|
||||
The *libreboot* policies are here: [binary blob deletion
|
||||
policy](https://libreboot.org/news/policy.html)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ If you're using SeaBIOS, the boot process will work similarly to traditional
|
|||
BIOS systems; refer to the SeaBIOS documentation
|
||||
on <https://seabios.org/SeaBIOS>
|
||||
|
||||
GNU+Linux is the operating system of choice, for Libreboot development. It is
|
||||
GNU+Linux is the operating system of choice, for libreboot development. It is
|
||||
highly recommended over any other operating system, precisely because it consists
|
||||
of [Free Software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) (free as in
|
||||
freedom). There *are* other free operating systems, such as BSD, but most of
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,8 +21,8 @@ Useful links
|
|||
|
||||
Refer to the following pages:
|
||||
|
||||
* [How to Prepare and Boot a USB Installer in Libreboot Systems](grub_boot_installer.md)
|
||||
* [Modifying the GRUB Configuration in Libreboot Systems](grub_cbfs.md)
|
||||
* [How to Prepare and Boot a USB Installer in libreboot Systems](grub_boot_installer.md)
|
||||
* [Modifying the GRUB Configuration in libreboot Systems](grub_cbfs.md)
|
||||
* [Installing Hyperbola GNU+Linux, with Full-Disk Encryption (including /boot)](https://wiki.hyperbola.info/en:guide:encrypted_installation)
|
||||
* [Installing Debian or Devuan GNU+Linux-Libre, with Full-Disk Encryption (including /boot)](encrypted_debian.md)
|
||||
* [Installing Guix System, with Full-Disk Encryption (including /boot)](guix.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,9 +34,6 @@ Guix, Parabola, Trisquel
|
|||
These guides were outdated, so they were deleted. You can find links to them
|
||||
here: <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww/issues/4>
|
||||
|
||||
The above issue page is the same as this entry on the TODO page:
|
||||
[../../tasks/#move-all-distro-fdeboot-guides-to-distro-wikimanuals](../../tasks/#move-all-distro-fdeboot-guides-to-distro-wikimanuals)
|
||||
|
||||
The Debian guide has been retained, because it's currently up to date. The
|
||||
Hyperbola guide is already on the Hyperbola website, and the above is just a
|
||||
link.
|
||||
|
|
@ -76,9 +73,9 @@ This may also apply to CentOS or Redhat. Chroot guide can be found on
|
|||
linux16 issue
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
When you use Libreboot's default GRUB config, and libreboot's grub uses fedora's
|
||||
default `grub.cfg` (in `/boot/grub2/grub.cfg`), fedora by default makes use of the
|
||||
`linux16` command, whereas it should be saying `linux`
|
||||
Libreboot's default GRUB config sources fedora's grub config
|
||||
`grub.cfg` (in `/boot/grub2/grub.cfg`), fedora by default makes use of the
|
||||
`linux16` command, where it should be saying `linux`
|
||||
|
||||
Do this in fedora:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,11 +7,11 @@ TODO: this guide should be reviewed and updated. Some info might be out of
|
|||
date.
|
||||
|
||||
[GNU GRUB](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/) already has excellent
|
||||
documentation, but there are aspects of Libreboot that deserve special
|
||||
treatment. Libreboot provides the option to boot GNU GRUB directly, running on
|
||||
documentation, but there are aspects of libreboot that deserve special
|
||||
treatment. libreboot provides the option to boot GNU GRUB directly, running on
|
||||
bare metal (instead of using BIOS or UEFI services).
|
||||
|
||||
[The GNU+Linux section](../gnulinux/) also has Libreboot-specific guides for
|
||||
[The GNU+Linux section](../gnulinux/) also has libreboot-specific guides for
|
||||
dealing with GNU+Linux distributions when using GNU GRUB directly, in this
|
||||
setup. [A similar section exists for BSD operating systems](../bsd/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,11 +39,11 @@ file (generated by ckbcomp) and run it through `grub-mklayout` like so:
|
|||
cat frazerty | ./grub/grub-mklayout -o frazerty.gkb
|
||||
|
||||
Place the newly created `.gkb` file under `resources/grub/keymap` in lbmk. When
|
||||
you build Libreboot, a ROM image with GRUB payload and your newly created
|
||||
you build libreboot, a ROM image with GRUB payload and your newly created
|
||||
keymap will be available under the `bin/` directory.
|
||||
[Learn how to build Libreboot ROM images](../build/)
|
||||
[Learn how to build libreboot ROM images](../build/)
|
||||
|
||||
Many keymaps exist in the Libreboot build system, but sometimes you must
|
||||
Many keymaps exist in the libreboot build system, but sometimes you must
|
||||
manually tweak the file created by `ckbcomp`, adjusting the scan codes in that
|
||||
file, before converting to a GRUB keymap file. Therefore, it would be unwise to
|
||||
automatically add all keymaps in GRUB.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,183 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ASUS Chromebook C201
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: support for this machine is dropped in recent Libreboot releases. It will
|
||||
be re-added at a later date. For now, please use Libreboot 20160907 on this
|
||||
machine.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: much of this page is outdated. for instance, it references cafe beverage
|
||||
who later revealed herself to be Alyssa Rosenzweig, who then launched the
|
||||
Panfrost project.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a Chromebook, using the Rockchip RK3288 SoC. It uses an ARM CPU,
|
||||
and has free EC firmware (unlike some other laptops). More RK3288-based
|
||||
laptops will be added to libreboot at a later date.
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/\#flashrom](../install/#flashrom)
|
||||
|
||||
Google's intent with CrOS devices
|
||||
==================================
|
||||
|
||||
CrOS (Chromium OS/Chrome OS) devices, such as Chromebooks, were not
|
||||
designed with the intent of bringing more freedom to users. However,
|
||||
they run with a lot of free software at the boot software and embedded
|
||||
controller levels, since free software gives Google enough flexibility
|
||||
to optimize various aspects such as boot time and most importantly, to
|
||||
implement the CrOS security system, that involves various aspects of the
|
||||
software. Google does hire a lot of Coreboot developers, who are
|
||||
generally friendly to the free software movement and try to be good
|
||||
members of the free software community, by contributing code back.
|
||||
|
||||
CrOS devices are designed (from the factory) to actually coax the user
|
||||
into using proprietary web services (SaaSS) that invade the user's
|
||||
privacy (ChromeOS is literally just the Google Chrome browser when you
|
||||
boot up, itself proprietary and comes with proprietary add-ons like
|
||||
flash. It's only intended for SaaSS, not actual, real computing).
|
||||
Google is even a member of the *PRISM* program, as outlined by Edward
|
||||
Snowden. See notes about ChromeOS below. The libreboot project
|
||||
recommends that the user replace the default *ChromeOS* with a
|
||||
distribution that can be used in freedom, without invading the user's
|
||||
privacy.
|
||||
|
||||
We also use a similar argument for the MacBook and the ThinkPads that
|
||||
are supported in libreboot. Those laptops are supported, in spite of
|
||||
Apple and Lenovo, companies which are actually *hostile* to the free
|
||||
software movement.
|
||||
|
||||
Considerations about ChromeOS and free operating systems
|
||||
========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
This laptop comes preinstalled (from the factory) with Google ChromeOS.
|
||||
This is a GNU+Linux distribution, but it's not general purpose and it
|
||||
comes with proprietary software. It's designed for SaaSS. Libreboot
|
||||
recommends that users of this laptop replace it with another
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian GNU+Linux
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
<https://wiki.debian.org/InstallingDebianOn/Asus/C201> shows how to
|
||||
install Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan GNU+Linux
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
<https://notabug.org/dimkr/devsus> produces bootable and installable
|
||||
Devuan images.
|
||||
|
||||
Parabola GNU+Linux
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See:
|
||||
<https://lists.gnu.org/archive/html/libreboot/2015-12/msg00026.html>
|
||||
|
||||
In this discussion thread (on the old GNU Libreboot mailing lists), there are
|
||||
instructions for installing Parabola on C201 and other rockchip chromebooks
|
||||
supported by Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Caution: Video acceleration requires a non-free blob, software rendering can be used instead.
|
||||
=============================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
The C201 has a Mali T GPU, which requires a non-free blob. A driver,
|
||||
Tamil, was written, but its source code has not been released. The
|
||||
developer has so-far [withheld
|
||||
it](http://libv.livejournal.com/27461.html). Use software rendering to
|
||||
avoid the blob instead. Most tasks can still be performed without video
|
||||
acceleration, without any noticeable performance penalty.
|
||||
|
||||
In practise, this means that certain things like games, blender and
|
||||
GNOME shell (or other fancy desktops) won't work well. The libreboot
|
||||
project recommends a lightweight desktop which does not need video
|
||||
acceleration, such as *XFCE* or *LXDE*.
|
||||
|
||||
As it is unlikely that Tamil will be released, the
|
||||
[chai](https://notabug.org/cafe/chai) project is writing a driver as
|
||||
well. Ask on IRC if you think you can contribute.
|
||||
|
||||
Caution: WiFi requires a non-free blob, a USB dongle can be used instead.
|
||||
=========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
These laptops have non-removeable (soldered on) M.2 Type 1216 card
|
||||
with WiFi+Bluetooth, which requires non-free firmware to be loaded by
|
||||
the Linux kernel in order to work.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot project recommends using an external USB wifi dongle that
|
||||
works with free software. See
|
||||
[\#recommended\_wifi](./#recommended_wifi).
|
||||
|
||||
There are 2 companies (endorsed by Free Software Foundation, under their
|
||||
*Respects your Freedom* guidelines), that sell USB WiFi dongles
|
||||
guaranteed to work with free software (i.e. linux-libre kernel):
|
||||
|
||||
- [ThinkPenguin sells
|
||||
them](https://www.thinkpenguin.com/gnu-linux/penguin-wireless-n-usb-adapter-gnu-linux-tpe-n150usb)
|
||||
(company based in USA)
|
||||
- [Tehnoetic sells
|
||||
them](https://tehnoetic.com/tehnoetic-wireless-adapter-gnu-linux-libre-tet-n150)
|
||||
(company based in Europe)
|
||||
|
||||
These wifi dongles use the AR9271 (atheros) chipset, supported by the
|
||||
free *ath9k\_htc* driver in the Linux kernel. They work in *linux-libre*
|
||||
too.
|
||||
|
||||
EC firmware is free software!
|
||||
=============================
|
||||
|
||||
It's free software. Google provides the source. Build scripts will be
|
||||
added later, with EC sources provided in libreboot, and builds of the EC
|
||||
firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
This is unlike the other current libreboot laptops (Intel based). In
|
||||
practise, you can (if you do without the video/wifi blobs, and replace
|
||||
ChromeOS with a distribution that respects your freedom) be more free
|
||||
when using one of these laptops.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot FAQ briefly describes what an *EC* is:
|
||||
[../../faq.md#firmware-ec](../../faq.md#firmware-ec)
|
||||
|
||||
No microcode!
|
||||
=============
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike x86 (e.g. Intel/AMD) CPUs, ARM CPUs do not use microcode, not
|
||||
even built in. On the Intel/AMD based libreboot systems, there is still
|
||||
microcode in the CPU (not considered problematic by the FSF, provided
|
||||
that it is reasonably trusted to not be malicious, since it's part of
|
||||
the hardware and read-only), but we exclude microcode updates (volatile
|
||||
updates which are uploaded at boot time by the boot firmware, if
|
||||
present), which are proprietary software.
|
||||
|
||||
On ARM CPUs, the instruction set is implemented in circuitry, without
|
||||
microcode.
|
||||
|
||||
Depthcharge payload
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
These systems do not use the GRUB payload. Instead, they use a payload
|
||||
called depthcharge, which is common on CrOS devices. This is free
|
||||
software, maintained by Google.
|
||||
|
||||
Flash chip write protection: the screw
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
|
||||
It's next to the flash chip. Unscrew it, and the flash chip is
|
||||
read-write. Screw it back in, and the flash chip is read-only. It's
|
||||
called the screw.
|
||||
|
||||
*The screw* is accessible by removing other screws and gently prying off
|
||||
the upper shell, where the flash chip and the screw are then directly
|
||||
accessible. User flashing from software is possible, without having to
|
||||
externally re-flash, but the flash chip is SPI (SOIC-8 form factor) so
|
||||
you can also externally re-flash if you want to. In practise, you only
|
||||
need to externally re-flash if you brick the laptop; read
|
||||
[../install/spi.md](../install/spi.md) for an example
|
||||
of how to set up an SPI programmer.
|
||||
|
||||
Write protection is useful, because it prevents the firmware from being
|
||||
re-flashed by any malicious software that might become executed on your
|
||||
GNU+Linux system, as root. In other words, it can prevent a
|
||||
firmware-level *evil maid* attack. It's possible to write protect on
|
||||
all current libreboot systems, but CrOS devices make it easy. The screw
|
||||
is such a stupidly simple idea, which all designs should implement.
|
||||
|
|
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: Intel D510MO and D410PT desktop boards
|
|||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This is a desktop board using intel hardware (circa \~2009, ICH7
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the Libreboot X200. It can make
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the ThinkPad X200. It can make
|
||||
for quite a nifty desktop. Powered by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: D410PT is another name and it's the same board. Flash the exact same
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ that it should also work but this is untested.
|
|||
Remarks about vendor bios:
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Without coreboot/libreboot this board is utery useless, since the
|
||||
- Without coreboot/libreboot this board is completely useless, since the
|
||||
vendor bios is very bad. It cannot boot from any HDD whether it is
|
||||
connected to the SATA port or USB. With libreboot it works just
|
||||
fine.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,11 +3,35 @@ title: Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L desktop board
|
|||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This is a desktop board using intel hardware (circa \~2009, ICH7
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the Libreboot X200. It can make
|
||||
southbridge, similar performance-wise to the ThinkPad X200. It can make
|
||||
for quite a nifty desktop. Powered by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: As of January 4th, 2021, video initialization is broken on this machine.
|
||||
It is advisable to use Libreboot 20160907, for the time being. You can build a
|
||||
ROM image from libreboot, and extract the CPU microcode updates to then insert in
|
||||
the Libreboot 20160907 ROM image, like so (using cbfstool):
|
||||
|
||||
cbfstool libreboot.rom extract -n cpu_microcode_blob.bin -f cpu_microcode_blob.bin
|
||||
cbfstool libreboot.rom add -n cpu_microcode_blob.bin -f cpu_microcode_blob.bin -t microcode
|
||||
|
||||
With this, you will then have a Libreboot ROM image, but with improved stability
|
||||
due to microcode updates. The code in coreboot that checks for this file, in
|
||||
CBFS, is present in every Libreboot release; Libreboot merely excludes the blob
|
||||
itself, but does not delete the code for loading it. The Libreboot 20160907
|
||||
release is reliable, on this board (but has a few issues, for example the PCI
|
||||
express slots don't work).
|
||||
|
||||
The advice above is only useful for the onboard graphics chipset (the Intel
|
||||
one). If you're using an add-on graphics card (PCI express), you can simply
|
||||
use libreboot, and it will work. If you're doing *that*, please use one of the
|
||||
ROM images with the *SeaBIOS* payload, booting in text mode. SeaBIOS will
|
||||
automatically execute the option ROM on your graphics card, implementing VBE
|
||||
(Video BIOS extension).
|
||||
|
||||
IDE on the board is untested, but it might be possible to use a SATA HDD
|
||||
using an IDE SATA adapter. The SATA ports do work.
|
||||
using an IDE SATA adapter. The SATA ports do work, but it's IDE emulation. The
|
||||
emulation is slow in DMA mode sia SeaBIOS, so SeaBIOS is configured to use PIO
|
||||
mode on this board. This SeaBIOS configuration does not affect the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
You need to set a custom MAC address in GNU+Linux for the NIC to work.
|
||||
In /etc/network/interfaces on debian-based systems like Debian or
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,7 +55,7 @@ in the build system:
|
|||
./build module cbutils
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about using the build system, lbmk, here:\
|
||||
[Libreboot build instructions](../build/)
|
||||
[libreboot build instructions](../build/)
|
||||
|
||||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/](../install/)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,6 +3,19 @@ title: Hardware compatibility list
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
**The libreboot project was rebooted on January 4th, 2022. Some boards were
|
||||
deleted as a result, but they will be re-added later, with documentation also
|
||||
re-added. The Libreboot and libreboot projects went completely out of sync, but
|
||||
the Libreboot project was more up to date, so libreboot, itself a fork of
|
||||
Libreboot originally, was PURGED and then RE-FORKED once again, but from
|
||||
Libreboot in late 2021. From now on, greater care will be taken to keep the
|
||||
two projects in sync. Both projects are lead and were also founded by Leah
|
||||
Rowe.**
|
||||
|
||||
The current version of libreboot already has several major differences. For
|
||||
example, microcode updates are enabled by default, on all boards, even those
|
||||
that Libreboot supports (this greatly increases system stability).
|
||||
|
||||
This sections relates to known hardware compatibility in libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
For installation instructions, refer to [../install/](../install/).
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,17 +25,17 @@ because coreboot lacks native video initialization for the ATI GPUs on these
|
|||
machines.
|
||||
|
||||
(for later machines like T500, T400, ATI GPU doesn't matter, because it also
|
||||
has an Intel GPU, and Libreboot uses the Intel one)
|
||||
has an Intel GPU, and libreboot uses the Intel one)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported hardware
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot supports the following systems in this release:
|
||||
libreboot currently supports the following systems in this release:
|
||||
|
||||
### Desktops (AMD, Intel, x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L motherboard](ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
||||
- Acer G43T-AM3 (**Libreboot 20210522 and later**)
|
||||
- Acer G43T-AM3
|
||||
- [Intel D510MO and D410PT motherboards](d510mo.md)
|
||||
- [Intel D945GCLF](d945gclf.md) (D945GCLF2D also reported working by a user)
|
||||
- [Apple iMac 5,2](imac52.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,22 +46,29 @@ Libreboot supports the following systems in this release:
|
|||
- [ASUS KGPE-D16 motherboard](kgpe-d16.md)
|
||||
- [ASUS KFSN4-DRE motherboard](kfsn4-dre.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Laptops (ARM)
|
||||
|
||||
- [ASUS Chromebook C201](c201.md) (**Libreboot 20160907 only**)
|
||||
|
||||
### Laptops (Intel, x86)
|
||||
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60 / X60S / X60 Tablet
|
||||
- ThinkPad T60 (with Intel GPU)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad X200 / X200S / X200 Tablet](x200.md)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad X301 (**Libreboot 20210522 and later**)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad X230 (documentation needs to be re-added, ever since the
|
||||
purge on 4 January 2022. It will be done asap)
|
||||
- Lenovo ThinkPad X301
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R400](r400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T400 / T400S](t400.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T500](t500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad W500](t500.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R500](r500.md)
|
||||
- [Apple MacBook1,1 and MacBook2,1](macbook21.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T440p](../install/t440p_external.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo Thinkpad X220](../install/ivy_has_common.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo Thinkpad X220t](../install/ivy_has_common.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo Thinkpad T420](../install/ivy_has_common.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo Thinkpad X230](../install/x230_external.md)
|
||||
- [Lenovo Thinkpad X230t](../install/x230_external.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: More hardware is supported. See `resources/coreboot/` in lbmk. Update
|
||||
the above list!
|
||||
|
||||
'Supported' means that the build scripts know how to build ROM images
|
||||
for these systems, and that the systems have been tested (confirmed
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,7 +88,7 @@ will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
|||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. Libreboot
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. better battery
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,9 +16,9 @@ CPU cores).
|
|||
|
||||
This is a desktop board using AMD hardware (Fam10h *and Fam15h* CPUs
|
||||
available). It can also be used for building a high-powered workstation.
|
||||
Libreboot also supports it. The coreboot port was done by Timothy Pearson of
|
||||
libreboot also supports it. The coreboot port was done by Timothy Pearson of
|
||||
Raptor Engineering Inc. and, working with them, merged into libreboot many
|
||||
years ago.
|
||||
years ago. It is also supported by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that not all boards are compatible. See [board status](#boardstatus)
|
||||
below to determine compatibility with your board.
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ below to determine compatibility with your board.
|
|||
Flashing instructions can be found at
|
||||
[../install/](../install/) - note that external
|
||||
flashing is required (e.g. RPi), if the proprietary (ASUS) firmware is
|
||||
currently installed. If you already have libreboot/osboot/coreboot, by default
|
||||
currently installed. If you already have libreboot/libreboot/coreboot, by default
|
||||
it is possible to re-flash using software running in GNU+Linux on the kcma-d8,
|
||||
without using external hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ this:
|
|||
|
||||
The default chip is a 2MiB one, but we recommend upgrading it to a 16MiB chip.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: If you're already running Libreboot, you probably don't
|
||||
NOTE: If you're already running libreboot, you probably don't
|
||||
need to re-flash externally. Refer instead to the generic instructions on
|
||||
this page: [../install/](../install/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,6 +58,7 @@ PCI option ROMs
|
|||
|
||||
Unlike Libreboot 20160907, Libreboot in newer releases now supports finding and
|
||||
loading PCI option ROMs automatically, both in GRUB and SeaBIOS on this machine.
|
||||
This was inherited by libreboot, when the Libreboot project was forked.
|
||||
|
||||
So for example, if you wish to use an add-on graphics card, you can! It's no
|
||||
problem, and should work just fine.
|
||||
|
|
@ -73,25 +74,8 @@ CPU compatibility
|
|||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
- Opteron 4100 series: Incompatible
|
||||
- Opteron 4200 series: Compatible, does not require microcode updates
|
||||
- Opteron 4300 series: Compatible, requires microcode updates (nonfree!)
|
||||
|
||||
"Requires" means needed for stability. Opteron 4200 series CPUs work very well,
|
||||
even without microcode updates. Because the updates are non-free, Libreboot does
|
||||
not include them.
|
||||
|
||||
In particular, the 4200 series works well with hardware virtualization even
|
||||
without the microcode updates; 4300 series on the other hand is more dependent
|
||||
upon these microcode updates.
|
||||
|
||||
Microcode configures the logic gate arrays inside your CPU, to implement the
|
||||
instruction set architecture, which in turn is what enables *instructions* to
|
||||
execute on your CPU. What do you think will happen if you don't have these
|
||||
updates? The answer is: bugs are possible, and the updates fix those bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
AMD CPUs are generally better engineered than Intel ones, and work much nicer
|
||||
without updates compared to Intel CPUs, but CPU manufacturers design their chips
|
||||
to accept updates for a reason!
|
||||
- Opteron 4200 series: Compatible
|
||||
- Opteron 4300 series: Compatible
|
||||
|
||||
Board status (compatibility) {#boardstatus}
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,7 +88,7 @@ There are two ways to identify a supported KCMA-D8 board:
|
|||
Supported boards begin with a serial number of **B9S2xxxxxxxx** or above where
|
||||
the first character refers to the year of manufacture (A = 2010, B = 2011, etc.)
|
||||
and the following character the month in hexadecimal (1...9, A, B, C). Thus, any
|
||||
board produced September 2011 *or later* are compatible with Libreboot. Boards
|
||||
board produced September 2011 *or later* are compatible with libreboot. Boards
|
||||
originally shipped with BIOS version **2001** or higher are also compatible.
|
||||
|
||||
For help locating these identifying markers, see [ASUS documentation for determining Opteron 4200 series compatibility](https://web.archive.org/web/20200710022605/https://dlcdnets.asus.com/pub/ASUS/mb/SocketC%281027%29/KCMA-D8/Manual&QVL/How_to_identify_MB_supporting_Opteron_4200_CPU.pdf)
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,7 +138,7 @@ framebuffer display (if it has KMS - kernel mode setting).
|
|||
|
||||
NOTE: This section relates to the onboard ASpeed GPU. You *can* use an add-on
|
||||
PCI-E GPU in one of the available slots on the mainboard. Nvidia GTX 780 cards
|
||||
are what Libreboot recommends; it has excellent support in Nouveau (free Linux
|
||||
are what libreboot recommends; it has excellent support in Nouveau (free Linux
|
||||
kernel / mesa driver for Nvidia cards) and generally works well; however, the
|
||||
performance won't be as high in Nouveau, compared to the non-free Nvidia driver
|
||||
because the Nouveau driver can't increase the GPU clock (it doesn't know how,
|
||||
|
|
@ -182,7 +166,7 @@ considerations:
|
|||
and as such a workaround using SGABIOS is necessary. You can find
|
||||
instructions on how to do this on the
|
||||
[Notabug issue tracker](http://web.archive.org/web/20210416011941/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/736)
|
||||
TODO: test whether this is still the case in Libreboot, which uses a newer
|
||||
TODO: test whether this is still the case in libreboot, which uses a newer
|
||||
version of coreboot nowadays)
|
||||
- SAS (via PIKE 2008 module) requires non-free option ROM (and
|
||||
SeaBIOS) to boot from it (theoretically possible to replace, but you
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,7 +174,7 @@ considerations:
|
|||
can be on a SAS drive. The linux kernel can use those SAS drives
|
||||
(via PIKE module) without an option ROM).
|
||||
NOTE: SeaBIOS can load PCI-E option ROMs, and by default it will do so in
|
||||
Libreboot, so you could use it. However, you could *also* simply
|
||||
libreboot, so you could use it. However, you could *also* simply
|
||||
install 16MiB NOR flash with linuxboot payload in it, and use linuxboot
|
||||
which has the Linux kernel, which can use SAS drives without needing that
|
||||
option ROM; then it can kexec another linux kernel, which in turn also can
|
||||
|
|
@ -200,7 +184,7 @@ considerations:
|
|||
Since it's for remote out-of-band management, it's theoretically a
|
||||
backdoor similar to the Intel Management Engine. Fortunately, unlike
|
||||
the ME, this firmware is unsigned which means that a free
|
||||
replacement is theoretically possible. For now, the Libreboot
|
||||
replacement is theoretically possible. For now, the libreboot
|
||||
project recommends not installing the module. [This
|
||||
project](https://github.com/facebook/openbmc) might be interesting
|
||||
to derive from, for those who want to work on a free replacement. In
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ This is a server board using AMD hardware (Fam10h *and Fam15h* CPUs
|
|||
available). It can also be used for building a high-powered workstation.
|
||||
Powered by libreboot. The coreboot port was done by Timothy Pearson of
|
||||
Raptor Engineering Inc. and, working with them (and sponsoring the
|
||||
work), merged into libreboot.
|
||||
work), merged into libreboot. It is also supported by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
*Memory initialization is still problematic, for some modules. We
|
||||
recommend avoiding Kingston modules.*
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,9 +26,7 @@ KGPE-D16, without using external hardware.
|
|||
CPU compatibility
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
*Use Opteron 6200 series (works without microcode updates, including hw
|
||||
virt).* 6300 series needs microcode updates, so avoid those CPUs. 6100
|
||||
series is too old, and mostly untested.
|
||||
Opteron 62xx and 63xx CPUs work just fine.
|
||||
|
||||
Board status (compatibility) {#boardstatus}
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,7 +59,7 @@ P-DIP 8 slot (SPI chip). The flash chip can be upgraded to higher sizes:
|
|||
compressed linux+initramfs image (BusyBox+Linux system) into CBFS and
|
||||
boot that, loading it into memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot has configs for 2, 4, 8 and 16 MiB flash chip sizes (default
|
||||
libreboot has configs for 2, 4, 8 and 16 MiB flash chip sizes (default
|
||||
flash chip is 2MiB).
|
||||
|
||||
*DO NOT hot-swap the chip with your bare hands. Use a P-DIP 8 chip
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,16 +114,9 @@ The information here is adapted, from the ASUS website.
|
|||
recommended - old. View errata datasheet here:
|
||||
<http://support.amd.com/TechDocs/41322_10h_Rev_Gd.pdf>)
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6200 series (Fam15h, with full IOMMU support in
|
||||
libreboot - *highly recommended - fast, and works well without
|
||||
microcode updates, including virtualization*)
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
- AMD Opteron 6300 series (Fam15h, with full IOMMU support in
|
||||
libreboot. *AVOID LIKE THE PLAGUE - virtualization is broken
|
||||
without microcode updates.*
|
||||
- NOTE: 6300 series CPUs have buggy microcode built-in, and
|
||||
libreboot recommends avoiding the updates. The 6200 series CPUs
|
||||
have more reliable microcode. Look at this errata datasheet:
|
||||
<http://support.amd.com/TechDocs/48063_15h_Mod_00h-0Fh_Rev_Guide.pdf>
|
||||
(see Errata 734 - this is what kills the 6300 series)
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
- 6.4 GT/s per link (triple link)
|
||||
|
||||
### Core logic
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
Introduction (GM45+e1000)
|
||||
=========================
|
||||
|
||||
This section is applicable to all Libreboot-supported laptops with the
|
||||
This section is applicable to all libreboot-supported laptops with the
|
||||
mobile 4 series chipset (as shown in `$ lspci`)
|
||||
that use the e1000 ethernet controller (e.g. T400, X200).
|
||||
The R500 is an exception to this as it does not use the built-in e1000.
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,20 +14,20 @@ The R500 is an exception to this as it does not use the built-in e1000.
|
|||
On all these laptops, the
|
||||
[MAC address](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAC_address)
|
||||
for the built-in gigabit ethernet controller is stored inside the flash chip,
|
||||
along with Libreboot and other configuration data. Therefore, installing
|
||||
Libreboot will overwrite it.
|
||||
along with libreboot and other configuration data. Therefore, installing
|
||||
libreboot will overwrite it.
|
||||
|
||||
Thus, for these laptops, prebuilt Libreboot already contains a generic
|
||||
Thus, for these laptops, prebuilt libreboot already contains a generic
|
||||
MAC address in the configuration section. This address is `00:f5:f0:40:71:fe
|
||||
in builds before 2018-01-16 and `00:4c:69:62:72:65` (see the ascii character
|
||||
set) afterwards.
|
||||
Unless you change it, your computer will boot and use it. This can lead
|
||||
to network problems if you have more than one Libreboot computer on
|
||||
to network problems if you have more than one libreboot computer on
|
||||
the same layer2 network (e.g. on the same network switch). The switch
|
||||
(postman) will simply not know who to deliver to as the MAC (house) addresses
|
||||
will be the same.
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent these address clashes, you can either modify prebuilt Libreboot
|
||||
To prevent these address clashes, you can either modify prebuilt libreboot
|
||||
to use an address of your own choosing or you can change the address in your
|
||||
operating system's boot scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,8 +6,8 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
There is an Apple laptop called the macbook1,1 from 2006 which uses the
|
||||
same i945 chipset as the ThinkPad X60/T60. A developer (Mono Moosbart) ported
|
||||
the Macbook2,1 to coreboot, working alongside Vladimir Serbinenko. The ROM
|
||||
images also work on the macbook1,1. Libreboot's support and documentation for
|
||||
this is based on the Libreboot project, which also supports macbook2,1
|
||||
images also work on the macbook1,1. libreboot's support and documentation for
|
||||
this is based on the libreboot project, which also supports macbook2,1
|
||||
|
||||
Some macbook2,1 models are late 2006, others are early 2007.
|
||||
You do not need to use external flashing equipment when flashing the MacBook2,1
|
||||
|
|
@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ External flashing
|
|||
|
||||
macbook1,1 requires external flashing, if running the default Apple firmware.
|
||||
macbook2,1 can be flased internally, regardless.
|
||||
If running coreboot, libreboot or Libreboot, you can already internally re-flash.
|
||||
If running coreboot or libreboot you can already internally re-flash.
|
||||
|
||||
[This page shows disassembly
|
||||
guides](https://www.ifixit.com/Device/MacBook_Core_2_Duo)
|
||||
|
|
@ -79,9 +79,9 @@ motherboard](https://www.ifixit.com/Guide/MacBook+Core+2+Duo+PRAM+Battery+Replac
|
|||
Refer to the following guide:\
|
||||
[Externally rewrite 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol](../install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
You need to replace OS X with GNU+Linux before flashing Libreboot. (OSX
|
||||
won't run at all in Libreboot), if you wish to internally flash on a macbook21.
|
||||
Libreboot won't boot OSX either (well, maybe with Tianocore it would, but that's
|
||||
You need to replace OS X with GNU+Linux before flashing libreboot. (OSX
|
||||
won't run at all in libreboot), if you wish to internally flash on a macbook21.
|
||||
libreboot won't boot OSX either (well, maybe with Tianocore it would, but that's
|
||||
untested and OSX is inferior to GNU+Linux). In general you should think of
|
||||
your Macbook like a regular laptop, for the purposes of anything coreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -122,11 +122,9 @@ remove it.*
|
|||
Make it overheat less
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
*This section is less relevant for Libreboot 20211122 and newer, because cstate
|
||||
level 3 support was added, thanks to vitali64 on IRC. This means that the CPU
|
||||
temperature is much lower most of the time, as is power consumption. However,
|
||||
you might still benefit from the steps below, just not as much as you would have
|
||||
previously benefited.*
|
||||
NOTE: on newer libreboot revisions, this section is less relevant, because C3
|
||||
states are supported now. However, this section may still be useful, so it will
|
||||
be retained.
|
||||
|
||||
The MacBook2,1 overheats a lot with libreboot, we still don't know why but a simple workaround is to install macfanctld.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,13 +183,6 @@ manually. Simply add the line
|
|||
|
||||
to the file /etc/vconsole.conf and then restart the computer.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable 3-finger tap
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
A user submitted a utility to enable 3-finger tap on this laptop. It's
|
||||
available at *resources/utils/macbook21-three-finger-tap* in the
|
||||
Libreboot git repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Make touchpad more responsive
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ There are two possible flash chip sizes for the R400: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
|||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The R400 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. Libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,29 +33,12 @@ will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
|||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. Libreboot
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
Compatibility (without blobs) {#compatibility_noblobs}
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Hardware virtualization (vt-x) {#hwvirt}
|
||||
|
||||
The R400, when run without CPU microcode updates in coreboot, currently
|
||||
kernel panics if running QEMU with vt-x enabled on 2 cores for the
|
||||
guest. With a single core enabled for the guest, the guest panics (but
|
||||
the host is fine). Working around this in QEMU might be possible; if
|
||||
not, software virtualization should work fine (it's just slower).
|
||||
|
||||
On GM45 hardware (with libreboot), make sure that the *kvm* and
|
||||
*kvm\_intel* kernel modules are not loaded, when using QEMU.
|
||||
|
||||
The following errata datasheet from Intel might help with investigation:
|
||||
<http://download.intel.com/design/mobile/specupdt/320121.pdf>
|
||||
|
||||
The R400 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,8 +11,8 @@ The chip is 4MiB NOR flash (SPI protocol) is SOIC8 form factory.
|
|||
Refer to the following guide:\
|
||||
[Externally rewrite 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol](../install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike other GM45+ICH9M thinkpads in Libreboot, the R500 doesn't have an Intel
|
||||
PHY (for Gigabit Ethernet). However, Libreboot still includes an Intel flash
|
||||
Unlike other GM45+ICH9M thinkpads in libreboot, the R500 doesn't have an Intel
|
||||
PHY (for Gigabit Ethernet). However, libreboot still includes an Intel flash
|
||||
descriptor, but with just the descriptor and BIOS region. The `ich9gen` program
|
||||
supports this fully.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ There are two possible flash chip sizes for the T400: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
|||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The T400 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. Libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,28 +36,11 @@ will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
|||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. Libreboot
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
Compatibility (without blobs) {#compatibility_noblobs}
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Hardware virtualization (vt-x) {#hwvirt}
|
||||
|
||||
The T400, when run without CPU microcode updates in coreboot, currently
|
||||
kernel panics if running QEMU with vt-x enabled on 2 cores for the
|
||||
guest. With a single core enabled for the guest, the guest panics (but
|
||||
the host is fine). Working around this in QEMU might be possible; if
|
||||
not, software virtualization should work fine (it's just slower).
|
||||
|
||||
On GM45 hardware (with libreboot), make sure that the *kvm* and
|
||||
*kvm\_intel* kernel modules are not loaded, when using QEMU.
|
||||
|
||||
The following errata datasheet from Intel might help with investigation:
|
||||
<http://download.intel.com/design/mobile/specupdt/320121.pdf>
|
||||
|
||||
The T400 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ There are two possible flash chip sizes for the T500: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
|||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The T500 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. Libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,28 +38,11 @@ will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
|||
- <http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/BIOS_update_without_optical_disk>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. Libreboot
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. bettery battery
|
||||
handling.
|
||||
|
||||
Compatibility (without blobs) {#compatibility_noblobs}
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Hardware virtualization (vt-x) {#hwvirt}
|
||||
|
||||
The T500, when run without CPU microcode updates in coreboot, currently
|
||||
kernel panics if running QEMU with vt-x enabled on 2 cores for the
|
||||
guest. With a single core enabled for the guest, the guest panics (but
|
||||
the host is fine). Working around this in QEMU might be possible; if
|
||||
not, software virtualization should work fine (it's just slower).
|
||||
|
||||
On GM45 hardware (with libreboot), make sure that the *kvm* and
|
||||
*kvm\_intel* kernel modules are not loaded, when using QEMU.
|
||||
|
||||
The following errata datasheet from Intel might help with investigation:
|
||||
<http://download.intel.com/design/mobile/specupdt/320121.pdf>
|
||||
|
||||
The T500 is almost identical to the X200, code-wise. See
|
||||
[x200.md](x200.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ There are two possible flash chip sizes for the X200: 4MiB (32Mbit) or
|
|||
the palmrest: 4MiB is SOIC-8, 8MiB is SOIC-16.
|
||||
|
||||
*The X200 laptops come with the ME (and sometimes AMT in addition)
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. Libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
before flashing libreboot. libreboot disables and removes it by using a
|
||||
modified descriptor: see [../install/ich9utils.md](../install/ich9utils.md)*
|
||||
(contains notes, plus instructions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ will update both the BIOS and EC version. See:
|
|||
- [X200t BIOS Update](http://pcsupport.lenovo.com/au/en/products/laptops-and-netbooks/thinkpad-x-series-tablet-laptops/thinkpad-x200-tablet/downloads/ds018814)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this can only be done when you are using Lenovo BIOS. How to
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. Libreboot
|
||||
update the EC firmware while running libreboot is unknown. libreboot
|
||||
only replaces the BIOS firmware, not EC.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated EC firmware has several advantages e.g. better battery
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,27 +55,6 @@ and only power your ThinkPad by plugging in the AC adapter and power cord."
|
|||
Upon battery verification, Lenovo will replace recalled batteries free of charge.
|
||||
Battery replacement instructions for the X200/X200s are found [on this page.](https://pcsupport.lenovo.com/cr/en/parts/pd003507/)
|
||||
|
||||
Compatibility (without blobs) {#compatibility_noblobs}
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### Hardware virtualization (vt-x) {#hwvirt}
|
||||
|
||||
The X200, when run without CPU microcode updates in coreboot, currently
|
||||
kernel panics if running QEMU with vt-x enabled on 2 cores for the
|
||||
guest. With a single core enabled for the guest, the guest panics (but
|
||||
the host is fine). Working around this in QEMU might be possible; if
|
||||
not, software virtualization should work fine (it's just slower).
|
||||
|
||||
On GM45 hardware (with libreboot), make sure that the *kvm* and
|
||||
*kvm\_intel* kernel modules are not loaded, when using QEMU.
|
||||
|
||||
The following errata datasheet from Intel might help with investigation:
|
||||
<https://web.archive.org/web/20150110195728/https://download.intel.com/design/mobile/specupdt/320121.pdf>
|
||||
|
||||
Anecdotal reports from at least 1 user suggests that some models with
|
||||
CPU microcode 1067a (on the CPU itself) might work with vt-x in
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
LCD compatibility list {#lcd_supported_list}
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,12 +63,6 @@ LCD panel list (X200 panels listed there):
|
|||
|
||||
All LCD panels for the X200, X200S and X200 Tablet are known to work.
|
||||
|
||||
The X200 Tablet has a screen rotation button on its bezel. Depending
|
||||
on the operating system it might or might not rotate the screen, the
|
||||
digitizer (stylus), or the trackpoint accordingly. Utilities are
|
||||
provided to fix this at *resources/utilities/x200t-screen-rotation* in
|
||||
the libreboot git repository.
|
||||
|
||||
### AFFS/IPS panels {#ips}
|
||||
|
||||
#### X200
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,10 +3,10 @@ title: Documentation
|
|||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Always check [libreboot.org](https://libreboot.org/) for the latest updates to
|
||||
Libreboot. News, including release announcements, can be found in
|
||||
libreboot. News, including release announcements, can be found in
|
||||
the [main news section](../news/).
|
||||
|
||||
[Answers to Frequently Asked Questions about Libreboot](../faq.md).
|
||||
[Answers to Frequently Asked Questions about libreboot](../faq.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Installing libreboot
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,6 @@ Information for developers
|
|||
|
||||
- [How to compile the libreboot source code](build/)
|
||||
- [Build system developer documentation](maintain/)
|
||||
- [Depthcharge payload](depthcharge/) (**Libreboot 20160907 only**)
|
||||
- [GRUB payload](grub/)
|
||||
|
||||
Other information
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,60 +33,3 @@ Other information
|
|||
- [Miscellaneous](misc/)
|
||||
- [List of codenames](misc/codenames.md)
|
||||
|
||||
How do I know what version I'm running? {#version}
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
|
||||
If you are at least 127 commits after release 20150518 (commit message
|
||||
*build/roms/helper: add version information to CBFS*) (or you have any
|
||||
*upstream* stable release of libreboot after 20150518), then you can
|
||||
press C at the GRUB console, and use this command to find out what
|
||||
version of libreboot you have:
|
||||
|
||||
cat (cbfsdisk)/lbversion
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you may run this command in GRUB:
|
||||
|
||||
lscoreboot
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using SeaBIOS, information is provided there aswell.
|
||||
|
||||
This will also work on non-release images (the version string is
|
||||
automatically generated, using `git describe --tags HEAD`), built from
|
||||
the git repository. A file named `version` will also be included in the
|
||||
archives that you downloaded (if you are using release archives).
|
||||
|
||||
If it exists, you can also extract this `lbversion` file by using the
|
||||
`cbfstool` utility which libreboot includes, from a ROM image that you
|
||||
either dumped or haven't flashed yet. In your distribution, run
|
||||
cbfstool on your ROM image (`libreboot.rom`, in this example):
|
||||
|
||||
./cbfstool libreboot.rom extract -n lbversion -f lbversion
|
||||
|
||||
You will now have a file, named `lbversion`, which you can read in
|
||||
whatever program it is that you use for reading/writing text files.
|
||||
|
||||
For git, it's easy. Just check the git log.
|
||||
|
||||
For releases on or below 20150518, or snapshots generated from the git
|
||||
repository below 127 commits after 20150518, you can find a file named
|
||||
*commitid* inside the archives. If you are using pre-built ROM images
|
||||
from the libreboot project, you can press C in GRUB for access to the
|
||||
terminal, and then run this command:
|
||||
|
||||
lscoreboot
|
||||
|
||||
You may find a date in here, detailing when that ROM image was built.
|
||||
For pre-built images distributed by the libreboot project, this is a
|
||||
rough approximation of what version you have, because the version
|
||||
numbers are dated, and the release archives are typically built on the
|
||||
same day as the release; you can correlate that with the release
|
||||
information in [release announcements on the news page](/news/).
|
||||
|
||||
For 20160818, note that the lbversion file was missing from CBFS on GRUB
|
||||
images. You can still find out what libreboot version you have by
|
||||
comparing checksums of image dumps (with the descriptor blanked out with
|
||||
00s, and the same done to the ROMs from the release archive, if you are
|
||||
on a GM45 laptop).
|
||||
|
||||
There may also be a ChangeLog file included in your release archive, so
|
||||
that you can look in there to figure out what version you have.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,224 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ASUS Chromebook C201 installation guide
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
**Libreboot 20160907 only. This board was dropped in subsequent releases, but
|
||||
may be added again in the future.**
|
||||
|
||||
**This documentation is retained from Libreboot 20160907, but it may also be
|
||||
prudent to check documentation from Libreboot 20160907 itself. It is included
|
||||
in the source code archive, for that release.**
|
||||
|
||||
The version of Depthcharge used here is very old, from 2016, and support for
|
||||
this laptop was dropped in recent releases. It will be re-added at a later
|
||||
date. If you wish to use Libreboot on this board, right now you must install
|
||||
Libreboot 20160907. This page has been retained on libreboot.org for now, but
|
||||
you should refer to the documentation provided in the Libreboot 20160907
|
||||
release if you want to learn more. NOTE: in that release, the documentation is
|
||||
written in raw HTML, because the Markdown-based static site generator used on
|
||||
libreboot.org had not yet been written at that point.
|
||||
|
||||
These instructions are for installing Libreboot to the ASUS Chromebook
|
||||
C201 (more known under a name [*veyron speedy*](../misc/codenames.md)).
|
||||
Since the device ships with Coreboot, the installation
|
||||
instructions are the same before and after flashing Libreboot for the
|
||||
first time.
|
||||
|
||||
Look at the [list of ROM images](#rom) to see which image is compatible
|
||||
with your device.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot can be installed internally from the device, with sufficient
|
||||
privileges. The installation process requires using *Google's modified
|
||||
version of flashrom*, that has support for reflashing the Chromebook's
|
||||
SPI flash. Otherwise, flashing externally will work with the upstream
|
||||
flashrom version.
|
||||
|
||||
*Google's modified version of flashrom* is free software and its
|
||||
source code is made available by Google:
|
||||
[flashrom](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromiumos/third_party/flashrom/).\
|
||||
It is not distributed along with Libreboot yet. However, it is
|
||||
preinstalled on the device, with ChromeOS.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Libreboot internally requires sufficient privileges on the system
|
||||
installed on the device. When the device has ChromeOS installed (as it does
|
||||
initially), it is necessary to gain root privileges in ChromeOS, to be able to
|
||||
access a root shell.
|
||||
|
||||
Gaining root privileges on ChromeOS
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
In order to gain root privileges on ChromeOS, developer mode has to be
|
||||
enabled from the recovery mode screen and debugging features have to be
|
||||
enabled in ChromeOS.
|
||||
|
||||
Instructions to access the [recovery mode
|
||||
screen](../depthcharge/#recovery_mode_screen) and [enabling developer
|
||||
mode](../depthcharge/#enabling_developer_mode) are available on the page
|
||||
dedicated to [depthcharge](../depthcharge/).
|
||||
|
||||
Once developer mode is enabled, the device will boot to the [developer
|
||||
mode screen](../depthcharge/#developer_mode_screen). ChromeOS can be
|
||||
booted by waiting for 30 seconds (the delay is shortened in Libreboot)
|
||||
or by pressing *Ctrl + D*
|
||||
|
||||
After the system has booted, root access can be enabled by clicking on
|
||||
the *Enable debugging features* link. A confirmation dialog will ask
|
||||
whether to proceed.\
|
||||
After confirming by clicking *Proceed*, the device will reboot and ask
|
||||
for the root password to set. Finally, the operation has to be confirmed
|
||||
by clicking *Enable*.
|
||||
|
||||
After setting the root password, it becomes possible to log-in as root.
|
||||
A tty prompt can be obtained by pressing *Ctrl + Alt + Next*. The
|
||||
*Next* key is the one on the top left of the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
Preparing the device for the installation
|
||||
Before installing Libreboot on the device, both its software and
|
||||
hardware has to be prepared to allow the installation procedure and to
|
||||
ensure that security features don't get in the way.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuring verified boot parameters
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to have access to the [developer mode
|
||||
screen](../depthcharge/#developer_mode_screen) and to [configure the
|
||||
following verified boot
|
||||
parameters](../depthcharge/#configuring_verified_boot_parameters):
|
||||
|
||||
- Kernels signature verification: *disabled*
|
||||
- External media boot: *enabled*
|
||||
|
||||
Those changes can be reverted later, when the device is known to be in a
|
||||
working state.
|
||||
|
||||
Removing the write protect screw
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Since part of the SPI flash is write-protected by a screw, it is
|
||||
necessary to remove the screw to remove the write protection and allow
|
||||
writing Libreboot to the *read-only* part of the flash.
|
||||
|
||||
To access the screw, the device has to be opened. There are 8 screws to
|
||||
remove from the bottom of the device, as shown on the picture below. Two
|
||||
are hidden under the top pads. After removing the screws, the keyboard
|
||||
plastic part can be carefully detached from the rest. *Beware: there
|
||||
are cables attached to it!* It is advised to flip the keyboard plastic
|
||||
part over, as shown on the picture below. The write protect screw is
|
||||
located next to the SPI flash chip, circled in red in the picture below.
|
||||
It has to be removed.
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://av.libreboot.org/c201/screws.jpg) [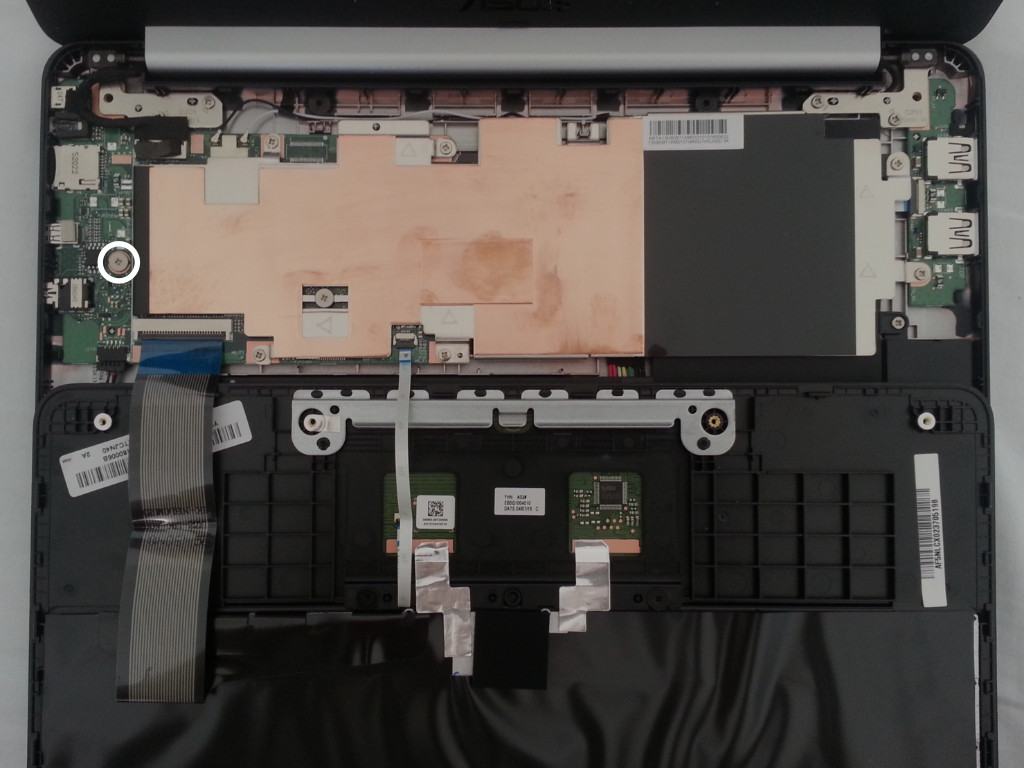](https://av.libreboot.org/c201/wp-screw.jpg)
|
||||
|
||||
The write protect screw can be put back in place later, when the device
|
||||
is known to be in a working state.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Libreboot to the SPI flash
|
||||
=====================================
|
||||
|
||||
The SPI flash (that holds Libreboot) is divided into various partitions
|
||||
that are used to implement parts of the CrOS security system. Libreboot
|
||||
is installed in the *read-only* coreboot partition, that becomes
|
||||
writable after removing the write-protect screw.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Libreboot internally, from the device
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing Libreboot to the SPI flash internally, the device has
|
||||
to be reassembled.
|
||||
|
||||
All the files from the `veyron_speedy` release (or build) have to be
|
||||
transferred to the device.
|
||||
|
||||
The following operations have to be executed with root privileges on the
|
||||
device (e.g. using the `root` account). In addition, the
|
||||
`cros-flash-replace` script has to be made executable:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod a+x cros-flash-replace
|
||||
|
||||
The SPI flash has to be read first:
|
||||
|
||||
flashrom -p host -r flash.img
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: it might be a good idea to copy the produced flash.img file at
|
||||
this point and store it outside of the device for backup purposes.*
|
||||
|
||||
Then, the `cros-flash-replace` script has to be executed as such:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo bash ./cros-flash-replace flash.img coreboot ro-frid
|
||||
|
||||
If any error is shown, it is definitely a bad idea to go further than
|
||||
this point.
|
||||
|
||||
The resulting flash image can then be flashed back:
|
||||
|
||||
flashrom -p host -w flash.img
|
||||
|
||||
You should also see within the output the following:
|
||||
|
||||
Verifying flash... VERIFIED.
|
||||
|
||||
Shut down. The device will now boot to Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Libreboot externally, with a SPI flash programmer
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing Libreboot to the SPI flash internally, the device has
|
||||
to be opened.
|
||||
|
||||
The SPI flash is located next to the write protect screw. Its layout is
|
||||
indicated in the picture below. Note that it is not necessary to connect
|
||||
`WP#` since after removing the screw it is pulled up weakly to 3v3. Before
|
||||
writing to the chip externally, the battery has to be unplugged.
|
||||
Battery connector is located under the heat spreader, that has to be
|
||||
unscrewed from the rest of the case. It is located on
|
||||
the right and has colorful cables, as shown on the picture below.
|
||||
|
||||
[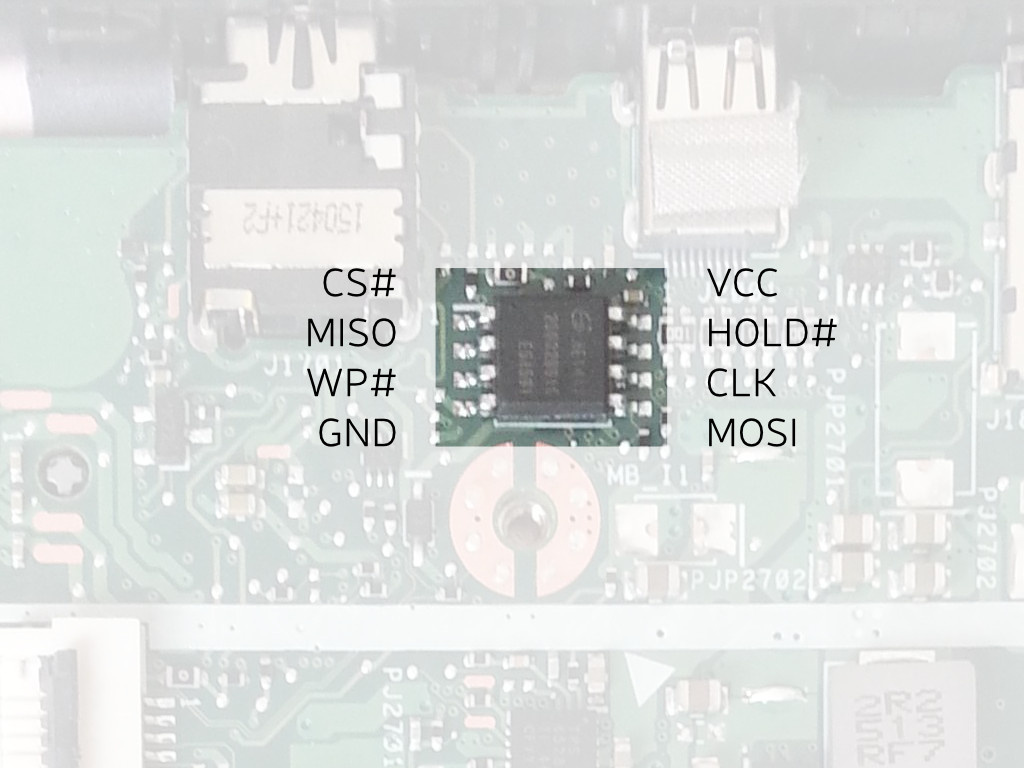](https://av.libreboot.org/c201/spi-flash-layout.jpg)
|
||||
[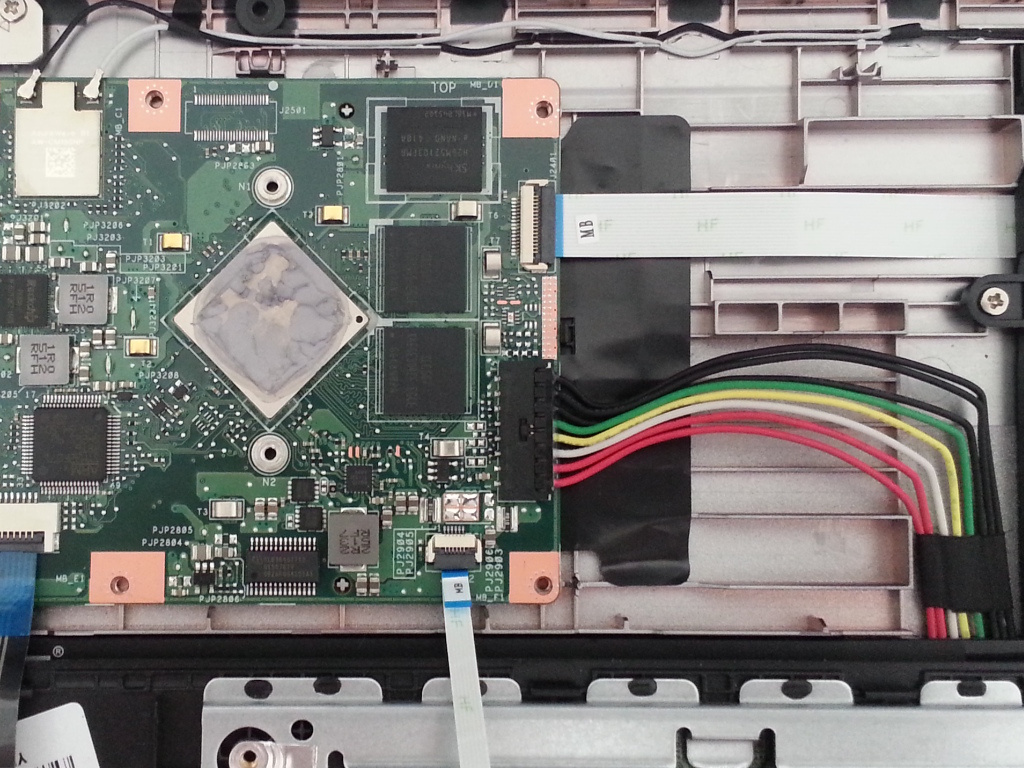](https://av.libreboot.org/c201/battery-connector.jpg)
|
||||
|
||||
All the files from the `veyron_speedy` release (or build) have to be
|
||||
transferred to the host.
|
||||
|
||||
The following operations have to be executed with root privileges on the
|
||||
host (e.g. using the `root` account). In addition, the
|
||||
`cros-flash-replace` script has to be made executable:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod a+x cros-flash-replace
|
||||
|
||||
The SPI flash has to be read first (using the right spi programmer):
|
||||
|
||||
flashrom -p *programmer* -r flash.img
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: it might be a good idea to copy the produced flash.img file at
|
||||
this point and store it outside of the device for backup purposes.*
|
||||
|
||||
Then, the `cros-flash-replace` script has to be executed as such:
|
||||
|
||||
./cros-flash-replace flash.img coreboot ro-frid
|
||||
|
||||
If any error is shown, it is definitely a bad idea to go further than
|
||||
this point.
|
||||
|
||||
The resulting flash image can then be flashed back (using the right spi
|
||||
programmer):
|
||||
|
||||
flashrom -p *programmer* -w flash.img
|
||||
|
||||
You should also see within the output the following:
|
||||
|
||||
Verifying flash... VERIFIED.
|
||||
|
||||
The device will now boot to Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Debian
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
Debian is recommended for this device (which is on that list.
|
||||
|
||||
See <https://wiki.debian.org/InstallingDebianOn/Asus/C201>.
|
||||
|
||||
Also look at the HCL entry for operating systems (Debian, Devuan, Parabola):
|
||||
<https://libreboot.org/docs/hardware/c201.md>
|
||||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
The `ich9utils` utility in Libreboot is used to manipulate Intel Flash
|
||||
The `ich9utils` utility from Libreboot is used to manipulate Intel Flash
|
||||
Descriptors for ICH9M on laptops such as ThinkPad X200 or T400. Specifically,
|
||||
the `ich9gen` utility can generate 12KiB descriptor+GbE files for inserting
|
||||
into the start of a ROM, where everything after that is the BIOS region. These
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,10 +18,10 @@ itself is hosted in a separate repository. You can check the Git repositories
|
|||
linked on [../../git.md](../../git.md) if you wish to download and use it.
|
||||
|
||||
It is very *uncommon*, on GM45/ICH9M systems, to have an Intel Flash Descriptor
|
||||
and GbE but *without* an Intel ME. On *most* of these systems (without Libreboot,
|
||||
and GbE but *without* an Intel ME. On *most* of these systems (without libreboot,
|
||||
Libreboot or coreboot), there is either descriptor+GbE+ME+BIOS or just BIOS,
|
||||
where on systems with just the BIOS region an Intel GbE NIC is not present.
|
||||
In Libreboot (and Libreboot), we provide descriptor+GbE images with Intel ME
|
||||
In libreboot (and Libreboot), we provide descriptor+GbE images with Intel ME
|
||||
disabled and not present in the ROM; this enables the Intel GbE NIC to be used,
|
||||
while not having an Intel ME present. A consequence of this is that the
|
||||
malicious features of ME (such as AMT) are not present, however the Intel ME
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,13 +59,13 @@ You can find `ich9utils` on the [Git page](../../git.md) or you can download
|
|||
|
||||
./build module ich9utils
|
||||
|
||||
You can also find it in the source code tar archives, on Libreboot releases.
|
||||
You may also find it in the source code tar archives, on releases.
|
||||
|
||||
In `lbmk`, you can use the following command to generate descriptors:
|
||||
|
||||
./build descriptors ich9m
|
||||
|
||||
The Libreboot build system will use the descriptors under `descriptors/ich9m`
|
||||
The libreboot build system will use the descriptors under `descriptors/ich9m`
|
||||
when building ROM images for these machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can just clone `ich9utils` directly and run `make` in the
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ These files contain the descriptor+GbE region and are suitable for systems
|
|||
that have an Intel GbE NIC present. The flash regions (as defined by the
|
||||
Intel Flash Descriptor) are set *read-write* which means that you can also
|
||||
re-flash using `flashrom -p internal` in your operating system running on
|
||||
that machine. This is the default setup used when Libreboot's build system
|
||||
that machine. This is the default setup used when libreboot's build system
|
||||
compiles ROM images.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternative versions of these files are also created, which have `ro` in the
|
||||
|
|
@ -117,13 +117,13 @@ The region setup created by these descriptors is as follows:
|
|||
|
||||
* First 4KiB of flash is: Intel Flash Descriptor
|
||||
* Next 8KiB after Descriptor: Intel GbE region
|
||||
* Rest of the flash, after GbE: BIOS region (BIOS region will have Libreboot)
|
||||
* Rest of the flash, after GbE: BIOS region (BIOS region will have libreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
The GbE region contains configuration data for your Intel GbE NIC. You can
|
||||
find information about this in Intel datasheets, and it is very well described
|
||||
in the `ich9utils` source code.
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that your Libreboot image is named **libreboot.rom**, copy the
|
||||
Assuming that your libreboot image is named **libreboot.rom**, copy the
|
||||
file to where **libreboot.rom** is located and then insert the
|
||||
descriptor+gbe file into the ROM image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,7 +154,7 @@ will just supply a descriptor-less setup. Those GbE-less descriptor images
|
|||
created by `ich9gen` are only 4KiB in size, and should *never be used* except
|
||||
for fun, like, basically shits and/or giggles.
|
||||
|
||||
For shits and giggles, R500 ROM images in Libreboot use these no-GbE descriptor
|
||||
For shits and giggles, R500 ROM images in libreboot use these no-GbE descriptor
|
||||
images generated by ich9gen. However, a descriptorless setup would also work
|
||||
just fine. ThinkPad R500 doesn't have an Intel PHY in it, and it instead uses
|
||||
a Broadcom NIC for ethernet. In descriptorless mode, ICH9M works very similarly
|
||||
|
|
@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ Read on for more information. Use the `ro` files mentioned below, and your
|
|||
flash will be read-only in software (you can still externally re-flash and read
|
||||
the contents of flash).
|
||||
|
||||
For ease of use, Libreboot provides ROMs that are read-write by default. In
|
||||
For ease of use, libreboot provides ROMs that are read-write by default. In
|
||||
practise, you can boot a Linux kernel with access to lower memory disabled
|
||||
which will make software re-flashing impossible (unless you reboot with such
|
||||
memory protections disabled, e.g. `iomem=relaxed` kernel parameter).
|
||||
|
|
@ -223,7 +223,7 @@ appear, if no GbE region was detected inside the ROM image. This is
|
|||
usually the case, when a discrete NIC is used (eg Broadcom) instead of
|
||||
Intel. Only the Intel NICs need a GbE region in the flash chip.
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that your Libreboot image is named **libreboot.rom**, copy the
|
||||
Assuming that your libreboot image is named **libreboot.rom**, copy the
|
||||
**deblobbed\_descriptor.bin** file to where **libreboot.rom** is located
|
||||
and then run:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ Keep the original factory.rom stored safely somewhere):
|
|||
|
||||
Use-case: a factory.rom image modified in this way would theoretically
|
||||
have no flash protections whatsoever, making it easy to quickly switch
|
||||
between factory/Libreboot in software, without ever having to
|
||||
between factory/libreboot in software, without ever having to
|
||||
disassemble and re-flash externally unless you brick the device.
|
||||
|
||||
The sections below are adapted from (mostly) IRC logs related to early
|
||||
|
|
@ -429,7 +429,7 @@ way through the 8K area, and the rest is all 0xFF. This is all
|
|||
documented in the datasheet.
|
||||
|
||||
The GBe region starts at 0x20A000 bytes from the \*end\* of a factory
|
||||
image and is 0x2000 bytes long. In Libreboot (deblobbed) the descriptor
|
||||
image and is 0x2000 bytes long. In libreboot (deblobbed) the descriptor
|
||||
is set to put gbe directly after the initial 4K flash descriptor. So the
|
||||
first 4K of the ROM is the descriptor, and then the next 8K is the gbe
|
||||
region.
|
||||
|
|
@ -450,7 +450,7 @@ not making this stuff up...
|
|||
regions on the X200 factory.rom dumps. The checksums of the backup
|
||||
regions match BABA, however. We think `0xBABA` is the only correct checksum,
|
||||
because those other, similar checksums were only ever found in the "backup"
|
||||
GbE regions on factory ROM dumps. In Libreboot, we simply use `0xBABA` and
|
||||
GbE regions on factory ROM dumps. In libreboot, we simply use `0xBABA` and
|
||||
ensure that both 4KiB regions in GbE NVM have that checksum.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the X200 (as shipped by Lenovo) actually has an invalid main
|
||||
|
|
@ -471,7 +471,7 @@ Flash descriptor region {#flash_descriptor_region}
|
|||
|
||||
<http://www.intel.co.uk/content/dam/doc/datasheet/io-controller-hub-9-datasheet.pdf>
|
||||
from page 850 onwards. This explains everything that is in the flash
|
||||
descriptor, which can be used to understand what Libreboot is doing
|
||||
descriptor, which can be used to understand what libreboot is doing
|
||||
about modifying it.
|
||||
|
||||
How to deblob:
|
||||
|
|
@ -495,7 +495,7 @@ There's an interesting parameter called 'ME Alternate disable', which
|
|||
allows the ME to only handle hardware errata in the southbridge, but
|
||||
disables any other functionality. This is similar to the 'ignition' in
|
||||
the 5 series and higher but using the standard firmware instead of a
|
||||
small 128K version. Useless for Libreboot, though.
|
||||
small 128K version. Useless for libreboot, though.
|
||||
|
||||
To deblob GM45, you chop out the platform and ME regions and correct the
|
||||
addresses in flReg1-4. Then you set meDisable to 1 in ICHSTRAP0 and
|
||||
|
|
@ -514,7 +514,7 @@ How to patch the descriptor from the factory.rom dump
|
|||
- Then it can be dd'd into the first 12K part of a coreboot image.
|
||||
- the GBe region always starts 0x20A000 bytes from the end of the ROM
|
||||
|
||||
This means that Libreboot's descriptor region will simply define the
|
||||
This means that libreboot's descriptor region will simply define the
|
||||
following regions:
|
||||
|
||||
- descriptor (4K)
|
||||
|
|
@ -532,8 +532,8 @@ If it's in descriptor mode, then the first 4 bytes will be 5A A5 F0 0F.
|
|||
platform data partition in boot flash (factory.rom / lenovo bios) {#platform_data_region}
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Basically useless for Libreboot, since it appears to be a blob. Removing
|
||||
it didn't cause any issues in Libreboot. We think it's just random data that
|
||||
Basically useless for libreboot, since it appears to be a blob. Removing
|
||||
it didn't cause any issues in libreboot. We think it's just random data that
|
||||
the manufacturer can put there, to use in their firmware. Intel datasheets seem
|
||||
to suggest that the platform region serves no specific function except to
|
||||
provide a region in flash for the hardware manufacturer to use, for whatever
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,18 +3,18 @@ title: Installation instructions
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This section relates to installing Libreboot on supported targets.
|
||||
This section relates to installing libreboot on supported targets.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: if running `flashrom -p internal` for software based flashing, and you
|
||||
get an error related to `/dev/mem` access, you should reboot with
|
||||
`iomem=relaxed` kernel parameter before running flashrom, or use a kernel that
|
||||
has `CONFIG_STRICT_DEVMEM` not enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot flashing can be risky business. Please ensure that you have external
|
||||
libreboot flashing can be risky business. Please ensure that you have external
|
||||
flashing equipment, in case anything goes wrong. The general rule of thumb with
|
||||
firmware is this: if it's non-free, replace it, but if you're already running
|
||||
free firmware and it works nicely for you, you do not need to update it.
|
||||
However, you might want to tweak it or try out newer releases of Libreboot if
|
||||
However, you might want to tweak it or try out newer releases of libreboot if
|
||||
they have bug fixes for your board, and/or new security fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're already running libre firmware on your board, you should decide for
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,12 +27,8 @@ About ROM image file names
|
|||
Init types and display mode
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: On Libreboot 20220710, `libgfxinit` is the only init type provided on
|
||||
the pre-compiled ROM images, but the build system does support other types
|
||||
defined below.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: regardless of init type, on desktops, an external/add-on GPU can always
|
||||
be used. On laptop hardware in Libreboot, libgfxinit will always be used. On
|
||||
be used. On laptop hardware in libreboot, libgfxinit will always be used. On
|
||||
desktop/server hardware, if available, libgfxinit will also always be used by
|
||||
default (but in that setup, SeaBIOS can be used if you want to use an add-on
|
||||
graphics card, e.g. on KCMA-D8, KGPE-D16, GA-G41M-ES2L)
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,7 +64,7 @@ NOTE: no configs in libreboot are currently available that use this method.
|
|||
|
||||
With this method, coreboot is finding, loading and executing a VGA option ROM
|
||||
for your graphics hardware. This would not be done on laptops, because that
|
||||
implies supplying non-free binary blobs in Libreboot, so this setup would only
|
||||
implies supplying non-free binary blobs in libreboot, so this setup would only
|
||||
ever be provided on desktop hardware where no GPU exists or where it is
|
||||
desirable for you to use an external/add-on graphics card
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,7 +84,7 @@ In this setup, coreboot is neither implementing libgfxinit / native graphics
|
|||
initialization nor is it finding/loading/executing VGA option ROMs. In this
|
||||
setup, SeaBIOS would most likely be used for that.
|
||||
|
||||
The `normal` setup is supported in the Libreboot 20220710 build system, but not
|
||||
The `normal` setup is supported in the libreboot build system, but not
|
||||
currently used. It is there for desktop hardware that will be added in the
|
||||
future, where those desktop boards do not have an onboard GPU and therefore an
|
||||
add-on GPU is always used..
|
||||
|
|
@ -136,9 +132,9 @@ following article:
|
|||
|
||||
[ich9utils documentation](ich9utils.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot puts a default MAC address in the available ROM images, but this is
|
||||
libreboot puts a default MAC address in the available ROM images, but this is
|
||||
a generic MAC address and it's identical on every ROM image. Technically, you
|
||||
can use it but if you encounter other Libreboot users on the same ethernet
|
||||
can use it but if you encounter other libreboot users on the same ethernet
|
||||
switch, using the same physical network as you, you will encounter a MAC
|
||||
address conflict.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,7 +142,7 @@ NOTE: R500 thinkpads do not have an Intel gigabit ethernet NIC, so on that
|
|||
laptop you can just flash the default ROM and you do not have to worry.
|
||||
|
||||
There are also some Intel X4X platforms that use an ICH10 southbridge,
|
||||
supported in Libreboot, but these are flashed in a *descriptorless* setup,
|
||||
supported in libreboot, but these are flashed in a *descriptorless* setup,
|
||||
which means that the MAC address is irrelevant (either there will be an Intel
|
||||
PHY module that is now unusable, and you use an add-on card, or it doesn't use
|
||||
an Intel PHY module and the onboard NIC is usable).
|
||||
|
|
@ -174,7 +170,7 @@ carefully.
|
|||
Run flashrom on host CPU
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You can simply take any ROM image from the Libreboot project, and flash it.
|
||||
You can simply take any ROM image from the libreboot project, and flash it.
|
||||
Boot a GNU+Linux distribution on the target device, and install flashrom.
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, this is not possible or there are other considerations. Please
|
||||
|
|
@ -229,12 +225,6 @@ the sections below:
|
|||
|
||||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### ASUS Chromebook C201 (Libreboot 20160907 only)
|
||||
|
||||
Ignore this section. Instead, refer to the following guide:
|
||||
|
||||
[ASUS Chromebook C201 installation guide](c201.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Lenovo ThinkPad X200/X200S/X200T/T400/T400S/T500/W500/R400/R500 running non-free Lenovo BIOS
|
||||
|
||||
If you're running one of these, it cannot be flashed internally if you're still
|
||||
|
|
@ -254,7 +244,7 @@ Intel NIC.
|
|||
[You must flash it externally](spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
D410PT is more or less the same board as D510MO, but we would like more info
|
||||
about this board. If you have a D410PT mainboard, please contact the Libreboot
|
||||
about this board. If you have a D410PT mainboard, please contact the libreboot
|
||||
project via IRC and ping `leah` before you flash it. When you do so, please
|
||||
reference this paragraph on this web page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -267,7 +257,7 @@ and you must flash both chips. Refer to the guide:\
|
|||
#### Macbook1,1 running non-free Apple EFI firmware
|
||||
|
||||
This laptop requires external flashing. Remove the mainboard and refer to
|
||||
the [external flashing guide](spi.md); if Libreboot is already running, you
|
||||
the [external flashing guide](spi.md); if libreboot is already running, you
|
||||
can flash internally.
|
||||
|
||||
MacBook2,1 can be flashed internally.
|
||||
|
|
@ -297,13 +287,10 @@ example of the push pin as a proof of concept:
|
|||
|
||||
#### ThinkPad X60/X60S/X60T/T60 with Lenovo BIOS {#flashrom_lenovobios}
|
||||
|
||||
**I forgot to actually add the flashrom patches in the Libreboot 20211122
|
||||
release. When you see the notes below about `_sst` and `_mx`, for now just use
|
||||
the `util` archive from Libreboot 20160907. That release has a utils archive
|
||||
with pre-compiled flashrom binaries, including patches binaries for Macronix
|
||||
and SST flash chips on these machines. Bucts is also included, pre compiled.
|
||||
They are statically linked binaries, so they should work on any distro. Use
|
||||
those binaries, but with the ROM images from the Libreboot 20211122 release!**
|
||||
You can just get bucts from the libreboot project, same thing for the patched
|
||||
flashrom. In the Libreboot 20160907 release, there is a *utility* archive, which
|
||||
has statically compiled executables. They still work just fine on modern
|
||||
systems, and they can be used for this purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a list of targets:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -320,7 +307,7 @@ Download and build flashrom, using the instructions
|
|||
on [the Git page](../../git.md), and download the `bucts` software using the
|
||||
notes on that very same page.
|
||||
|
||||
You can replace Lenovo BIOS with Libreboot, using flashrom running on the host
|
||||
You can replace Lenovo BIOS with libreboot, using flashrom running on the host
|
||||
CPU. However, there are some considerations.
|
||||
|
||||
Firstly, make sure that the yellow CMOS battery is installed, and functioning
|
||||
|
|
@ -343,7 +330,7 @@ can set the machine to boot using that lower 64KiB bootblock, which is
|
|||
read-write. You do this by setting the BUC.TS register to 1, using the `bucts`
|
||||
program referenced below.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot ROM images already have the upper 64KiB bootblock copied to the lower
|
||||
The libreboot ROM images already have the upper 64KiB bootblock copied to the lower
|
||||
one, so you don't have to worry about copying it yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
If you build flashrom using the libreboot build system, there will be three
|
||||
|
|
@ -435,7 +422,7 @@ If it said VERIFIED, shut down. If it didn't say VERIFIED, make sure bucts is
|
|||
still set to 1, and consult the libreboot project on IRC for advice, and avoid
|
||||
shutting down your system until you get help.
|
||||
|
||||
If all went well, Libreboot should now be booting and you should be able to
|
||||
If all went well, libreboot should now be booting and you should be able to
|
||||
boot into your operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
If you messed up, there are external flashing instructions. See main navigation
|
||||
|
|
@ -476,7 +463,7 @@ TARGET: Apple Macbook2,1, Macbook1,1 and iMac5,2 (i945 platform)
|
|||
----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
iMac5,2 is essentially the same board as Macbook2,1, and it is compatible with
|
||||
Libreboot.
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the following article:\
|
||||
[Macbook2,1 and MacBook1,1 installation guide](../hardware/macbook21.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -590,3 +577,25 @@ TARGET: Lenovo ThinkPad R500 laptop
|
|||
|
||||
Refer to the following laptop:\
|
||||
[ThinkPad R500](../hardware/r500.md)
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Thinkpad X230
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [ivybridge/haswell common guide.](ivy_has_common.md) for how to
|
||||
make the rom image usable for external flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
Read [board documentation](/docs/install/x230_external.html) for disassembly.
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Thinkpad X230t
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [ivybridge/haswell common guide.](ivy_has_common.md) for how to
|
||||
make the rom image usable for external flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
TARGET: Thinkpad t440p
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [ivybridge/haswell common guide.](ivy_has_common.md) for how to
|
||||
make the rom image usable for external flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
Read [board documentation](/docs/install/t440p_external.html) for disassembly.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Ivybridge/Haswell Common
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
For how to use an external programmer see the [25xx NOR flashing guide](/docs/install/spi.html)
|
||||
|
||||
The Intel Flash Descriptor defines that the first 5MiB of the 12MiB boot flash consists of
|
||||
the Intel Flash Descriptor, GbE and Intel ME regions. The final 7MiB of that
|
||||
12MiB flash is the BIOS region. However, this 12MiB of flash is physically split
|
||||
into an 8MiB NOR flash and a 4MiB NOR flash; the OS sees a continuous 12MiB of
|
||||
flash, with the lower part being the contents of 8MiB NOR flash and the upper
|
||||
contents being the 4MiB NOR flash.
|
||||
|
||||
Do not worry too much about which flash chip your programmer is connected to.
|
||||
Flashrom will fail if you try to flash the wrong sized image for the chip you are connected
|
||||
to.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot roms released or built for haswell or ivybridge boards come as 12/16MiB roms.
|
||||
The size of the rom in question refers to the total size of *both* chips.
|
||||
In order to flash a full rom externally, you need to split the rom into two sections to fit the size of the two chips you wish to flash.
|
||||
This guide will show examples for the Thinkpad X230, but all of the information will apply to other boards.
|
||||
|
||||
Ivybridge boards require *at least* the intel management engine in order to boot.
|
||||
Haswell boards additionally require the mrc blob.
|
||||
Neither of these blobs are redistributable, so roms for these boards must be built from source or patched with the required blobs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're planning to flash a release rom to your board then you need only patch the existing rom.
|
||||
Alternatively, you can attempt to build a rom from source for your board.
|
||||
|
||||
Obtaining Binary Blobs
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
If you have built your rom from source then all of the blobs are generally downloaded automatically.
|
||||
Some boards however, do not have sources for all blobs and require manual blob extraction.
|
||||
If you try to build a rom from source and lbmk fails to locate the blobs, you can extract them from an existing rom backup.
|
||||
To do this, start by obtaining a full backup rom from your machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have connected your programmer and read from both flash chips, you will have to combine the two images to a single rom.
|
||||
In general, the 4mb image is the top, and the 8mb image is the bottom.
|
||||
To create a readable rom file, simply concatenate the two files.
|
||||
|
||||
cat bottom.rom top.rom > full_backup.bin
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have a backup of your vendor rom, you can use lbmk to automatically extract the necessary blobs.
|
||||
The blob extraction script takes a board name as the first argument and a path to a rom as the second argument.
|
||||
For example, here is how you would extract the blobs from an x230 rom backup.
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil extract x230_12mb full_backup.bin
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the above command must be run from the root of the lbmk directory.
|
||||
See [building instructions](/docs/build/index.html) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
Injecting Blobs into an Existing Rom
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Release roms cannot include certain blobs for legal reasons.
|
||||
You therefore **cannot** directly flash a release rom to your board.
|
||||
You must patch the release rom with the necessary blobs *and then* flash it to your board.
|
||||
|
||||
Osbmk includes a script that will automatically inject the necessary blobs into a rom file.
|
||||
The script can determine the board automatically if you have not changed the name, but you can also manually set the board name with the `-b` flag.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to inject the necessary blobs into a rom image, run the script from the root of lbmk and point to the rom image.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil inject -r x230_libreboot.rom -b x230_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can use this script to modify the mac address of the rom with the `-m` flag.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil inject -r x230_libreboot.rom -b x230_12mb -m 00:f6:f0:40:71:fd
|
||||
|
||||
Splitting The Rom
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `dd` to easily split your rom into the two separate portions for
|
||||
external flashing.
|
||||
For example, here is how you would split a 12mb rom for installation:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=libreboot.rom of=top.rom bs=1M skip=8
|
||||
dd if=libreboot.rom of=bottom.rom bs=1M count=8
|
||||
|
||||
You would then flash the 4MiB chip with `top.rom` and the 8MiB chip with `bottom.rom`.
|
||||
For a larger rom image, the same logic would apply.
|
||||
|
||||
In dd `skip` means that you want the program to ignore the first n blocks, whereas
|
||||
`count` means you want it to stop writing after n blocks.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have your rom image split you can proceed to [flashing.](/docs/install/spi.html)
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,12 +14,6 @@ ROM properly first. Although ROM images are provided pre-built in
|
|||
libreboot, there are some modifications that you need to make to the one
|
||||
you chose before flashing. (instructions referenced later in this guide)
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot T400 {#t400}
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
You may also be interested in the smaller, more portable [Libreboot
|
||||
T400](t400_external.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Serial port {#serial_port}
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +44,7 @@ Intel GPU; this is referred to as "Dual Graphics" (previously
|
|||
you can specify that the system will use one or the other (but not
|
||||
both).
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is known to work on systems with only the Intel GPU, using
|
||||
libreboot is known to work on systems with only the Intel GPU, using
|
||||
native graphics initialization. On systems with switchable graphics, the
|
||||
Intel GPU is used and the ATI GPU is disabled, so native graphics
|
||||
initialization works all the same.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
This guide will teach you how to use various tools for externally reprogramming
|
||||
a 25xx NOR flash via SPI protocol. This is the most common type of flash IC for
|
||||
computers that coreboot runs on. Almost every system currently supported by
|
||||
Libreboot uses this type of boot flash; the only exception is ASUS KFSN4-DRE,
|
||||
libreboot uses this type of boot flash; the only exception is ASUS KFSN4-DRE,
|
||||
which uses LPC flash in a PLCC32 socket, which you can simply hot-swap after
|
||||
booting the vendor firmware, and then flash internally. Simple!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ We will be using
|
|||
the [flashrom](https://flashrom.org/Flashrom) software which is written to
|
||||
dump, erase and rewrite these flash chips.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot currently documents how to use these SPI programmers:
|
||||
libreboot currently documents how to use these SPI programmers:
|
||||
|
||||
* Raspberry Pi (RPi)
|
||||
* BeagleBone Black (BBB)
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,10 +22,10 @@ Libreboot currently documents how to use these SPI programmers:
|
|||
Many other SPI programmers exist. More of them will be documented on this page,
|
||||
at a date in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
Most systems in Libreboot have to be re-flashed externally, using instructions
|
||||
Most systems in libreboot have to be re-flashed externally, using instructions
|
||||
on this and similar guides, the first time you flash. However, on all currently
|
||||
supported systems, it's possible that you can re-flash *internally* when
|
||||
Libreboot is running.
|
||||
libreboot is running.
|
||||
|
||||
*Internal* flashing means that the host CPU on your system can re-program the
|
||||
SPI flash, using an on-board SPI programmer (which all boards have). You do this
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ is called *external* because it's not the *internal* one on your mainboard.
|
|||
Do not use CH341A!
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
NOR flashes on Libreboot systems run on 3.3V DC, and this includes data lines.
|
||||
NOR flashes on libreboot systems run on 3.3V DC, and this includes data lines.
|
||||
CH341A has 5V logic levels on data lines, which will damage your SPI flash and
|
||||
also the southbridge that it's connected to, plus anything else that it's
|
||||
connected to.
|
||||
|
|
@ -214,12 +214,6 @@ They then removed it, after a public backlash, via the following commits:
|
|||
* <https://github.com/RPi-Distro/raspberrypi-sys-mods/commit/ed96790e6de281bc393b575c38aa8071ce39b555>
|
||||
* <https://github.com/RPi-Distro/raspberrypi-sys-mods/commit/4d1afece91008f3787495b520ac03b53fef754c6>
|
||||
|
||||
For now, Raspbian / Raspberry Pi OS (which is based on Debian) should be safe,
|
||||
but this whole episode proves that the distro can no longer be trusted to
|
||||
respect its users. Therefore, it's now on the [tasks page](../../tasks/)
|
||||
a TODO entry for recommending and documenting alternative GNU+Linux distros
|
||||
on the Raspberry Pi, for the purposes of SPI flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
Install flashrom
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -228,9 +222,9 @@ If you're using a BBB or RPi, you will do this while SSH'd into those.
|
|||
Flashrom is the software that you will use, for dumping, erasing and rewriting
|
||||
the contents of your NOR flash.
|
||||
|
||||
In the Libreboot build system, from the Git repository, you can download and
|
||||
In the libreboot build system, from the Git repository, you can download and
|
||||
install flashrom. Do this after downloading the
|
||||
[lbmk Git repository](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk):
|
||||
[lbmk Git repository](https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbmk):
|
||||
|
||||
cd lbmk
|
||||
sudo ./build dependencies ubuntu2004
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,7 +258,7 @@ binary is also available that you can simply run. Pass the `--workaround-mx`
|
|||
argument in flashrom. This mitigates stability issues.
|
||||
|
||||
If you downloaded the flashrom source code directly, you can go into the
|
||||
directory and simply type `make`. In the Libreboot build system, build
|
||||
directory and simply type `make`. In the libreboot build system, build
|
||||
dependencies are documented in script located
|
||||
at `resources/scripts/build/dependencies/` which you can install
|
||||
using the `apt-get` software.
|
||||
|
|
@ -322,6 +316,19 @@ they should all be the same length (3.3V VCC and GND wires can be longer).
|
|||
|
||||
This advice is *especially* applicable to the BBB, which is highly unreliable.
|
||||
|
||||
For boards with more than one flash chip you will need to read from both chips
|
||||
and combine them into a single file.
|
||||
Most of the time, a two chip setup includes one 8mb 'bottom' chip and one 4mb
|
||||
'top' chip.
|
||||
The setup just described applies to the x230, t430, t530, and t440p.
|
||||
For other boards, make sure you know which chip contains the lower and upper
|
||||
portions of the rom.
|
||||
You can combine both flashes together with `cat` for example:
|
||||
|
||||
cat bottom_8mb.rom top_4mb.rom > full_12mb.rom
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you will need this combined rom if you intend to manually extract blobs.
|
||||
|
||||
Writing
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -348,6 +355,16 @@ successfully. If not, just flash again.
|
|||
If it says "VERIFIED" or says that the chip contents are identical to the
|
||||
requested image, then the chip is properly flashed.
|
||||
|
||||
If the board you are writing to has two chips you'll need to split the rom into
|
||||
two sections.
|
||||
For example, to split a rom for the x230, t430, t530, or t440p run:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=libreboot_12mb.rom bs=1M of=bottom.rom count=8
|
||||
dd if=libreboot_12mb.rom bs=1M of=top.rom skip=8
|
||||
|
||||
Flash the resulting roms to each of their respective chips according to the above instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware configuration
|
||||
======================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -364,7 +381,7 @@ Do not *disconnect* your chip from the flasher until you've disconnected or
|
|||
turned off the 3.3V DC power source.
|
||||
|
||||
BE CAREFUL that you are indeed supplying 3.3V DC to the chip. All SPI flashes
|
||||
on all currently supported Libreboot hardware run on 3.3V DC and logic at that
|
||||
on all currently supported libreboot hardware run on 3.3V DC and logic at that
|
||||
level too.
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to CHECK that you are running on the correct voltage, when you
|
||||
|
|
@ -388,7 +405,7 @@ ISP programming and VCC diode
|
|||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
ISP means in-system programming. It's when you flash a chip that is already
|
||||
mounted to the mainboard of your computer that you wish to install Libreboot
|
||||
mounted to the mainboard of your computer that you wish to install libreboot
|
||||
on.
|
||||
|
||||
It may be beneficial to modify the mainboard so that the SPI flash is powered
|
||||
|
|
@ -421,7 +438,7 @@ WSON8 or DIP8, whatever you want), because then you could easily just insert
|
|||
the flash into a breadboard when flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: Make a page on libreboot.org, showing how to do this on all mainboards
|
||||
supported by Libreboot.
|
||||
supported by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
GPIO pins on BeagleBone Black (BBB)
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -440,7 +457,7 @@ This diagram shows the pinout for most modern Pi's and Pi derivatives.
|
|||
The diagram shows the pins of an RPi on the left and the two SOIC clips
|
||||
on the left.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
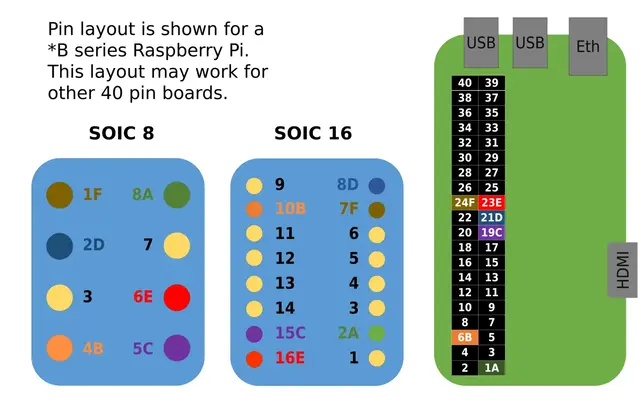
|
||||
|
||||
GPIO pins on Raspberry Pi (RPi) 26 Pin
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -575,7 +592,7 @@ SOIC8/WSON8/DIP8/SOIC16 not mounted to a mainboard
|
|||
|
||||
If your system has lower capacity SPI flash, you can upgrade. On *most* systems,
|
||||
SPI flash is memory mapped and the maximum (in practise) that you can use is a
|
||||
16MiB chip. For example, KGPE-D16 and KCMA-D8 mainboards in Libreboot have
|
||||
16MiB chip. For example, KGPE-D16 and KCMA-D8 mainboards in libreboot have
|
||||
2MiB flash by default, but you can easily upgrade these. Another example is the
|
||||
ThinkPad X200S, X200 Tablet and T400S, all of which have WSON8 where the best
|
||||
course of action is to replace it with a SOIC8 flash chip.
|
||||
|
|
@ -680,7 +697,7 @@ for flashing. You might want to de-solder the chip, using a solder vacuum
|
|||
(extractor) tool, and then you can install a socket in its place. You can then
|
||||
insert the DIP8 IC into the socket.
|
||||
|
||||
In the Libreboot project, we have never heard of a board where the DIP8 is
|
||||
In the libreboot project, we have never heard of a board where the DIP8 is
|
||||
directly soldered. It is almost always mounted in a socket.
|
||||
|
||||
Your DIP8 IC has the same pinout as a SOIC8 IC.
|
||||
|
|
@ -696,7 +713,7 @@ can easily damage the pads that way.
|
|||
WSON8 has the same pinout as SOIC8, but it's a ball mounted QFN (quad flat
|
||||
pack, no leads). There are no clips for it. Sometimes referred to as QFN8
|
||||
|
||||
On all currently supported Libreboot hardware, boards that have WSON8 can also
|
||||
On all currently supported libreboot hardware, boards that have WSON8 can also
|
||||
have a SOIC8 because the pads are long enough to accomodate either type of
|
||||
chip.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -807,15 +824,15 @@ This page and the photos on it are available under
|
|||
[CC BY SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode.txt)
|
||||
Check the Git repository for history of who owns what part of the document.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of these resources originate from the *old* Libreboot git repository,
|
||||
before Libreboot split into separate repositories that include its `lbmk`
|
||||
repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Photos showing a BeagleBone Black are under the normal GNU Free Documentation
|
||||
license like other pages and images on this website, or you can use them under
|
||||
the CC-BY-SA 4.0 license if you wish (I, Leah Rowe, own all BBB photos shown
|
||||
on this page, except for the one on the beaglebone website, and that one is
|
||||
merely linked here, instead of being hosted on the av.libreboot.org server).
|
||||
|
||||
This version of the page is hosted in the `lbwww` git repository, with images
|
||||
for it hosted in the `lbwww-img` repository. Images and this page were both
|
||||
forked from the *old* Libreboot git repository, which was available here:
|
||||
<https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/> (you can still download it but this
|
||||
repository is no longer worked on. You can find both the website and images
|
||||
under the `www/` and/or `docs/` directory, in that repository)
|
||||
This version of the page is hosted in the `osbwww` git repository, with images
|
||||
for it hosted in the `lbwww-img` repository (from libreboot).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Intel GPU; this is referred to as "switchable graphics". In the *BIOS
|
|||
setup* program for lenovobios, you can specify that the system will use
|
||||
one or the other (but not both).
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is known to work on systems with only the Intel GPU, using
|
||||
libreboot is known to work on systems with only the Intel GPU, using
|
||||
native graphics initialization. On systems with switchable graphics, the
|
||||
Intel GPU is used and the ATI GPU is disabled, so native graphics
|
||||
initialization works all the same.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad T420 external flashing
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to read the [Ivybridge/Haswell common guide](/docs/install/ivy_has_common.html) before attempting to flash this board.
|
||||
After you have prepared a rom and split it into two section, refer to this guide for disassembly instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
We don't currently have disassembly instructions for this board.
|
||||
See [coreboot docs](https://www.coreboot.org/Board:lenovo/t420) for how to disassemble this machine to reveal the flash chips.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad X230/X230T external flashing
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Read the [Ivybridge/Haswell common guide](/docs/install/ivy_has_common.html) if you want more information.
|
||||
All of the following instructions assume that you've cloned lbmk and are operating from the
|
||||
root of that project. To do so, run
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk
|
||||
cd lbmk
|
||||
|
||||
You can now follow the rest of the instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
Preparing a release Rom
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You must patch the release rom with the necessary blobs *and then* flash it to your board.
|
||||
|
||||
Osbmk includes a script that will automatically inject the necessary blobs into a rom file.
|
||||
The script can determine the board automatically if you have not changed the name, but you can also manually set the board name with the `-b` flag.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to inject the necessary blobs into a rom image, run the script from the root of lbmk and point to the rom image.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil inject -r t440p_libreboot.rom -b t440p_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can use this script to modify the mac address of the rom with the `-m` flag.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil inject -r t440p_libreboot.rom -b t440p_12mb -m 00:f6:f0:40:71:fd
|
||||
|
||||
Splitting The Rom
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `dd` to easily split your rom into the two separate portions for
|
||||
external flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=libreboot.rom of=top.rom bs=1M skip=8
|
||||
dd if=libreboot.rom of=bottom.rom bs=1M count=8
|
||||
|
||||
Flash the top chip with top.rom, and tho bottom chip with bottom.rom.
|
||||
Don't worry about knowing which chip is which on a standard setup; flashrom will let you know if the
|
||||
image size is incorrect for the chip you're flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Disassembly
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
Start by removing the back cover screws and the main battery.\
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_back.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_back_orig.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
|
||||
You can then remove the back cover by sliding it off.
|
||||
Next you need to:
|
||||
|
||||
+ Unplug the cmos battery
|
||||
+ Unplug and unroute the fan cable
|
||||
+ Unplug and unroute the black LED cable
|
||||
+ Remove all visible screws
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: the ultrabay screw will loosen, but not come out of the assembly*\
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_nocover.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_nocover_orig.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can pull up around the sides of the bottom assembly to release it.
|
||||
Pull it upwards and lift it open to the front of the machine like a clamshell.
|
||||
Make sure not to break the wires connecting the assembly to the rest of the machine.\
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_open.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_open_orig.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
|
||||
You should now be able to see the two flash chips near the RAM.\
|
||||
<img tabindex=1 src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_chipLocation.jpg" /><span class="f"><img src="https://av.libreboot.org/board/t440p/t440p_chipLocation_orig.jpg" /></span>
|
||||
|
||||
You can now proceed to [flashing](/docs/install/spi.html) this machine.
|
||||
|
|
@ -11,12 +11,6 @@ followed (adapted) if you brick your T500, to know how to recover.
|
|||
|
||||
W500 is also mostly compatible with this guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot T400 {#t400}
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
You may also be interested in the smaller, more portable [Libreboot
|
||||
T400](t400_external.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Serial port {#serial_port}
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,7 +53,7 @@ Intel GPU; this is referred to as "switchable graphics". In the *BIOS
|
|||
setup* program for lenovobios, you can specify that the system will use
|
||||
one or the other (but not both).
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is known to work on systems with only the Intel GPU, using
|
||||
libreboot is known to work on systems with only the Intel GPU, using
|
||||
native graphics initialization. On systems with switchable graphics, the
|
||||
Intel GPU is used and the ATI GPU is disabled, so native graphics
|
||||
initialization works all the same.
|
||||
|
|
@ -225,10 +219,6 @@ Of course, make sure to turn on your PSU:\
|
|||
|
||||
Now, you should be ready to install libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Flashrom binaries for ARM (tested on a BBB) are distributed in
|
||||
libreboot\_util. Alternatively, libreboot also distributes flashrom
|
||||
source code which can be built.
|
||||
|
||||
Log in as root on your BBB, using the instructions in
|
||||
[bbb\_setup.html\#bbb\_access](bbb_setup.html#bbb_access).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ your ThinkPad T60 from booting.
|
|||
This section documents how to recover from a bad flash that prevents
|
||||
your ThinkPad X60 from booting.
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images for this machine are well-tested in Libreboot, so bricks are rare.
|
||||
ROM images for this machine are well-tested in libreboot, so bricks are rare.
|
||||
The most common cause of a brick is operator error, when flashing a ROM image.
|
||||
In *most* cases, the cause will be that there is no bootblock, or an invalid
|
||||
one.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ could discover how this works, by debugging the Lenovo BIOS update utility (in
|
|||
Windows), and then replicate what it is doing, with some tool for GNU+Linux,
|
||||
then load a flashrom binary into memory and the ROM to flash (for the BIOS
|
||||
region). You would do this with GPIO33 grounded, and the payload program would
|
||||
actually flash the entire chip, with just a normal Libreboot image.
|
||||
actually flash the entire chip, with just a normal libreboot image.
|
||||
|
||||
It's possible. The above is likely the only way that the Lenovo BIOS updater
|
||||
program works. So if we discover precisely how to do that, then you could
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad X220/X220T external flashing
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to read the [Ivybridge/Haswell common guide](/docs/install/ivy_has_common.html) before attempting to flash this board.
|
||||
After you have prepared a rom and split it into two section, refer to this guide for disassembly instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
We don't currently have disassembly instructions for this board.
|
||||
See [coreboot docs](https://www.coreboot.org/Board:lenovo/x220) for how to disassemble this machine to reveal the flash chips.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: ThinkPad X230/X230T external flashing
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Read the [Ivybridge/Haswell common guide](/docs/install/ivy_has_common.html) if you want more information.
|
||||
All of the following instructions assume that you've cloned lbmk and are operating from the
|
||||
root of that project. To do so, run
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk
|
||||
cd lbmk
|
||||
|
||||
You can now follow the rest of the instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
Preparing a release Rom
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You must patch the release rom with the necessary blobs *and then* flash it to your board.
|
||||
|
||||
Osbmk includes a script that will automatically inject the necessary blobs into a rom file.
|
||||
The script can determine the board automatically if you have not changed the name, but you can also manually set the board name with the `-b` flag.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to inject the necessary blobs into a rom image, run the script from the root of lbmk and point to the rom image.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil inject -r x230_libreboot.rom -b x230_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can use this script to modify the mac address of the rom with the `-m` flag.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil inject -r x230_libreboot.rom -b x230_12mb -m 00:f6:f0:40:71:fd
|
||||
|
||||
Splitting The Rom
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `dd` to easily split your rom into the two separate portions for
|
||||
external flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=libreboot.rom of=top.rom bs=1M skip=8
|
||||
dd if=libreboot.rom of=bottom.rom bs=1M count=8
|
||||
|
||||
Flash the top chip with top.rom, and tho bottom chip with bottom.rom.
|
||||
Don't worry about knowing which chip is which on a standard setup; flashrom will let you know if the
|
||||
image size is incorrect for the chip you're flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Disassembly
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
Start by removing the battery.
|
||||
Remove every screw from the bottom of the machine marked with a keyboard/touchpad indicator.
|
||||
|
||||
Pry up the keyboard and separate it from the palmrest.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unplug the ribbon cable from the palmrest and pry it off as well.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Pull up the protective cover to reveal the two soic chips for flashing.
|
||||

|
||||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
This section documents how to recover from a bad flash that prevents
|
||||
your ThinkPad X60 from booting.
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images for this machine are well-tested in Libreboot, so bricks are rare.
|
||||
ROM images for this machine are well-tested in libreboot, so bricks are rare.
|
||||
The most common cause of a brick is operator error, when flashing a ROM image.
|
||||
In *most* cases, the cause will be that there is no bootblock, or an invalid
|
||||
one.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ x-toc-enable: true
|
|||
This section documents how to recover from a bad flash that prevents
|
||||
your ThinkPad X60 Tablet from booting.
|
||||
|
||||
ROM images for this machine are well-tested in Libreboot, so bricks are rare.
|
||||
ROM images for this machine are well-tested in libreboot, so bricks are rare.
|
||||
The most common cause of a brick is operator error, when flashing a ROM image.
|
||||
In *most* cases, the cause will be that there is no bootblock, or an invalid
|
||||
one.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3,88 +3,50 @@ title: lbmk maintenance manual
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Automated freedom
|
||||
=================
|
||||
Automated pragmatism
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
This manual describes the nature of `lbmk` (LibreBoot MaKe), the automated
|
||||
build system used to produce Libreboot releases. It is intended as a reference
|
||||
This manual describes the nature of `lbmk` (OSBoot MaKe), the automated
|
||||
build system used to produce libreboot releases. It is intended as a reference
|
||||
for *libreboot development*.
|
||||
|
||||
If you simply wish to compile Libreboot from source, you should instead refer
|
||||
If you simply wish to compile libreboot from source, you should instead refer
|
||||
to the [build instructions](../build/)
|
||||
|
||||
This documentation covers *modern* Libreboot; version 20160907 and below use a
|
||||
much older, less polished version, from before it was actually
|
||||
called `lbmk` (it was simply called "the libreboot build system" back then).
|
||||
Information about those build systems are provided in the documentation
|
||||
provided with those releases.
|
||||
|
||||
Generally speaking, *testing* releases of Libreboot do not come with
|
||||
documentation; if you're using *old* testing releases, it is prudent to check
|
||||
the `lbwww.git` repository on a revision from around the same time as those
|
||||
releases. Future stable releases of Libreboot will come with a snapshot of
|
||||
the `lbwww.git` repository, for documentation pertaining to such releases. One
|
||||
way to do this, for releases from 2021 onwards, is to simply run `git log` on
|
||||
the `news/` section of `lbwww.git` and find the revision that added
|
||||
the *announcement* for a given release (again, 2021 onwards), and then you can
|
||||
Generally speaking, *testing* releases of libreboot will not come with
|
||||
documentation; if you're later using *old* testing releases, it is prudent to
|
||||
check the `osbwww.git` repository on a revision from around the same time as
|
||||
those releases. Future stable releases of libreboot will come with a snapshot of
|
||||
the `osbwww.git` repository, for documentation pertaining to such releases. One
|
||||
way to do this, all testing releases of libreboot, will be to simply run `git log`
|
||||
on the `news/` section of `osbwww.git` and find the revision that added
|
||||
the *announcement* for a given release (when available), and then you can
|
||||
just reset to that revision.
|
||||
|
||||
As such, you should always refer to the *live* version of this page, on
|
||||
libreboot.org, when working on the `lbmk.git` repository; the live version is
|
||||
intended for development on the Git repository!
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot blob policy
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
libreboot blob reduction policy
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot has a strict policy of *excluding* non-free software. It is to only
|
||||
distribute *free software*. Please keep this in mind, when you work on the
|
||||
Libreboot build system, if you will later submit patches to the project.
|
||||
The coreboot software is nominally free, but it requires additional binary
|
||||
blobs on many supported systems. These *blobs* lack source code, and the
|
||||
coreboot project does not control them, but they can be used to perform
|
||||
specific initialization tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
[Learn more about Libreboot's policies](../../news/policy.md)
|
||||
The libreboot project *allows* binary blobs from coreboot, but there is *still* a
|
||||
lot of nuance to precisely what is allowed. It is important that you understand
|
||||
these nuances, when working on *libreboot*.
|
||||
|
||||
osbmk
|
||||
=====
|
||||
[Please read the blob reduction guidelines](../../news/policy.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Another project, named osboot, is also maintained by Leah Rowe, forked from
|
||||
Libreboot: <https://osboot.org/> - this project is just the same as Libreboot,
|
||||
with the same build system, except for some tweaks: *all* blobs are allowed,
|
||||
and CPU microcode updates are enabled by default, and the build system is
|
||||
modified accordingly, but mostly the same.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot build system is `lbmk`. The osboot build system is `osbmk`.
|
||||
These two build systems are almost identical, except for a few differences.
|
||||
They are both actively maintained, in parallel, and lead/founded by Leah Rowe.
|
||||
|
||||
Why bring up osboot? Because it's relevant for licensing and compliance, in
|
||||
case of audit in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
The `osboot` project was forked from Libreboot 20160907's build system (which
|
||||
did not have a name back then), but with Libreboot documentation from December
|
||||
in 2020. It was then expanded upon, fixing many flaws in the 20160907 build
|
||||
system. At that time, a failed experimental re-write of Libreboot's build
|
||||
system had to either be revived and succeed (but that build system was very
|
||||
badly designed), or scrapped; the latter was decided, and osboot-libre was
|
||||
born, which was used to create `lbmk`. With this act, the Libreboot project,
|
||||
formerly a *dead project* for all intents and purposes, was completely restored.
|
||||
All of these acts took place during the early months of the year 2021; the
|
||||
failed Libreboot re-write took place after the Libreboot 20160907 release, and
|
||||
was scrapped during March of 2021, in favour of lbmk which is a fork of osbmk.
|
||||
(and lbmk is now, as of 2 January 2021, being re-forked to bring osbmk/lbmk
|
||||
back into feature parity. so you can fork your forks of your forks, and
|
||||
maybe fork the fork of your fork of your fork)
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot and osboot are two sides of a coin; neither should exist alone.
|
||||
The osboot project scrapts
|
||||
Libreboot's [zero blobs policy](https://libreboot.org/news/policy.html)
|
||||
and it is targeted at those who don't
|
||||
want to (or can't) use Libreboot, but who still want some freedoms compared
|
||||
to otherwise fully non-free vendor firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
What is lbmk?
|
||||
=============
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
In the same way that Trisquel and Debian are GNU+Linux distributions, Libreboot
|
||||
is a **coreboot distribution**. The `lbmk` build system *is* that distribution,
|
||||
In the same way that Trisquel and Debian are GNU+Linux distributions, Libreboot
|
||||
is a **coreboot distribution**. The `lbmk` build system *is* that distro,
|
||||
providing the glue necessary to integrate coreboot plus anything else that's
|
||||
needed, unifying everything in a completely automated and pre-configured
|
||||
fashion, so as to provide a distribution that is ease to install and use by
|
||||
|
|
@ -103,7 +65,7 @@ one thing well*.
|
|||
|
||||
Technically, `lbmk` isn't necessarily a build system, but rather, a handful of
|
||||
small scripts that run other scripts, or even C programs if you wish. What
|
||||
makes `lbmk` *be* `lbmk` is what each individual script does, and how scripts
|
||||
makes `lbmk` *be* `osbmk` is what each individual script does, and how scripts
|
||||
interact with or call each other to produce working ROM images. It takes
|
||||
a *light touch* approach, providing only the most minimal glue necessary to
|
||||
build working ROM images that the user can install, with sane defaults, while
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,7 +74,7 @@ describing how to do just that. User-friendly documentation is provided, with
|
|||
simple installation steps, automating as much of it as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
*This* document is different. The document you're reading right now is written
|
||||
for *technical* users who want to know how Libreboot is put together.
|
||||
for *technical* users who want to know how libreboot is put together.
|
||||
|
||||
The lbmk design also helps to ease copyright licensing and compliance, because
|
||||
each part of lbmk is literally its own separate program. With this design, it
|
||||
|
|
@ -128,17 +90,17 @@ are under the same license, and most of those different licenses are not
|
|||
compatible with each other; this is perfectly OK there, and it's OK here too.
|
||||
|
||||
The purpose of this document is to (hopefully) cause you to understand the
|
||||
entire build system in Libreboot, so that you can contribute patches or
|
||||
entire build system in libreboot, so that you can contribute patches or
|
||||
otherwise make whatever changes you like. As such, this is a reference guide
|
||||
for Libreboot development.
|
||||
for libreboot development.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is a *coreboot distro*, focusing on integration. As such, direct
|
||||
development on software such as coreboot, GNU GRUB, SeaBIOS etc should ideally
|
||||
be done upstream, or if it's a project hosted by Libreboot (such as ich9utils)
|
||||
be done upstream, or if it's a project hosted by libreboot (such as ich9utils)
|
||||
developed in the corresponding separate repository.
|
||||
|
||||
This document is written for developers and power users alike, or otherwise for
|
||||
anyone who is curious enough to learn more about what *makes* Libreboot!
|
||||
anyone who is curious enough to learn more about what *makes* libreboot!
|
||||
|
||||
A major planned addition to lbmk in the future is: use it to implement a small
|
||||
busybox+linux distribution, with musl libc, plus u-root, and implement a
|
||||
|
|
@ -156,13 +118,13 @@ or SeaBIOS, and these all have *their* own build systems aswell. The `lbmk`
|
|||
build system is the glue that puts all of these together to produce ROM images
|
||||
for users, in a completely automated fashion. The purpose of `lbmk` is to
|
||||
provide an *unattended* build process, with as little user interaction as
|
||||
possible. Thus, `lbmk` is an *automated build system*. It says on the Libreboot
|
||||
home page that Libreboot is a *coreboot distribution* in much the same way that
|
||||
possible. Thus, `lbmk` is an *automated build system*. It says on the libreboot
|
||||
home page that libreboot is a *coreboot distribution* in much the same way that
|
||||
Trisquel is a *GNU+Linux distribution*, and `lbmk` is what implements that!
|
||||
|
||||
Continue reading, and you will learn of each file contained in `lbmk`. This
|
||||
document largely pertains to the version of `lbmk` as hosted in `lbmk.git`, but
|
||||
this manual also covers source code archives containing the full downloaded
|
||||
document largely pertains to the version of `lbmk` as hosted in `lbmk.git`,
|
||||
but this manual also covers source code archives containing the full downloaded
|
||||
set of modules such as coreboot and GRUB.
|
||||
|
||||
In general, it is advisable to open *every* file in lbmk, after you downloaded
|
||||
|
|
@ -173,7 +135,7 @@ simply *studying* the logic directly.
|
|||
AUTOMATED automation
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
Every part of lbmk checks if the prerequisite steps are done, and performs them
|
||||
Every part of lbmk checks if the prerequisite steps are done, and does them
|
||||
automatically if not. The `roms_helper` script is no different; for example, it
|
||||
automatically downloads coreboot if not present, aswell as GRUB and everything
|
||||
else. You can run each and every part of lbmk without having to worry about
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,7 +143,7 @@ running something before it, because it is handled automatically; if that is
|
|||
ever not the case, it's a bug that should be fixed immediately (in Libreboot
|
||||
20160907, such fine tuned automation did not exist and you did have to run
|
||||
specific parts of the build system manually, in a precise order, but this is
|
||||
no longer the case in `lbmk` for Libreboot from 2021 onwards).
|
||||
no longer the case in modern `lbmk` or `lbmk`).
|
||||
|
||||
Another example: if you run `./build payload grub` but `./build module grub` is
|
||||
not completed, it will automatically run that first, to produce
|
||||
|
|
@ -191,10 +153,10 @@ Another example: if you run `./build boot roms` and crossgcc isn't yet built
|
|||
for the revision used on each given board, it will automatically compile that
|
||||
version of it, using *that* coreboot tree's own build system to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
This level of automation means that `lbmk` from 2021 onwards is much easier to
|
||||
use, compared to the build system present in Libreboot 20160907. Massive
|
||||
improvements to that build system were made, during most of 2021, when
|
||||
implementing both the `osbmk` *and* `lbmk` build systems.
|
||||
This level of automation means that modern `lbmk` is much
|
||||
easier to use, compared to the build system present in Libreboot 20160907.
|
||||
Massive improvements to that build system were made, during most of 2021, when
|
||||
implementing the `lbmk` build system.
|
||||
|
||||
All sections below pertain to actual files in lbmk:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -217,13 +179,13 @@ root directory of `lbmk`).
|
|||
README.md
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||
This file contains a brief description of Libreboot, along with information
|
||||
This file contains a brief description of libreboot, along with information
|
||||
about the project
|
||||
|
||||
build
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
This is the main BASH script, part of `lbmk`, used for running most `lbmk`
|
||||
This is the main BASH script, part of `lbmk`, used for running most `osbmk`
|
||||
commands. You could say that this file *is* `lbmk`. Run `./build help` for
|
||||
usage instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -312,13 +274,9 @@ projectname
|
|||
|
||||
This file contains a single line of text, with the string "libreboot".
|
||||
|
||||
This file exists because of [osboot](https://osboot.org/) existing, which uses
|
||||
a modified version of `lbmk`. Leah Rowe, the founder of Libreboot, is also the
|
||||
founder of osboot and actively maintains both projects. A lot of scripts
|
||||
in `lbmk` make use of the `projectname` file.
|
||||
|
||||
If you were to fork Libreboot, you could very easily just modify this file, so
|
||||
as to rename your fork in a largely automated way.
|
||||
If you were to fork libreboot, you could very easily just modify this file, so
|
||||
as to rename your fork in a largely automated way. Many parts of lbmk use this
|
||||
file.
|
||||
|
||||
resources/coreboot/
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
|
@ -518,7 +476,7 @@ REMINDER: Do not enable a payload in coreboot's build system. Set it
|
|||
to *none*, and enable whatever payload you want in lbmk.
|
||||
|
||||
If a payload is not supported in lbmk, patches are very much welcome! It is
|
||||
the policy of Libreboot, to only ever use the *coreboot* build system inside
|
||||
the policy of libreboot, to only ever use the *coreboot* build system inside
|
||||
coreboot, but not use any of *coreboot's* own integration for payloads. It is
|
||||
far more flexible and *robust* to handle payloads externally, relative to the
|
||||
coreboot build system.
|
||||
|
|
@ -534,70 +492,6 @@ all DRAM upon boot. This is for security reasons. An exception is made when
|
|||
such functionality is not available, on the specific board/revision that you're
|
||||
configuring in coreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
resources/coreboot/DEFAULT/blobs.list
|
||||
=====================================
|
||||
|
||||
For directories in `resources/coreboot/` that specify `cbrevision`,
|
||||
a `blobs.list` file can be included. When running `./download coreboot`, lbmk
|
||||
will delete whatever files are listed in `blobs.list` for that coreboot tree.
|
||||
|
||||
When downloading coreboot, lbmk checks out coreboot 3rdparty submodules, but
|
||||
only does `git submodule update --init`; on coreboot's side, it is set up so
|
||||
that this doesn't download most of the non-free software that coreboot
|
||||
distributes (for that, you run `git submodule --init --checkout` (you'll note
|
||||
that the `--checkout` option is included).
|
||||
|
||||
However, some binary blobs still remain even when only doing `--init`. These
|
||||
are discovered, whenever a new coreboot revision is added to lbmk, by running
|
||||
the *linux-libre* deblob script on the coreboot source tree, *after* doing
|
||||
the `git submodule update --init` command.
|
||||
|
||||
See `deblob-check` from the fsfla website:\
|
||||
<https://www.fsfla.org/ikiwiki/selibre/linux-libre/>
|
||||
|
||||
The `deblob-check` script in fact *does* work quite well on the coreboot
|
||||
source tree! However, coreboot is far simpler than the Linux kernel, and much
|
||||
more conservative in its general scope, that the script was never actually
|
||||
forked specifically for Libreboot. Simply speaking, the way deblobbing is
|
||||
handled in Libreboot is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
* Copy the `blobs.list` from the *last* deblobbed coreboot revision
|
||||
* Run `deblob-check` on the *new* coreboot revision
|
||||
* Run `deblob-check` on the *last* deblobbed coreboot revision
|
||||
* Diff the results
|
||||
* Any file that was deleted on coreboot side, remove from the new `blobs.list`
|
||||
* Any new files get added to the new `blobs.list`
|
||||
|
||||
Doing it manually, and in such a crude fashion as this, is perfectly acceptable
|
||||
because coreboot makes a good habit of always separating binary code blobs into
|
||||
completely *separate* files.
|
||||
|
||||
There is some nuance in exactly how Libreboot handles binary blobs. As far as
|
||||
Libreboot is concerned, only *software* is deleted if a blob. Non-software
|
||||
blobs are retained, so long as they are in a well-understood format or are
|
||||
otherwise trivial. Of course, such data must not be under a non-free license!
|
||||
On the other hand, blobs such as CPU microcode are always to be deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
For example: DDR training data is retained. These are data patterns used for
|
||||
memory controller initialization, specifically during *training* (bruteforcing
|
||||
the precise timings required at boot time).
|
||||
|
||||
More nuance: lbmk does *not* disable any code for *loading* blobs, but rather,
|
||||
it only deletes the actual blobs. For example, you can still add CPU microcode
|
||||
updates to Libreboot ROM images, and libreboot's version of coreboot will still
|
||||
use them, if present. This has always been the case. Libreboot will never try
|
||||
to prevent you from running blobs; it merely does not *include* them. This is
|
||||
for the sake of efficiency, because deblobbing is actually only a very minor
|
||||
aspect of what Libreboot is, and time is better spent on other areas of
|
||||
development. Deblobbing is done in the most low-effort way possible, just so as
|
||||
to comply with the *GNU Free System Distribution Guidelines*.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, deleting blobs from coreboot *breaks* coreboot, in situations where
|
||||
you actually want to build for a board where those blobs are used, but since
|
||||
those boards are not to be supported in lbmk anyway, it's moot (the boards that
|
||||
lbmk does support will all boot just fine, because all of the required files
|
||||
exist, and are free).
|
||||
|
||||
resources/coreboot/BOARDNAME/patches/\*
|
||||
=======================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -613,14 +507,6 @@ for instance, and `lbmk` will not erroneously try to apply `README` as though
|
|||
it were a patch file. This might be useful if you have a *lot* of patches, and
|
||||
you want to provide some explanations about specific files.
|
||||
|
||||
FUN FACT: If you run `NODELETE= ./download coreboot`, lbmk will *skip* deleting
|
||||
blobs, and also skip deleting the `.git` files and directories in those
|
||||
coreboot clones. By default, the Git history is deleted, because it contains
|
||||
blobs. However, you may want to make changes and then create a patch
|
||||
using `git format-patch`, and you can do just that! Afterwards, you would
|
||||
simply delete the blobs manually and delete the Git history (or you could just
|
||||
run `./download coreboot` again, without `NODELETE`).
|
||||
|
||||
resources/grub/background/
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -719,7 +605,7 @@ for `romtype`:
|
|||
|
||||
* `4MiB IFD BIOS region` will cause only the upper 4MB section of the ROM
|
||||
to be included in a release. This option is largely deprecated, a hangover
|
||||
from osboot, which also no longer uses this option on any boards, and it is
|
||||
from libreboot, which also no longer uses this option on any boards, and it is
|
||||
thus subject for removal.
|
||||
* `d8d16sas` will cause *fake* (empty) files named `pci1000,0072.rom`
|
||||
and `pci1000,3050.rom` to be inserted in CBFS. This prevents SeaBIOS from
|
||||
|
|
@ -746,7 +632,7 @@ for `romtype`:
|
|||
part). In all cases, the default *ME* (Intel Management Engine) region is
|
||||
disabled, as is the ME itself, based on bits set to disable it in the Intel
|
||||
Flash Descriptor. The descriptor is used in such a setup, because on all
|
||||
such boards in Libreboot, GbE NVM is needed to get gigabit ethernet working
|
||||
such boards in libreboot, GbE NVM is needed to get gigabit ethernet working
|
||||
correctly; it is the sole reason `ich9gen` was written, because it is
|
||||
otherwise possible to boot these machines in a *descriptorless* setup, where
|
||||
ICH9M behaves similarly to ICH7: all one region of flash, for the boot
|
||||
|
|
@ -781,8 +667,8 @@ the default anyway) to enable *all* option ROMs, unless `vgarom` setups are
|
|||
used, in which case the option is set to *0* (disabled) because coreboot is
|
||||
then expected to handle option ROMs, and SeaBIOS should not do it.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, the `roms_helper` script makes use of each and every part of lbmk.
|
||||
It is the heart of Libreboot.
|
||||
Essentially, the `roms_helper` script makes use of each and every part of
|
||||
lbmk. It is the heart of libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
When the ROM is finished compiling, it will appear under a directory in `bin/`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -966,27 +852,27 @@ on all coreboot source trees.
|
|||
|
||||
Command: `./build release src`
|
||||
|
||||
resources/scripts/build/release/u-boot-libre
|
||||
============================================
|
||||
This builds a release of u-boot-libre. Once released officially, the
|
||||
files produced by the command below are then expected to be used by
|
||||
FSDG distributions packages.
|
||||
|
||||
While this isn't useful as-is for Libreboot, it enables to share the
|
||||
deblobbing code between various FSDG distributions and also enables
|
||||
Libreboot to reuse that deblobbing process to support boards with
|
||||
u-boot in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
Command: `./build release u-boot-libre`
|
||||
|
||||
resources/scripts/download/coreboot
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
This downloads, patches and deblobs coreboot, as per `board.cfg` files
|
||||
This downloads, and patches coreboot, as per `board.cfg` files
|
||||
in `resources/coreboot/`.
|
||||
|
||||
Command: `./download coreboot`
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This version of the script also performs the full git checkout in each
|
||||
coreboot tree, like so:
|
||||
|
||||
git submodule update --init --checkout
|
||||
|
||||
The `lbmk` version only does this:
|
||||
|
||||
git submodule update --init
|
||||
|
||||
The coreboot project sets up its Git repository, in such a way where most blobs
|
||||
are skipped if you omit `--checkout`. Since lbmk's policy is to *include*
|
||||
these in its distribution, it makes sense to use `--checkout`.
|
||||
|
||||
resources/scripts/download/flashrom
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Porting Guide
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This guide is intended for those with very little knowledge of firmware
|
||||
in general and coreboot in particular.
|
||||
Most boards in coreboot can be quite easily ported to libreboot.
|
||||
You don't need any knowledge of a particular programming language or
|
||||
technology in general to port a board.
|
||||
If you want to make more major contributions to the build system,
|
||||
please read the [main maintenance page.](/docs/maintain/index.html)
|
||||
|
||||
You will certainly need flashing equipment if you wish to follow this guide.
|
||||
See the [flashing guide](/docs/install/spi.html) to find out what you'll need.
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot is replacement firmware for the firmware chips on the printed
|
||||
circuit board (PCB) of the machine in question.
|
||||
Osboot is a *distribution* of Coreboot.
|
||||
You may be used to referring to your machine as *machine, device, laptop*
|
||||
or it's name (ex: thinkpad t420).
|
||||
Because we're targeting chips on the PCB, we refer to all of the above terms
|
||||
synonymously as `board.`
|
||||
The rest of this article will refer to the board you wish to port to
|
||||
libreboot as `board.`
|
||||
|
||||
If `board` is not supported in coreboot then you need to start there first.
|
||||
Osboot developers will generally not port new boards to coreboot on request.
|
||||
If you're not sure whether your board is in coreboot check the [coreboot table of hardware.](https://coreboot.org/status/board-status.html)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have determined that `board` is supported by coreboot, but is not
|
||||
supported by libreboot, then follow the rest of this guide to try to port it yourself.
|
||||
If you're still unable to port the board, or anything in this guide is
|
||||
unclear, then contact libreboot developers.
|
||||
The best way to get in touch is via [libreboot irc.](/contact.html#irc-chatroom)
|
||||
|
||||
Cloning Osbmk
|
||||
=============
|
||||
|
||||
Before you try to get any work done, you'll need to clone the lbmk (libreboot make)
|
||||
project.
|
||||
To do so, you'll need to have git installed on your machine. You can then clone
|
||||
the project.
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk
|
||||
|
||||
If you want more information on building lbmk see [the build instructions.](/docs/build/index.html)
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot Config
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot payloads (GRUB, Seabios, etc) are built separately.
|
||||
You therefore only need to focus on the coreboot config(s) for `board.`
|
||||
All of these configs are stored under resources/coreboot/`board`
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to start a new configuration for a given board is to copy an existing
|
||||
configuration and make the necessary modifications.
|
||||
For example, if one wanted to port the t420s, then the t420 config would be an excellent
|
||||
starting point.
|
||||
|
||||
cp -r resources/coreboot/t420_12mb/ resources/coreboot/t420s_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
You can then easily modify the existing coreboot configs for you board via lbmk.
|
||||
|
||||
./modify coreboot configs t420s_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
This script will provide a curses interface through which you can easily modify the
|
||||
necessary variables and settings.
|
||||
The most important thing to change is `Mainboard.`
|
||||
You must make sure that the mainboard definition in this config matches `board.`
|
||||
For example, you would want to change lenovo/t420 to lenovo/t420s.
|
||||
Selecting `exit` in the curses interface will prompt you to ask if you want to save your
|
||||
changes, make sure to answer yes.
|
||||
Note that you will generally have to go through this process twice, since there is
|
||||
a corebootfb and txtmode config for each board (the script will handle this for you).
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can build and test the rom for `board.`
|
||||
Once you have finished this, you can try flashing the resulting rom to your board as a test.
|
||||
|
||||
./build boot roms t420s_12mb
|
||||
|
||||
If you try to flash this rom and it fails, then there are two probable reasons:
|
||||
|
||||
1) CBFS size or ROM size is wrong
|
||||
2) The blobs are incompatible
|
||||
|
||||
Solutions to these problems follow in the proceeding sections.
|
||||
|
||||
Wrong CBFS and or ROM size
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
Different boards have different flash chip setups.
|
||||
Generally, you have one or two flash chips with a combined size of 4-16MB.
|
||||
Thankfully, flashrom will let you know the size of the flash chip you're flashing.
|
||||
For example: when flashing an X230, you'll see that one chip is 8192, and the other is 4096.
|
||||
The total rom size should therefore be set as 12MB.
|
||||
|
||||
The CBFS size depends directly on the size of the flash chip selected.
|
||||
Make sure that your CBFS size is not larger than the maximum for your board.
|
||||
CBFS sizes are stated as hex values, here is a table showing the correct maximums
|
||||
for various rom sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
| ROM Size | CBFS size |
|
||||
|:--------:|:---------:|
|
||||
| 8MB | 0x7E0000 |
|
||||
| 12MB | 0xBE0000 |
|
||||
| 16MB | 0xFE0000 |
|
||||
|
||||
Obtaining Blobs
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to see if your coreboot config is valid is to extract the required
|
||||
binary blobs from a backup of your vendor rom.
|
||||
You'll need a unified rom for dual chip setups; see [the ivybridge haswell guide](/docs/install/ivy_has_common.html)
|
||||
for instructions on creating a unified rom image.
|
||||
|
||||
Extracting the blobs from a vendor rom image is automated in lbmk.
|
||||
Simply run `./blobutil extract [board] [/path/to/backup.bin]`
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
./blobutil extract t420s_12mb t420s_backup.bin
|
||||
|
||||
You can then modify your coreboot configs again and set the path for the
|
||||
intel firmware descriptor, intel management engine, and gigabit ethernet firmware.
|
||||
|
||||
Getting Help
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have tried everything above, you might find that the board still doesn't
|
||||
work.
|
||||
If that is the case, then you should contact libreboot developers for more help.
|
||||
You can ping `shmalebx9` and/or `leah` on irc or submit an issue on git.
|
||||
In either case, make sure to include a detailed description of everything you
|
||||
tried, and what exactly happened when you tried to flash the rom.
|
||||
If your board is not supported in libreboot, then you can assume that our
|
||||
developers don't have it.
|
||||
You'll therefore be expected to test roms created by libreboot developers on
|
||||
your own machine.
|
||||
|
||||
In the meantime, you can always externally flash a backup of your vendor rom
|
||||
to keep your machine working while development progresses on your board.
|
||||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Introduction
|
|||
|
||||
This document lists product codenames for some hardware.
|
||||
Please note that just because a certain device is listed here does NOT mean
|
||||
that it is supported in Libreboot. For supported devices refer to the
|
||||
that it is supported in libreboot. For supported devices refer to the
|
||||
installation documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### A note on GPUs
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,9 +68,6 @@ under RAM sticks.
|
|||
- with dGPU: SWG (SWitchable Graphics)
|
||||
- with only iGPU: UMA (Unified Memory Access)
|
||||
|
||||
*Note that Intel platforms newer than Montevina are not supported by libreboot
|
||||
yet!. Currently only Calistoga and Montevina platforms are supported.
|
||||
|
||||
- These are the known model codenames:
|
||||
- ThinkPad T410: NOZOMI-1 # EXT/INT
|
||||
- ThinkPad T410s: SHINAI-2 # SWG/UMA
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -292,10 +292,3 @@ across subnets on the same interface (NIC).
|
|||
|
||||
More information, including logs, can be found on [this
|
||||
page](http://web.archive.org/web/20210416010634/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/23).
|
||||
|
||||
USB keyboard wakeup on GM45 laptops
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
Look at resources/scripts/helpers/misc/libreboot\_usb\_bugfix
|
||||
|
||||
Put this script in /etc/init.d/ on debian-based systems.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Libreboot releases
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This page has [merged with the main news section](/news/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Libreboot releases
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
This page has merged with the default news section.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to: [Libreboot release announcements](/news/)
|
||||
176
site/download.md
176
site/download.md
|
|
@ -1,179 +1,21 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Downloads
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
New releases are announced in the [main news section](news/).
|
||||
|
||||
If you're more interested in libreboot development, go to the
|
||||
[libreboot development page](../git.md), which also includes links to the
|
||||
Git repositories. The page on [/docs/maintain/](docs/maintain/) describes how
|
||||
Libreboot is put together, and how to maintain it. If you wish to build
|
||||
Libreboot from source, [read this page](docs/build/).
|
||||
|
||||
GPG signing key
|
||||
---------------
|
||||
|
||||
**The latest release is Libreboot 20220710, under the `stable` directory.**
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: KGPE-D16, KCMA-D8 and GA-G41M-ES2L ROM images are excluded in that
|
||||
release; use an older release, unless these are re-added in future releases.
|
||||
You can still compile ROM images for these boards yourself, from the latest
|
||||
version of Libreboot in the Git repository.
|
||||
|
||||
### NEW KEY
|
||||
|
||||
Full key fingerprint: `98CC DDF8 E560 47F4 75C0 44BD D0C6 2464 FA8B 4856`
|
||||
|
||||
The above key is for Libreboot 20220710, and subsequent releases.
|
||||
|
||||
Download the key here: [lbkey.asc](lbkey.asc)
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot releases are signed using GPG.
|
||||
|
||||
### OLD KEY:
|
||||
|
||||
This key is for Libreboot 20160907 and all older releases:
|
||||
|
||||
Full key fingerprint: CDC9 CAE3 2CB4 B7FC 84FD C804 969A 9795 05E8 C5B2
|
||||
|
||||
The GPG key can also be downloaded with this exported dump of the
|
||||
pubkey: [lbkeyold.asc](lbkeyold.asc).
|
||||
|
||||
sha512sum -c sha512sum.txt
|
||||
gpg --verify sha512sum.txt.sig
|
||||
Future releases will be announced in the [main news section](news/).
|
||||
|
||||
Git repository
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
Links to regular release archives are listed on this page.
|
||||
There are no binary releases for `libreboot` yet, so you must download from the
|
||||
available Git repository and compile it yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
However, for the absolute most bleeding edge up-to-date version of Libreboot,
|
||||
there is a Git repository that you can download from. Go here:
|
||||
Please ensure that you have the [Git](https://git-scm.com/) software installed.
|
||||
It is available in *most* distributions, via *package management*.
|
||||
|
||||
[How to download Libreboot from Git](git.md)
|
||||
Please refer to the following resources:
|
||||
|
||||
HTTPS mirrors {#https}
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
* [How to download libreboot from Git](git.md)
|
||||
* [How to compile libreboot from source](docs/build/)
|
||||
* [lbmk maintenance manual](docs/maintain/)
|
||||
|
||||
**The latest release is Libreboot 20220710, under the `stable` directory.**
|
||||
|
||||
These mirrors are recommended, since they use TLS (https://) encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Libreboot from these mirrors:
|
||||
|
||||
* <https://rsync.libreboot.org/> (Libreboot project official mirror, UK)
|
||||
* <https://www.mirrorservice.org/sites/libreboot.org/release/> (University
|
||||
of Kent, UK)
|
||||
* <https://mirrors.mit.edu/libreboot/> (MIT university, USA)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.math.princeton.edu/pub/libreboot/> (Princeton
|
||||
university, USA)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.libremind.org/libreboot/> (libremind.org, Iceland)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.splentity.com/libreboot/> (Splentity Software, USA)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.sugol.org/libreboot/> (sugol.org)
|
||||
(formerly nephelai.zanity.net/mirror/libreboot)
|
||||
* <https://mirrors.qorg11.net/libreboot/> (qorg11.net, Spain)
|
||||
* <https://elgrande74.net/libreboot/> (elgrande74.net, France)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.koddos.net/libreboot/> (koddos.net, Netherlands)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.swordarmor.fr/libreboot/> (swordarmor.fr, France)
|
||||
* <https://mirror-hk.koddos.net/libreboot/> (koddos.net, Hong Kong)
|
||||
* <https://mirror.cyberbits.eu/libreboot/> (cyberbits.eu, France)
|
||||
|
||||
RSYNC mirrors {#rsync}
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Useful for mirroring Libreboot's entire set of release archives. You can put
|
||||
an rsync command into crontab and pull the files into a directory on your
|
||||
web server.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are going to mirror the entire set, it is recommended that you allocate
|
||||
at least 25GiB. Libreboot's rsync is currently about 12GiB, so allocating 25GiB
|
||||
will afford you plenty of space for the future. At minimum, you should ensure
|
||||
that at least 15-20GiB of space is available, for your Libreboot mirror.
|
||||
|
||||
*It is highly recommended that you use the libreboot.org mirror*, if you wish
|
||||
to host an official mirror. Otherwise, if you simply want to create your own
|
||||
local mirror, you should use one of the other mirrors, which sync from
|
||||
libreboot.org.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you create the mirror, make a directory on your web server. For
|
||||
example:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /var/www/html/libreboot/
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can run rsync, for instance:
|
||||
|
||||
rsync -avz --delete-after rsync://rsync.libreboot.org/mirrormirror/ /var/www/html/libreboot/
|
||||
|
||||
**It's extremely important to have the final forward slash (/) at the end of each path,
|
||||
in the above rsync command. Otherwise, rsync will behave very strangely.**
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to regularly keep your rsync mirror updated, you can add it to a
|
||||
crontab. This page tells you how to use crontab:
|
||||
<https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/crontab.5.html>
|
||||
|
||||
The following rsync mirrors are available:
|
||||
|
||||
* <rsync://rsync.libreboot.org/mirrormirror/> (Libreboot project official mirror)
|
||||
* <rsync://rsync.mirrorservice.org/libreboot.org/release/> (University of Kent,
|
||||
UK)
|
||||
* <rsync://mirror.math.princeton.edu/pub/libreboot/> (Princeton university, USA)
|
||||
* <rsync://rsync.libremind.org/libreboot/> (libremind.org, Iceland)
|
||||
* <rsync://qorg11.net/mirrors/libreboot/> (qorg11.net, Spain)
|
||||
* <rsync://ftp.linux.ro/libreboot/> (linux.ro, Romania)
|
||||
* <rsync://mirror.koddos.net/libreboot/> (koddos.net, Netherlands)
|
||||
* <rsync://mirror-hk.koddos.net/libreboot/> (koddos.net, Hong Kong)
|
||||
|
||||
Are you running a mirror? Contact the libreboot project, and the link will be
|
||||
added to this page!
|
||||
|
||||
You can make your rsync mirror available via your web server, and also configure
|
||||
your *own* mirror to be accessible via rsync. There are many resources online
|
||||
that show you how to set up an rsync server.
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP mirrors {#http}
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
**The latest release is Libreboot 20220710, under the `stable` directory.**
|
||||
|
||||
WARNING: these mirrors are non-HTTPS which means that they are
|
||||
unencrypted. Your traffic could be subject to interference by
|
||||
adversaries. Make especially sure to check the GPG signatures, assuming
|
||||
that you have the right key. Of course, you should do this anyway, even
|
||||
if using HTTPS.
|
||||
|
||||
* <http://mirror.linux.ro/libreboot/> (linux.ro, Romania)
|
||||
* <http://mirror.helium.in-berlin.de/libreboot/> (in-berlin.de, Germany)
|
||||
|
||||
FTP mirrors {#ftp}
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
**The latest release is Libreboot 20220710, under the `stable` directory.**
|
||||
|
||||
WARNING: FTP is also unencrypted, like HTTP. The same risks are present.
|
||||
|
||||
* <ftp://ftp.mirrorservice.org/sites/libreboot.org/release/> (University
|
||||
of Kent, UK)
|
||||
* <ftp://ftp.linux.ro/libreboot/> (linux.ro, Romania)
|
||||
|
||||
Statically linked
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot includes statically linked executables in some releases, built from
|
||||
the available source code. Those executables have certain libraries built into
|
||||
them, so that the executables will work on many GNU+Linux distros.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot 20160907 was built in Trisquel GNU+Linux, version 7.0 64-bit.
|
||||
Some older Libreboot releases will have been built in Trisquel 6.0.1.
|
||||
|
||||
To comply with GNU GPL v2, Trisquel 6 and 7 source ISOs are supplied by the
|
||||
Libreboot project. You can find these source ISOs in the `ccsource` directory
|
||||
on the `rsync` mirrors.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot releases past version 20160907 do not distribute statically linked
|
||||
binaries. Instead, these releases are source-only, besides pre-compiled ROM
|
||||
images for which the regular Libreboot source code archives suffice. These newer
|
||||
releases instead automate the installation of build dependencies, with instructions
|
||||
in the documentation for building various utilities from source.
|
||||
|
||||
These executables are utilities such as `flashrom`.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
361
site/faq.md
361
site/faq.md
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ AKA Frequently Questioned Answers
|
|||
Important issues
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
How to compile Libreboot from source
|
||||
How to compile libreboot from source
|
||||
------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [lbmk build instructions](docs/build/).
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Refer to the [lbmk build instructions](docs/build/).
|
|||
How does the build system work?
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [lbmk maintenance instructions](docs/maintain/).
|
||||
Refer to the [lbmk maintenance manual](docs/maintain/).
|
||||
|
||||
Do not use CH341A!
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,10 +78,6 @@ configuration)
|
|||
My KCMA-D8 or KGPE-D16 doesn't boot with the PIKE2008 module installed
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot 20160818, 20160902 and 20160907 all have this behaviour: in SeaBIOS,
|
||||
PCI options ROMs are loaded when available, by default. This is not
|
||||
technically a problem, because an option ROM can be free or non-free.
|
||||
|
||||
Loading the option ROM from the PIKE2008 module on either ASUS KCMA-D8
|
||||
or KGPE-D16 causes the system to hang at boot. It's possible to use
|
||||
this in the payload (if you use a linux kernel payload, like linuxboot),
|
||||
|
|
@ -91,7 +87,7 @@ module without loading the option ROM.
|
|||
|
||||
Refer to the [linuxboot website](https://www.linuxboot.org/). This is a special
|
||||
busybox+linux system, which goes in the boot flash as a coreboot payload. You
|
||||
can insert it into your Libreboot ROM image using cbfstool, if it's big enough.
|
||||
can insert it into your libreboot ROM image using cbfstool, if it's big enough.
|
||||
On KCMA-D8/KGPE-D16 it's trivial to upgrade the boot flash to 16MiB, which is
|
||||
more than enough to fit Linuxboot. See:\
|
||||
[External flashing guide](docs/install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,14 +97,14 @@ which can boot other Linux kernels using kexec. It can parse GNU GRUB configs,
|
|||
and it can also provide some basic UEFI features. Because it's using the Linux
|
||||
kernel, this means that LinuxBoot can make use of the PIKE2008 module.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: Integrate this in Libreboot, as a payload option, but also:
|
||||
TODO: Integrate this in libreboot, as a payload option, but also:
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: Fork LinuxBoot, and make a version of it that uses linux-libre. Ensure
|
||||
that it is a fully free distribution, so that the FSF can endorse it.
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxBoot is *perfect*, especially if you're setting up one of these systems to
|
||||
be used as a server. LinuxBoot is *much* more flexible and configurable than
|
||||
GNU GRUB, which right now is the payload that Libreboot prefers.
|
||||
GNU GRUB, which right now is the payload that libreboot prefers.
|
||||
|
||||
How to save kernel panic logs on thinkpad laptops?
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -175,38 +171,22 @@ the target (`target$`):
|
|||
|
||||
6. Try to reproduce the kernel panic.
|
||||
|
||||
Machine check exceptions on some Montevina (Penryn CPU) laptops
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Some GM45 laptops have been freezing or experiencing a kernel panic
|
||||
(blinking caps lock LED and totaly unresponsive machine, sometimes followed
|
||||
by an automatic reboot within 30 seconds).
|
||||
We do not know what the problem(s) is(are), but a CPU microcode
|
||||
update in some cases prevents this from happening again.
|
||||
See the following bug reports for more info:
|
||||
|
||||
- [T400 Machine check: Processor context corrupt](http://web.archive.org/web/20210325195107/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/493)
|
||||
- [X200 Machine check: Processor context corrupt](http://web.archive.org/web/20210128161939/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/289)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Unrelated, RAM incompatibility and suspend-to-ram issues on X200](https://libreboot.org/docs/hardware/x200.html#ram_s3_microcode)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware compatibility
|
||||
======================
|
||||
|
||||
What systems are compatible with libreboot?
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See the [hardware compatibility list](docs/hardware/).
|
||||
Any system can easily be added, so *compatibility* merely refers to whatever
|
||||
boards are integrated in the `lbmk` build system, which libreboot uses.
|
||||
|
||||
Why is the latest Intel hardware unsupported in libreboot? {#intel}
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Please read the [hardware compatibility list](docs/hardware/).
|
||||
|
||||
It is unlikely that any post-2008 Intel hardware will ever be supported in
|
||||
libreboot, due to severe security and freedom issues; so severe, that *the
|
||||
libreboot project recommends avoiding all modern Intel hardware. If you have an
|
||||
Intel based system affected by the problems described below, then you should
|
||||
get rid of it as soon as possible*. The main issues are as follows:
|
||||
Freedom pitfalls with modern Intel hardware {#intel}
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot is nominally Free Software, but requires binary blobs on most x86
|
||||
targets that it supports, on both Intel and AMD.
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel Management Engine (ME) {#intelme}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,10 +201,12 @@ to disable Intel ME after BringUp. See:
|
|||
|
||||
<https://github.com/corna/me_cleaner>\
|
||||
|
||||
On all Libreboot systems that have an Intel ME in it (GM45+ICH9M laptops and
|
||||
On all GM45+ICH9M laptops that have an Intel ME in it (additionally, this means
|
||||
X4X+ICH10 desktops), the ME firmware is not needed in the boot flash. Either a
|
||||
modified descriptor is used, which disables the ME and removes the region for
|
||||
it in the boot flash, or a descriptorless setup is used.
|
||||
it in the boot flash, or a descriptorless setup is used. However, all modern
|
||||
Intel platforms otherwise require an Intel ME image to be present in the main
|
||||
boot flash.
|
||||
|
||||
Now onto the main topic:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -327,9 +309,9 @@ privacy that can't be ignored.
|
|||
Before version 6.0 (that is, on systems from 2008/2009 and earlier), the
|
||||
ME can be disabled by setting a couple of values in the SPI flash
|
||||
memory. The ME firmware can then be removed entirely from the flash
|
||||
memory space. libreboot [does this](docs/install/ich9utils.md) on
|
||||
the Intel 4 Series systems that it supports, such as the [Libreboot
|
||||
X200](../docs/install/x200_external.md) and [Libreboot
|
||||
memory space. The libreboot project [does this](docs/install/ich9utils.md) on
|
||||
the Intel 4 Series systems that it supports, such as the [ThinkPad
|
||||
X200](../docs/install/x200_external.md) and [ThinkPad
|
||||
T400](../docs/install/t400_external.md). ME firmware versions 6.0 and
|
||||
later, which are found on all systems with an Intel Core i3/i5/i7 CPU
|
||||
and a PCH, include "ME Ignition" firmware that performs some hardware
|
||||
|
|
@ -354,6 +336,15 @@ project strongly recommends avoiding it entirely. Since recent versions
|
|||
of it can't be removed, this means avoiding all recent generations of
|
||||
Intel hardware.**
|
||||
|
||||
The *above* paragraph is only talking about setups where the *full* Intel ME
|
||||
firmware is used, containing networking code and especially *Active Management
|
||||
Technology* (AMT).
|
||||
|
||||
Use of the `me_cleaner` utility is believed to minimize any security risk when
|
||||
using these Intel platforms, and coreboot *does* contain fully free code for
|
||||
sandybridge/ivybridge platforms. Freedom-wise, these are similar to libreboot
|
||||
compatible ThinkPads, and they are quite nice machines.
|
||||
|
||||
More information about the Management Engine can be found on various Web
|
||||
sites, including [me.bios.io](http://me.bios.io/Main_Page),
|
||||
[unhuffme](http://io.netgarage.org/me/), [coreboot
|
||||
|
|
@ -367,10 +358,6 @@ If you're stuck with the ME (non-libreboot system), you might find this
|
|||
interesting:
|
||||
<http://hardenedlinux.org/firmware/2016/11/17/neutralize_ME_firmware_on_sandybridge_and_ivybridge.html>
|
||||
|
||||
Also see (effort to disable the ME):
|
||||
<https://www.coreboot.org/pipermail/coreboot/2016-November/082331.html>
|
||||
- look at the whole thread
|
||||
|
||||
### Firmware Support Package (FSP) {#fsp}
|
||||
|
||||
On all recent Intel systems, coreboot support has revolved around
|
||||
|
|
@ -392,42 +379,13 @@ find them).
|
|||
|
||||
### CPU microcode updates {#microcode}
|
||||
|
||||
All modern x86 CPUs (from Intel and AMD) use what is called *microcode*.
|
||||
CPUs are extremely complex, and difficult to get right, so the circuitry
|
||||
is designed in a very generic way, where only basic instructions are
|
||||
handled in hardware. Most of the instruction set is implemented using
|
||||
microcode, which is low-level software running inside the CPU that can
|
||||
specify how the circuitry is to be used, for each instruction. The
|
||||
built-in microcode is part of the hardware, and read-only. Both the
|
||||
circuitry and the microcode can have bugs, which could cause reliability
|
||||
issues.
|
||||
The microcode configures logic gates in your CPU, to implement an instruction
|
||||
set architecture. Your CPU will already contain them, but it also supplies a
|
||||
way to update the microcode at boot time, fixing bugs and greatly enhancing
|
||||
the general reliability of your system.
|
||||
|
||||
Microcode *updates* are proprietary blobs, uploaded to the CPU at boot
|
||||
time, which patches the built-in microcode and disables buggy parts of
|
||||
the CPU to improve reliability. In the past, these updates were handled
|
||||
by the operating system kernel, but on all recent systems it is the boot
|
||||
firmware that must perform this task. Coreboot does distribute microcode
|
||||
updates for Intel and AMD CPUs, but libreboot cannot, because the whole
|
||||
point of libreboot is to be 100% [free
|
||||
software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html).
|
||||
|
||||
On some older Intel CPUs, it is possible to exclude the microcode
|
||||
updates and not have any reliability issues in practise. All current
|
||||
libreboot systems work without microcode updates (otherwise, they
|
||||
wouldn't be supported in libreboot). However, all modern Intel CPUs
|
||||
require the microcode updates, otherwise the system will not boot at
|
||||
all, or it will be extremely unstable (memory corruption, for example).
|
||||
|
||||
Intel CPU microcode updates are *signed*, which means that you could not
|
||||
even run a modified version, even if you had the source code. If you try
|
||||
to upload your own modified updates, the CPU will reject them.
|
||||
|
||||
The microcode updates alter the way instructions behave on the CPU. That
|
||||
means they affect the way the CPU works, in a very fundamental way. That
|
||||
makes it software. The updates are proprietary, and are software, so we
|
||||
exclude them from libreboot. The microcode built into the CPU already is
|
||||
not so much of an issue, since we can't change it anyway (it's
|
||||
read-only).
|
||||
Microcode is already discussed in great detail, on the [binary blobs
|
||||
policy](news/policy.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel is uncooperative
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -444,38 +402,17 @@ corporate NDA (non-disclosure agreement), but even that is not
|
|||
guaranteed. Even ODMs and IBVs can't get source code from Intel, in
|
||||
most cases (they will just integrate the blobs that Intel provides).
|
||||
|
||||
Recent Intel graphics chipsets also [require firmware
|
||||
Newer Intel graphics chipsets also [require firmware
|
||||
blobs](https://01.org/linuxgraphics/intel-linux-graphics-firmwares?langredirect=1).
|
||||
|
||||
Intel is [only going to get
|
||||
worse](https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Intel-Gfx-GuC-SLPC)
|
||||
when it comes to user freedom. Libreboot has no support recent Intel
|
||||
platforms, precisely because of the problems described above. The only
|
||||
way to solve this is to get Intel to change their policies and to be
|
||||
more friendly to the [free
|
||||
software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) community.
|
||||
Reverse engineering won't solve anything long-term, unfortunately, but
|
||||
we need to keep doing it anyway. Moving forward, Intel hardware is a
|
||||
non-option unless a radical change happens within Intel.
|
||||
The `libreboot` project *does* provide some support for newer Intel platforms, but
|
||||
you should be aware of these issues if you choose to run those machines.
|
||||
|
||||
**Basically, all Intel hardware from year 2010 and beyond will never be
|
||||
supported by libreboot. The libreboot project is actively ignoring all
|
||||
modern Intel hardware at this point, and focusing on alternative
|
||||
platforms.**
|
||||
|
||||
Why is the latest AMD hardware unsupported in libreboot? {#amd}
|
||||
Freedom pitfalls to consider on AMD hardware {#amd}
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
It is extremely unlikely that any modern AMD hardware will ever be
|
||||
supported in libreboot, due to severe security and freedom issues; so
|
||||
severe, that *the libreboot project recommends avoiding all modern AMD
|
||||
hardware. If you have an AMD based system affected by the problems
|
||||
described below, then you should get rid of it as soon as possible*. The
|
||||
main issues are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
[We call on AMD to release source code and specs for the new AMD Ryzen
|
||||
platforms! We call on the community to put pressure on AMD. Click here
|
||||
to read more](amd-libre.md)
|
||||
AMD has more or less the same problem as Intel, when it comes to software
|
||||
freedom.
|
||||
|
||||
### AMD Platform Security Processor (PSP)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -524,8 +461,12 @@ CPUs.
|
|||
|
||||
Read <https://www.coreboot.org/AMD_IMC>.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This section is oudated, and it is in need of cleanup.
|
||||
|
||||
### AMD SMU firmware
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: This section may be outdated, and it is in need of cleanup.
|
||||
|
||||
Handles some power management for PCIe devices (without this, your
|
||||
laptop will not work properly) and several other power management
|
||||
related features.
|
||||
|
|
@ -538,11 +479,14 @@ demonstration](https://media.ccc.de/v/31c3_-_6103_-_en_-_saal_2_-_201412272145_-
|
|||
and based on this work, Damien Zammit (another coreboot hacker)
|
||||
[partially replaced it](https://github.com/zamaudio/smutool/) with free
|
||||
firmware, but on the relevant system (ASUS F2A85-M) there were still
|
||||
other blobs present (Video BIOS, and others) preventing the hardware
|
||||
from being supported in libreboot.
|
||||
other blobs present (Video BIOS, and others).
|
||||
|
||||
### AMD AGESA firmware
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: More needs to be written about this, to reflect the current reality.
|
||||
The situation with AMD has evolved in recent years. The information on this FAQ
|
||||
page is a few years out of date.
|
||||
|
||||
This is responsible for virtually all core hardware initialization on
|
||||
modern AMD systems. In 2011, AMD started cooperating with the coreboot
|
||||
project, releasing this as source code under a free license. In 2014,
|
||||
|
|
@ -556,7 +500,11 @@ practically the same, though it was found with much later hardware in
|
|||
AMD that you could run without microcode updates. It's unknown whether
|
||||
the updates are needed on all AMD boards (depends on CPU).
|
||||
|
||||
### AMD is incompetent (and uncooperative)
|
||||
The libreboot project does not consider microcode updates a problem, and it
|
||||
enables them by default on all supported hardware, even libreboot-compatible
|
||||
hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
### AMD is uncooperative
|
||||
|
||||
AMD seemed like it was on the right track in 2011 when it started
|
||||
cooperating with and releasing source code for several critical
|
||||
|
|
@ -583,79 +531,16 @@ addition to the "usual" engineering and software development firms.
|
|||
This also affects whistleblowers, or anyone who needs actual privacy and
|
||||
security.
|
||||
|
||||
What *can* I use, then? {#whatcaniuse}
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot has support for AMD hardware of Family 15h (Bulldozer or
|
||||
Piledriver, ~2012 gen) and some older Intel platforms like Napa,
|
||||
Montevina, Eagle Lake, Lakeport (2004-2006). We also have support for
|
||||
some ARM chipsets (rk3288). On the Intel side, we're also interested in
|
||||
some of the chipsets that use Atom CPUs (rebranded from older chipsets,
|
||||
mostly using ich7-based southbridges).
|
||||
|
||||
Will libreboot work on a ThinkPad T400 or T500 with an ATI GPU?
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Short answer: yes. These laptops also have an Intel GPU inside, which
|
||||
libreboot uses. The ATI GPU is ignored by libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
These laptops use what is called *switchable graphics*, where it will
|
||||
have both an Intel and ATI GPU. Coreboot will allow you to set (using
|
||||
nvramtool) a parameter, specifying whether you would like to use Intel
|
||||
or ATI. The ATI GPU lacks free native graphics initialization in
|
||||
coreboot, unlike the Intel GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot modifies coreboot, in such a way where this nvramtool setting
|
||||
is ignored. Libreboot will just assume that you want to use the Intel
|
||||
GPU. Therefore, the ATI GPU is completely disabled on these laptops.
|
||||
Intel is used instead, with the free native graphics initialization
|
||||
(VBIOS replacement) that exists in coreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Will desktop/server hardware be supported?
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot now supports desktop hardware:
|
||||
[(see list)](../docs/hardware/)
|
||||
(with full native video initialization).
|
||||
|
||||
A common issue with desktop hardware is the Video BIOS, when no onboard
|
||||
video is present, since every video card has a different Video BIOS.
|
||||
Onboard GPUs also require one, so those still have to be replaced with
|
||||
free software (non-trivial task). Libreboot has to initialize the
|
||||
graphics chipset, but most graphics cards lack a free Video BIOS for
|
||||
this purpose. Some desktop motherboards supported in coreboot do have
|
||||
onboard graphics chipsets, but these also require a proprietary Video
|
||||
BIOS, in most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
Hi, I have <insert random system here>, is it supported?
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Most likely not. First, you must consult coreboot's own hardware
|
||||
compatibility list at <http://www.coreboot.org/Supported_Motherboards>
|
||||
and, if it is supported, check whether it can run without any
|
||||
proprietary blobs in the ROM image. If it can: wonderful! Libreboot can
|
||||
support it, and you can add support for it. If not, then you will need
|
||||
to figure out how to reverse engineer and replace (or remove) those
|
||||
blobs that do still exist, in such a way where the system is still
|
||||
usable in some defined way.
|
||||
If it's supported by coreboot, you can add it immediately.
|
||||
Read the [porting guide](/docs/maintain/porting.html) for how to port for a new board.
|
||||
If you are able to generate a working rom for your system, please read
|
||||
[lbmk maintenance manual](docs/maintain/) for how to add it to libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
For those systems where no coreboot support exists, you must first port
|
||||
it to coreboot and, if it can then run without any blobs in the ROM
|
||||
image, it can be added to libreboot. See: [Motherboard Porting
|
||||
Guide](http://www.coreboot.org/Motherboard_Porting_Guide) (this is just
|
||||
the tip of the iceberg!)
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that board development should be done upstream (in coreboot)
|
||||
and merged downstream (into libreboot). This is the correct way to do
|
||||
it, and it is how the libreboot project is coordinated so as to avoid
|
||||
too much forking of the coreboot source code.
|
||||
|
||||
What about ARM?
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot has support for some ARM based laptops, using the *Rockchip
|
||||
RK3288* SoC. Check the libreboot [hardware compatibility
|
||||
list](../docs/hardware/#supported_list), for more information.
|
||||
If coreboot lacks support for your hardware, you must add support for it.
|
||||
Please consult the coreboot project for guidance.
|
||||
|
||||
General questions
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
|
@ -698,13 +583,13 @@ other methods on AMD systems.
|
|||
How do I change the BIOS settings?
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot actually uses the [GRUB
|
||||
Most libreboot setups actually use the [GRUB
|
||||
payload](http://www.coreboot.org/GRUB2). More information about payloads
|
||||
can be found at
|
||||
[coreboot.org/Payloads](http://www.coreboot.org/Payloads). SeaBIOS is also
|
||||
available. The *CMOS* config is hardcoded in Libreboot.
|
||||
available. The *CMOS* config is hardcoded in libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot inherits the modular payload concept from coreboot, which
|
||||
The libreboot project inherits the modular payload concept from coreboot, which
|
||||
means that pre-OS bare-metal *BIOS setup* programs are not very
|
||||
practical. Coreboot (and libreboot) does include a utility called
|
||||
*nvramtool*, which can be used to change some settings. You can find
|
||||
|
|
@ -718,8 +603,8 @@ coreboot wiki for more information.
|
|||
In practise, you don't need to change any of those settings, in most
|
||||
cases.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot locks the CMOS table, to ensure consistent functionality for
|
||||
all users. You can use:
|
||||
Default libreboot setups lock the CMOS table, to ensure consistent functionality
|
||||
for all users. You can use:
|
||||
|
||||
nvramtool -C yourrom.rom -w somesetting=somevalue
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -735,10 +620,10 @@ How do I pad a ROM before flashing?
|
|||
|
||||
It is advisable to simply use a larger ROM image. This section was written
|
||||
mostly for ASUS KCMA-D8 and KGPE-D16 mainboards, where previously we only
|
||||
provided 2MiB ROM images in Libreboot, but we now provide 16MiB ROM images.
|
||||
provided 2MiB ROM images in libreboot, but we now provide 16MiB ROM images.
|
||||
Other sizes are not provided because in practise, someone upgrading one of
|
||||
these chips will just use a 16MiB one. Larger sizes are available, but 16MiB
|
||||
is the maximum that you can use on all currently supported Libreboot systems
|
||||
is the maximum that you can use on all currently supported libreboot systems
|
||||
that use SPI flash.
|
||||
|
||||
Required for ROMs where the ROM image is smaller than the flash chip
|
||||
|
|
@ -773,7 +658,7 @@ With padding removed cbfstool will be able to operate on the image as usual.
|
|||
Do I need to install a bootloader when installing a distribution?
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot integrates the GRUB bootloader already, as a
|
||||
Most libreboot setups integrate the GRUB bootloader already, as a
|
||||
*[payload](http://www.coreboot.org/Payloads)*. This means that the GRUB
|
||||
bootloader is actually *flashed*, as part of the boot firmware
|
||||
(libreboot). This means that you do not have to install a boot loader on
|
||||
|
|
@ -797,7 +682,7 @@ automatically switch to a GRUB configuration on the HDD or SSD, if it
|
|||
exists. You can also load a different GRUB configuration, from any kind
|
||||
of device that is supported in GRUB (such as a USB flash drive). For
|
||||
more information, see
|
||||
[Modifying the GRUB Configuration in Libreboot Systems](../docs/gnulinux/grub_cbfs.md)
|
||||
[Modifying the GRUB Configuration in libreboot Systems](../docs/gnulinux/grub_cbfs.md)
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using the SeaBIOS payload, it's even easier. It works just like you
|
||||
would expect. SeaBIOS implements a normal x86 BIOS interface.
|
||||
|
|
@ -808,40 +693,12 @@ What does a flash chip look like?
|
|||
You can find photos of various chip types on the following page:\
|
||||
[External 25xx NOR flashing guide](docs/install/spi.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Who did the logo?
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See the [license information](https://av.libreboot.org/logo/license.md).
|
||||
|
||||
The Libreboot logo is available as a [bitmap](https://av.libreboot.org/logo/logo.png), a
|
||||
[vector](https://av.libreboot.org/logo/logo.svg), or a [greyscale vector](https://av.libreboot.org/logo/logo_grey.svg).
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot Inside stickers are available as a
|
||||
[PDF](https://av.libreboot.org/logo/stickers/libreboot-inside-simple-bold-1.60cmx2.00cm-diecut-3.pdf) or
|
||||
a
|
||||
[vector](https://av.libreboot.org/logo/stickers/libreboot-inside-simple-bold-1.60cmx2.00cm-diecut-3.svg)
|
||||
|
||||
You can find all of the available logos by browsing this directory:\
|
||||
<https://av.libreboot.org/logo/>
|
||||
|
||||
What other firmware exists outside of libreboot?
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
The main freedom issue on any system, is the boot firmware (usually
|
||||
referred to as a BIOS or UEFI). Libreboot replaces the boot firmware
|
||||
with fully free code, but even with libreboot, there may still be other
|
||||
hardware components in the system (e.g. laptop) that run their own
|
||||
dedicated firmware, sometimes proprietary. These are on secondary
|
||||
processors, where the firmware is usually read-only, written for very
|
||||
specific tasks. While these are unrelated to libreboot, technically
|
||||
speaking, it makes sense to document some of the issues here.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that these issues are not unique to libreboot systems. They apply
|
||||
universally, to most systems. The issues described below are the most
|
||||
common (or otherwise critical).
|
||||
|
||||
Dealing with these problems will most likely be handled by a separate
|
||||
project.
|
||||
You can also read information about these in the [libreboot binary blob
|
||||
reduction policy](docs/policy.md), where it goes into more detail about some
|
||||
of them.
|
||||
|
||||
### External GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -853,19 +710,12 @@ only difference is that SeaBIOS can execute it (alternatively, you embed it
|
|||
in a coreboot ROM image and have coreboot executes it, if you use a
|
||||
different payload, such as GRUB).
|
||||
|
||||
On current libreboot systems, instead of VBIOS, coreboot native GPU init is used,
|
||||
which is currently only implemented for Intel GPUs.
|
||||
Other cards with proper KMS drivers can be initialized once Linux boots,
|
||||
but copy of VBIOS may be still needed to fetch proper VRAM frequency
|
||||
and other similar parameters (without executing VBIOS code).
|
||||
The *coreboot project* provides free initialization code, on many boards, and
|
||||
libreboot will use this code when it is available, depending on the configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
In configurations where SeaBIOS and native GPU init are used together,
|
||||
a special shim VBIOS is added that uses coreboot linear framebuffer.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: on desktop/server mainboards, coreboot is configured to load the option
|
||||
ROM from an add-on GPU if present. This is the default behaviour on such systems
|
||||
in Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
### EC (embedded controller) firmware
|
||||
|
||||
Most (all?) laptops have this. The EC (embedded controller) is a small,
|
||||
|
|
@ -982,9 +832,9 @@ Other links:
|
|||
|
||||
It is recommended that you use full disk encryption, on HDDs connected
|
||||
via USB. There are several adapters available online, that allow you to
|
||||
connect SATA HDDs via USB. Libreboot documents how to install several
|
||||
distributions with full disk encryption. You can adapt these for use
|
||||
with USB drives:
|
||||
connect SATA HDDs via USB. The libreboot documentation says how to install
|
||||
several distributions with full disk encryption. You can adapt these for
|
||||
use with USB drives:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Full disk encryption with Debian](../docs/gnulinux/encrypted_debian.md)
|
||||
- [Full disk encryption with Parabola](../docs/gnulinux/encrypted_parabola.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1009,20 +859,12 @@ issues. A USB NIC can also be used, which does not have DMA.
|
|||
|
||||
### CPU microcode
|
||||
|
||||
Implements an instruction set. See
|
||||
description. Here we mean microcode built in to the CPU. We are not
|
||||
talking about the updates supplied by the boot firmware (libreboot does
|
||||
not include microcode updates, and only supports systems that will work
|
||||
without it) Microcode can be very powerful. No proof that it's
|
||||
malicious, but it could theoretically
|
||||
Microcode configures logic gate arrays in a microprocessor, to implement the
|
||||
instruction set architecture. Special *decoders* in the microprocessor will
|
||||
configure the circuitry, based on that microcode.
|
||||
|
||||
There isn't really a way to solve this, unless you use a CPU which does
|
||||
not have microcode. (ARM CPUs don't, but most ARM systems require blobs
|
||||
for the graphics hardware at present, and typically have other things
|
||||
like soldered wifi which might require blobs)
|
||||
|
||||
CPUs often on modern systems have a processor inside it for things like
|
||||
power management. ARM for example, has lots of these.
|
||||
The [libreboot blob reduction policy](news/policy.md) goes into great detail
|
||||
about microcode.
|
||||
|
||||
### Sound card
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1035,22 +877,13 @@ workaround.
|
|||
Webcams have firmware integrated into them that process the image input
|
||||
into the camera; adjusting focus, white balancing and so on. Can use USB
|
||||
webcam hardware, to work around potential DMA issues; integrated webcams
|
||||
(on laptops, for instance) are discouraged by the libreboot project.
|
||||
(on laptops, for instance) are discouraged by the libreboot project, for
|
||||
security reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
### USB host controller
|
||||
|
||||
Doesn't really apply to current libreboot systems (none of them have
|
||||
USB 3.0 at the moment), but USB 3.0 host controllers typically rely on
|
||||
firmware to implement the XHCI specification. Some newer coreboot ports
|
||||
also require this blob, if you want to use USB 3.0.
|
||||
|
||||
This doesn't affect libreboot at the moment, because all current
|
||||
systems that are supported only have older versions of USB available.
|
||||
USB devices also don't have DMA (but the USB host controller itself
|
||||
does).
|
||||
|
||||
With proper IOMMU, it might be possible to mitigate the DMA-related
|
||||
issues (with the host controller).
|
||||
USB host controllers require firmware. Sometimes, this has to be supplied
|
||||
by coreboot itself.
|
||||
|
||||
### WWAN firmware
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1078,11 +911,6 @@ disabling any external entities from tracking your location.
|
|||
Use of ethernet or wifi is recommended, as opposed to mobile networks,
|
||||
as these are generally much safer.
|
||||
|
||||
On all current libreboot laptops, it is possible to remove the WWAN card
|
||||
and sim card if it exists. The WWAN card is next to the wifi card, and
|
||||
the sim card (if installed) will be in a slot underneath the battery, or
|
||||
next to the RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
Operating Systems
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1106,8 +934,8 @@ Refer to [the GNU+Linux page](docs/gnulinux/).
|
|||
Can I use BSD?
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Absolutely! Libreboot has native support for NetBSD, OpenBSD and LibertyBSD.
|
||||
Other distros are untested.
|
||||
Absolutely! The libreboot firmware has native support for NetBSD, OpenBSD and
|
||||
LibertyBSD. Other distros are untested.
|
||||
|
||||
See:
|
||||
[docs/bsd/](docs/bsd/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1117,10 +945,15 @@ Are other operating systems compatible?
|
|||
|
||||
Unknown. Probably not.
|
||||
|
||||
Does libreboot make my machine 100% free?
|
||||
==========================================
|
||||
What level of software freedom does libreboot give me?
|
||||
===================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot on all devices only provides host hardware init firmware images,
|
||||
TODO: Re-write this section. It has been adapted, poorly, from the Libreboot
|
||||
FAQ section.
|
||||
|
||||
Please read the [libreboot binary blob minimization policy](docs/policy.md).
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot firmware provides host hardware init firmware images,
|
||||
that can be written 25XX SPI NOR Flash. But on many systems there are
|
||||
a lot more computers running blob firmware.
|
||||
Some of them are not practicable to replace due to being located on Mask ROM.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
64
site/git.md
64
site/git.md
|
|
@ -3,37 +3,41 @@ title: Code review
|
|||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot repositories
|
||||
======================
|
||||
libreboot repositories
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
Information about who works on Libreboot and who runs the project can be
|
||||
Information about who works on libreboot and who runs the project can be
|
||||
found on [who.md](who.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot has 5 Git repositories:
|
||||
The `libreboot` project has 3 main Git repositories:
|
||||
|
||||
* Build system: <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk>
|
||||
* Website (+docs): <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww>
|
||||
* Images (for website): <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww-img>
|
||||
* Website (+docs): <https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww>
|
||||
* Images (for website): <https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww-img>
|
||||
|
||||
There is also these programs, hosted by the Libreboot project, and libreboot
|
||||
either recommends them or makes use of them:
|
||||
|
||||
* Bucts (utility): <https://notabug.org/libreboot/bucts>
|
||||
* ich9utils (utility): <https://notabug.org/libreboot/ich9utils>
|
||||
|
||||
You can download any of these repositories, make whatever changes you like, and
|
||||
then submit your changes using the instructions below.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you build Libreboot (all parts of it) in a GNU+Linux
|
||||
It is recommended that you build libreboot (all parts of it) in a GNU+Linux
|
||||
distribution. For example, the build system (lbmk) is untested on BSD systems.
|
||||
Install `git` in your GNU+Linux system, and download one of the repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot development is done using the Git version control system.
|
||||
Development of libreboot is done using the Git version control system.
|
||||
Refer to the [official Git documentation](https://git-scm.com/doc) if you don't
|
||||
know how to use Git.
|
||||
|
||||
The `bucts` repository is hosted by the Libreboot project, because the original
|
||||
The `bucts` repository is hosted by the libreboot project, because the original
|
||||
repository on `stuge.se` is no longer available, last time we checked. The
|
||||
`bucts` program was written by Peter Stuge. You need `bucts` if you're flashing
|
||||
internally a Libreboot ROM onto a ThinkPad X60 or T60 that is currently running
|
||||
internally an libreboot ROM onto a ThinkPad X60 or T60 that is currently running
|
||||
the non-free Lenovo BIOS. Instructions for that are available here:\
|
||||
[Libreboot installation guides](docs/install/)
|
||||
[libreboot installation guides](docs/install/)
|
||||
|
||||
The `ich9utils` repository is used heavily, by the `lbmk` build system. However,
|
||||
you can also download `ich9utils` on its own and use it. It generates ICH9M
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,12 +49,12 @@ Documentation for `ich9utils` is available here:\
|
|||
lbmk (libreboot-make)
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This is the core build system in Libreboot. You could say that `lbmk` *is*
|
||||
Libreboot! Download the Git repository:
|
||||
This is the core build system in libreboot. You could say that `lbmk` *is*
|
||||
libreboot! Download the Git repository:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk
|
||||
|
||||
The `git` command, seen above, will download the Libreboot build system `lbmk`.
|
||||
The `git` command, seen above, will download the libreboot build system `lbmk`.
|
||||
You can then go into it like so:
|
||||
|
||||
cd lbmk
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,36 +65,36 @@ build `lbmk`, refer to the [build instructions](docs/build/).
|
|||
Information about the build system itself, and how it works, is available in
|
||||
the [lbmk maintenance guide](docs/maintain/).
|
||||
|
||||
lbwww and lbwww-img
|
||||
osbwww and osbwww-img
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The *entire* Libreboot website and documentation is hosted in a Git repository.
|
||||
The *entire* libreboot website and documentation is hosted in a Git repository.
|
||||
Download it like so:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww
|
||||
|
||||
Images are hosted on <https://av.libreboot.org/> and available in a separate
|
||||
repository:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww-img
|
||||
git clone https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww-img
|
||||
|
||||
Make whatever changes you like. See notes below about how to send patches.
|
||||
|
||||
The entire website is written in Markdown, specifically the Pandoc version of
|
||||
it. The static HTML pages are generated with [Untitled](https://untitled.vimuser.org/).
|
||||
Leah Rowe, the founder of Libreboot, is also the founder of the Untitled static
|
||||
Leah Rowe, the founder of libreboot, is also the founder of the Untitled static
|
||||
site generator project.
|
||||
|
||||
If you like, you can set up a local HTTP server and build your own local
|
||||
version of the website. Please note that images will still link to the ones
|
||||
hosted on <https://av.libreboot.org/>, so any images that you add to `lbwww-img`
|
||||
hosted on <https://av.libreboot.org/>, so any images that you add to `osbwww-img`
|
||||
will not show up on your local `lbwww` site if you make the image links (for
|
||||
images that you add) link to av.libreboot.org. However, it is required that such
|
||||
images that you add) link to `av.libreboot.org`. However, it is required that such
|
||||
images be hosted on av.libreboot.org.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, if you wish to add images to the website, please also submit to the
|
||||
`lbwww-img` repository, with the links to them being
|
||||
<https://av.libreboot.org/path/to/your/new/image/in/lbwww-img> for each one.
|
||||
<https://av.libreboot.org/path/to/your/new/image/in/osbwww-img> for each one.
|
||||
When it is merged on the libreboot website, your images will appear live.
|
||||
|
||||
For development purposes, you might make your images local links first, and
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +115,7 @@ everyone can access. This includes the name and email address of the
|
|||
contributor.
|
||||
|
||||
In Git, for author name and email address, you do not have to use identifying
|
||||
data. You can use Libreboot Contributor and your email address could be
|
||||
data. You can use `libreboot Contributor` and your email address could be
|
||||
specified as contributor@libreboot.org. You are permitted to do this, if
|
||||
you wish to maintain privacy. We believe in privacy. If you choose to remain
|
||||
anonymous, we will honour this.
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,29 +146,29 @@ We require all patches to be submitted under a free license:
|
|||
the default, restrictive copyright laws apply, which would make your work
|
||||
non-free.
|
||||
|
||||
GNU+Linux is generally recommended as the OS of choice, for Libreboot
|
||||
development. However, BSD operating systems also boot on Libreboot machines.
|
||||
GNU+Linux is generally recommended as the OS of choice, for libreboot
|
||||
development. However, BSD operating systems also boot on libreboot machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Send patches
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
Make an account on <https://notabug.org/> and navigate (while logged in) to the
|
||||
repository that you wish to work on. Click *Fork* and in your account,
|
||||
you will have your own repository of Libreboot. Clone your repository, make
|
||||
you will have your own repository of libreboot. Clone your repository, make
|
||||
whatever changes you like to it and then push to your repository, in your
|
||||
account on NotABug. You can also do this on a new branch, if you wish.
|
||||
|
||||
In your Notabug account, you can then navigate to the official Libreboot
|
||||
In your Notabug account, you can then navigate to the official libreboot
|
||||
repository and submit a Pull Request. The way it works is similar to other
|
||||
popular web-based Git platforms that people use these days.
|
||||
|
||||
You can submit your patches there. Alternative, you can log onto the Libreboot
|
||||
You can submit your patches there. Alternative, you can log onto the libreboot
|
||||
IRC channel and notify the channel of which patches you want reviewed, if you
|
||||
have your own Git repository with the patches.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have issued a Pull Request, the Libreboot maintainers will be notified
|
||||
Once you have issued a Pull Request, the libreboot maintainers will be notified
|
||||
via email. If you do not receive a fast enough response from the project, then
|
||||
you could also notify the project via the #libreboot channel on Libera Chat.
|
||||
you could also notify the project via the `#libreboot` channel on Libera Chat.
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to submit patches is to email Leah Rowe directly:
|
||||
[leah@libreboot.org](mailto:leah@libreboot.org) is Leah's project email address.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Libreboot project
|
||||
title: libreboot project
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is
|
||||
The `libreboot` project provides
|
||||
[freedom-respecting](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) *boot
|
||||
firmware* that initializes the hardware (e.g. memory controller, CPU,
|
||||
peripherals) on [specific Intel/AMD x86 computers](docs/hardware/) and starts
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,11 +13,8 @@ firmware. Help is available
|
|||
via [\#libreboot](https://web.libera.chat/#libreboot)
|
||||
on [Libera](https://libera.chat/) IRC.
|
||||
|
||||
The latest version is [Libreboot 20220710](news/libreboot20220710.md), released
|
||||
on 10 July 2022.
|
||||
|
||||
Why use Libreboot?
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
Why should you use *libreboot*?
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
You have rights. The right to privacy, freedom of thought, freedom of speech
|
||||
and the right to read. [Free
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,48 +24,40 @@ Your freedom matters.
|
|||
Many people use [proprietary](https://www.gnu.org/proprietary/proprietary.html)
|
||||
boot firmware, even if they use [GNU+Linux](https://www.gnu.org/distros/).
|
||||
Non-free firmware often [contains](faq.html#intel) [backdoors](faq.html#amd),
|
||||
and can be buggy. Libreboot was founded in in December 2013, with the express
|
||||
purpose of making Free Software accessible for non-technical users at the
|
||||
firmware level. Libreboot can be called Open Source, [but you should call it
|
||||
Free
|
||||
and can be buggy. The libreboot project was founded in in December 2020, with the
|
||||
express purpose of making Free Software accessible for non-technical users at
|
||||
the firmware level. It's true that `libreboot` can be called Open Source, [but you
|
||||
should call it Free
|
||||
Software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/open-source-misses-the-point.en.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot uses [coreboot](https://www.coreboot.org/) for [hardware
|
||||
The `libreboot` project uses [coreboot](https://www.coreboot.org/) for [hardware
|
||||
initialization](https://doc.coreboot.org/getting_started/architecture.html).
|
||||
Coreboot is notoriously difficult to install for most non-technical users; it
|
||||
handles only basic initialization and jumps to a separate
|
||||
[payload](https://doc.coreboot.org/payloads.html) program (e.g.
|
||||
[GRUB](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/),
|
||||
[Tianocore](https://www.tianocore.org/)), which must also be configured.
|
||||
*Libreboot solves this problem*; it is a *coreboot distribution* with
|
||||
*The libreboot software solves this problem*; it is a *coreboot distribution* with
|
||||
an [automated build system](docs/build/) that builds complete *ROM images*, for
|
||||
more robust installation. Documentation is provided.
|
||||
|
||||
**Libreboot excludes binary blobs, shipping only Free Software and, as such,
|
||||
only supports a handful of machines from coreboot. You can read Libreboot's
|
||||
zero-blobs policy on the [Libreboot blob policy page](news/policy.md).**
|
||||
How does libreboot differ from regular coreboot?
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
How does Libreboot differ from regular coreboot?
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Contrary to popular opinion, Libreboot's primary purpose is not to provide a
|
||||
de-blobbed coreboot setup; it is merely one of Libreboot's policies, and an
|
||||
important one, but it is nonetheless a minor aspect of Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
In the same way that Trisquel is a GNU+Linux distribution, Libreboot is
|
||||
In the same way that *Debian* is a GNU+Linux distribution, `libreboot` is
|
||||
a *coreboot distribution*. If you want to build a ROM image from scratch, you
|
||||
otherwise have to perform expert-level configuration of coreboot, GRUB and
|
||||
whatever other software you need, to prepare the ROM image. With *Libreboot*,
|
||||
whatever other software you need, to prepare the ROM image. With *libreboot*,
|
||||
you can literally download from Git or a source archive, and run `make`, and it
|
||||
will build entire ROM images. Libreboot's automated build system, named `lbmk`
|
||||
will build entire ROM images. An automated build system, named `lbmk`
|
||||
(Libreboot MaKe), builds these ROM images automatically, without any user input
|
||||
or intervention required. Configuration has already been performed in advance.
|
||||
|
||||
If you were to build regular coreboot, without using Libreboot's automated
|
||||
If you were to build regular coreboot, without using libreboot's automated
|
||||
build system, it would require a lot more intervention and decent technical
|
||||
knowledge to produce a working configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
Regular binary releases of Libreboot provide these
|
||||
Regular binary releases of `libreboot` provide these
|
||||
ROM images pre-compiled, and you can simply install them, with no special
|
||||
knowledge or skill except the ability to
|
||||
follow [simplified instructions, written for non-technical
|
||||
|
|
@ -76,13 +66,13 @@ users](docs/install/).
|
|||
How to help
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
Check the [tasks](tasks/) page and pick a task to work on. You can also check
|
||||
bugs listed on the [bug tracker](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk/issues).
|
||||
You can check bugs listed on
|
||||
the [bug tracker](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
If you spot a bug and have a fix, [here are instructions for how to send
|
||||
patches](git.md), and you can also report it. Also, this entire website is
|
||||
written in Markdown and hosted in a [separate
|
||||
repository](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww) where you can send patches.
|
||||
repository](https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww) where you can send patches.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot development discussion and user support are all done on the IRC
|
||||
Any and all development discussion and user support are all done on the IRC
|
||||
channel. More information is on the [contact page](contact.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
138
site/index.uk.md
138
site/index.uk.md
|
|
@ -1,81 +1,113 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Звільни свій BIOS сьогодні!
|
||||
title: проект libreboot
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot це
|
||||
[поважаюча свободу](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) *прошивка*,
|
||||
яка виконує ініціалізацію апаратного забезпечення (такого як - контролер памяті, центральний процесор,
|
||||
переферія) на [деяких комп'ютерах Intel/AMD x86](docs/hardware/) та розпочинає завантажувач
|
||||
для вашої операційної системи. [GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/)
|
||||
та [BSD](docs/bsd/) добре підтримуються. Замінює пропрієтарну прошивку BIOS/UEFI. Допомога доступна
|
||||
Проект `libreboot` надає
|
||||
[поважаючу свободу](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) *прошивку*,
|
||||
яка виконує ініціалізацію апаратного забезпечення (такого як - контролер пам'яті, ЦП,
|
||||
периферія) на [деяких комп'ютерах Intel/AMD x86](docs/hardware/) та розпочинає
|
||||
завантажувач для вашої операційної системи. [GNU+Linux](docs/gnulinux/)
|
||||
та [BSD](docs/bsd/) добре підтримуються. Це заміняє невільну BIOS/UEFI
|
||||
прошивку. Допомога доступна
|
||||
через [\#libreboot](https://web.libera.chat/#libreboot)
|
||||
на [Libera](https://libera.chat/) IRC.
|
||||
на IRC [Libera](https://libera.chat/).
|
||||
|
||||
Остання версія [Libreboot 20220710](news/libreboot20220710.md), була випущена
|
||||
10 липень 2022 року.
|
||||
Чому вам варто використовувати *libreboot*?
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Приєднуйтесь до нас зараз і прошивайте прошивку!
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
У вас є права. Право на конфіденційність, свобода думки, свобода мови
|
||||
У вас є права. Право на конфіденційність, свобода думки, свобода мови,
|
||||
а також право читати. [Вільне
|
||||
програмне забезпечення](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.uk.html) дає вам ці права.
|
||||
програмне забезпечення](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.uk.html) надає вам ці права.
|
||||
Ваша свобода має значення.
|
||||
[Право на ремонт](https://vid.puffyan.us/watch?v=Npd_xDuNi9k) має значення.
|
||||
Багато людей використовує [пропрієтарну](https://www.gnu.org/proprietary/proprietary.html)
|
||||
Багато людей використовує [невільну](https://www.gnu.org/proprietary/proprietary.html)
|
||||
прошивку, навіть якщо вони використовують [GNU+Linux](https://www.gnu.org/distros/).
|
||||
Невільна прошивка часто [містить](faq.html#intel) [лазівки](faq.html#amd),
|
||||
та може бути забагованою. Libreboot був заснований в грудні 2013 року, з
|
||||
метою зробити вільне програмне забезпечення на рівні прошивки доступним для нетехнічних користувачів. Можна сказати, що Libreboot з відкритим вихідним кодом, [але вам варто називати його
|
||||
вільне програмне
|
||||
забезпечення](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/open-source-misses-the-point.uk.html).
|
||||
та може бути забагованою. Проект libreboot був заснований в грудні 2020 року, з
|
||||
чіткою метою зробити вільне програмне забезпечення доступним для нетехнічних користувачів на
|
||||
рівні прошивки. Це правда, що `libreboot` можна назвати з відкритим джерельним кодом, [але вам
|
||||
варто називати його вільне
|
||||
програмне забезпечення](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/open-source-misses-the-point.uk.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot використовує [coreboot](https://www.coreboot.org/) для [апаратної
|
||||
Проект `libreboot` використовує [coreboot](https://www.coreboot.org/) для [апаратної
|
||||
ініціалізації](https://doc.coreboot.org/getting_started/architecture.html).
|
||||
Coreboot неординарно складно встановити для більшості нетехнічних користувачів; він
|
||||
виконує лише базову ініціалізацію та перестрибує до окремої програми
|
||||
[корисного навантаження](https://doc.coreboot.org/payloads.html) (таких як -
|
||||
[корисного навантаження](https://doc.coreboot.org/payloads.html) (такої як -
|
||||
[GRUB](https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/),
|
||||
[Tianocore](https://www.tianocore.org/)), які також потрібно налаштовувати.
|
||||
*Libreboot вирішує цю проблему*; це *дистрибутив coreboot* з
|
||||
[автоматизованою системою побудови](docs/build/), який створює *ROM образи*, для більш
|
||||
міцної установки. Документація надається.
|
||||
[Tianocore](https://www.tianocore.org/)), які також потрібно налаштувати.
|
||||
*Програмне забезпечення libreboot вирішує цю проблему*; це *дистрибутив coreboot* з
|
||||
[автоматизованою системою побудови](docs/build/), який створює *ROM образи*, для
|
||||
більш міцної установки. Документація надається.
|
||||
|
||||
**Libreboot виключає бінарні блоби, доставляючи тільки вільне програмне забезпечення і,
|
||||
власним станом, підтримує тільки невелику кількість пристроїв з coreboot. Ви можете ознайомитись з політикою відсутності двійкових блобів Libreboot [Сторінка політики блобів в Libreboot](news/policy.md).**
|
||||
Чим відрізняється libreboot від звичайного coreboot?
|
||||
---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Чим Libreboot відрізняється від звичайного coreboot?
|
||||
------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Таким же самим чином, як *Debian* є дистрибутивом GNU+Linux, `libreboot` є
|
||||
*дистрибутивом coreboot*. Якщо ви хочете створити образ ROM з нуля, вам в
|
||||
інакшому випадку доведеться виконати експертну конфігурацію coreboot, GRUB та
|
||||
будь-якого іншого програмного забезпечення, яке вам потрібно, щоб підготувати образ ROM. З *libreboot*,
|
||||
ви можете завантажити з Git або архіву вихідного коду, та запустити `make`, і таким чином
|
||||
будуть побудовані всі образи ROM. Автоматизована система побудови libreboot, названа `lbmk`
|
||||
(OSBoot MaKe), будує ці ROM образи автоматично, без будь-якого введення
|
||||
або втручання користувача. Конфігурація вже була виконана заздалегідь.
|
||||
|
||||
Всупереч поширеній думці, первинна мета Libreboot не полягає в тому, щоб забезпечити налаштування
|
||||
вичищеного від двійкових блобів coreboot; це просто одна з політик Libreboot, і
|
||||
вона важлива, але це не зовсім значний аспект Libreboot.
|
||||
Якщо складати звичайний coreboot, без використання автоматизованої
|
||||
системи побудови libreboot, це потребувало би набагато більше інтервенцій та пристойних технічних
|
||||
знань для створення працюючої конфігурації.
|
||||
|
||||
Таким самим чином, як Trisquel є дистрибутивом GNU+Linux, Libreboot є *дистрибутивом coreboot*. Якщо ви хочете створити образ ROM від нуля, вам
|
||||
в інакшому випадку треба виконати експертну конфігурацію coreboot, GRUB та
|
||||
будь-якого іншого програмного забезпечення, яке вам потрібно, щоб підготувати образ ROM.
|
||||
З *Libreboot* ви можете буквально завантажити з Git або архіву вихідного коду, та запустити `make`, і
|
||||
таким чином будуть побудовані всі образи ROM. Автоматична система побудови Libreboot, названа `lbmk`
|
||||
(Libreboot MaKe), будує ці образи ROM автоматично, без будь-якого введення або втручання користувача. Конфігурація вже була виконана заздалегідь.
|
||||
Регулярні двійкові випуски `libreboot` надають ці
|
||||
образи ROM попередньо зібраними, і ви можете просто встановити їх, не маючи спеціальних
|
||||
знань або навичок, крім можливості
|
||||
дотримуватися [спрощених інструкцій, написаних для нетехнічних користувачів](docs/install/).
|
||||
|
||||
Якщо складати звичайний coreboot, без використання автоматизованої системи побудови Libreboot, це потребувало би набагато більше інтервенцій та пристойних технічних знань
|
||||
для створення робочої конфігурації.
|
||||
Чим libreboot відрізняється від *Libreboot*?
|
||||
----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Регулярні бінарні релізи Libreboot надають
|
||||
ці ROM образи попередньо зібраними, і ви можете просто встановити їх, не маючи
|
||||
спеціальних знань або навичок, крім можливості
|
||||
дотримуватися [спрощених інструкцій, написаних для нетехнічних
|
||||
користувачів](docs/install/).
|
||||
Libreboot та libreboot обидва розроблюються паралельно. Обидва проекта були засновані
|
||||
Лією Роу, яка керує обома проектами.
|
||||
|
||||
**Проект libreboot є відгалудженням від Libreboot, але він позбавився від [Політики відсутності
|
||||
двійкових компонентів Libreboot](news/policy.md). Він іде з оновленням мікрокоду ЦП, увімкненим за
|
||||
замовченням, навіть на libreboot-сумісному обладнанні (на libreboot-сумісному
|
||||
обладнанні, це є єдиною різницею). Система побудови libreboot автоматично
|
||||
завантажує повний набір `3rdparty` підмодулей з coreboot. Програмне забезпечення coreboot
|
||||
номінально вільне, але потребує деяких двійкових компонентів на окремих
|
||||
машинах, які додаються в підмодулях `3rdparty`.**
|
||||
|
||||
[Оновлення мікрокодів ЦП не завдає шкоди вашій свободі, тому що ЦП вже має
|
||||
старіший, з більшою кількістю помилок мікрокод у вбудованій ROM. Вам варто вибирати libreboot, не
|
||||
Libreboot, навіть на Libreboot-сумісному обладнанні, тому що оновлення мікрокоду
|
||||
підвищує стабільність та надійність системи.](news/policy.md) Випливає з цього принципу те, що
|
||||
`libreboot` буде завжди включати оновлення мікрокоду. Libreboot нижчьої якості за libreboot,
|
||||
з будь-якого погляду, але його будуть продовжувати розробляти та полірувати, пліч-о-пліч з
|
||||
розробкою libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Метою `libreboot` є надати настільки
|
||||
багато свободи, скільки можливо, для тих, хто бажає кинути свою в іншому разі
|
||||
повністю невільну прошивку. Система побудови `libreboot` не видаляє двійкові
|
||||
компоненти, як робить Libreboot, тому що вона *хоче* надати допомогу всім
|
||||
тим, хто бажає мати деякі свободи зі своїм обладнанням, навіть якщо це обладнання
|
||||
не підтримується Libreboot наразі. Підтримка Libreboot є досі дуже сильно
|
||||
бажаною, на всьому обладнанні, і працювати до цієї мети дуже заохочується!
|
||||
|
||||
Ви можете дізнатись більше, прочитавши надихнувшу libreboot [політику двійкових
|
||||
компонентів](news/policy.md), що різко контрастує з політикою Libreboot.
|
||||
Проект libreboot видаляє усі обмеження в своєму відгалудженні системи побудови Libreboot,
|
||||
дозволяючи підтримувати будь-яку плату з coreboot (метою є
|
||||
буквально підтримка їх всіх).
|
||||
|
||||
Як допомогти
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
Перевірити сторінку [завдань](tasks/) і підібрати завдання на роботу. Ви також можете
|
||||
перевірити помилки, перераховані на [трекері помилок](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk/issues).
|
||||
Ви можете перевірити баги, перелічені
|
||||
на [баг трекері](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
Якщо ви помітите помилку і маєте виправлення, [ось інструкції щодо того, як відправити патчі](git.md), також ви можете повідомити про це. Також, цей сайт написаний в
|
||||
Markdown і розміщений в [окремому
|
||||
репозиторію](https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww), де можна надсилати патчі.
|
||||
Якщо ви виявите помилку та маєте вирішення, [ось інструкції, як відправити
|
||||
виправлення](git.md), і ви можете також повідомити про це. Також, увесь цей веб-сайт
|
||||
написано Markdown та розміщено в [окремому
|
||||
репозиторії](https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww), де можна надсилати виправлення.
|
||||
|
||||
Обговорення розробки Libreboot та підтримка користувачів відбувається в IRC
|
||||
каналі. Більше інформації на [сторінці зворотнього зв'язку](contact.md).
|
||||
Будь-яке та усе обговорення розробки та підтримка користувачів виконується на каналі IRC.
|
||||
Більше інформації на [сторінці зворотнього зв'язку](contact.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,6 +11,15 @@ Foundation](https://www.fsf.org/), with no Invariant Sections, no Front Cover
|
|||
Texts and no Back Cover
|
||||
Texts.
|
||||
|
||||
The *logo* for libreboot is Copyright (C) 2022 Ioan Moldovan, released under an
|
||||
Expat license which you can find here:
|
||||
<https://av.libreboot.org/logo/COPYING>
|
||||
|
||||
The original logo files are here: <https://av.libreboot.org/logo/>
|
||||
|
||||
You can download the logo files from `osbwww-img.git`. See:
|
||||
<https://libreboot.org/git.html>
|
||||
|
||||
These pages are static HTML, generated from Markdown files, which you can find
|
||||
a link to at the bottom of each HTML page, for the corresponding Markdown file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Libreboot logo license
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
The Libreboot logo is copyright 2014 Marcus Moeller, and it was also created by
|
||||
that person. It is released under the terms of the Creative Commons Zero
|
||||
license, version 1.0.
|
||||
|
||||
The sticker files, based on that logo, are made by Patrick McDermott in 2015,
|
||||
released under the same license.
|
||||
|
||||
A copy of this license (CC-0 1.0) can be found at:
|
||||
<https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/legalcode>
|
||||
|
||||
The font on the sticker designs is `lato`. Install this, otherwise the vectors
|
||||
won't look correct for the text.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see the logo files here: <https://av.libreboot.org/logo/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,29 +1,2 @@
|
|||
libreboot20220710.md
|
||||
policy.md
|
||||
usa-libre.md
|
||||
translations.md
|
||||
libreboot20211122.md
|
||||
libreboot20210522.md
|
||||
libreboot20160907.md
|
||||
libreboot20160902.md
|
||||
libreboot20160818.md
|
||||
libreboot20150518.md
|
||||
libreboot20150208.md
|
||||
libreboot20150126.md
|
||||
libreboot20150124.md
|
||||
libreboot20141015.md
|
||||
libreboot20140911.md
|
||||
libreboot20140903.md
|
||||
libreboot20140811.md
|
||||
libreboot20140729.md
|
||||
libreboot20140720.md
|
||||
libreboot20140716.md
|
||||
libreboot20140711.md
|
||||
libreboot20140622.md
|
||||
libreboot20140611.md
|
||||
libreboot20140605.md
|
||||
libreboot20140309.md
|
||||
libreboot20140221.md
|
||||
libreboot20131214.md
|
||||
libreboot20131213.md
|
||||
libreboot20131212.md
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20131212
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 12 December 2013
|
||||
|
||||
r20131212 (1st release) {#release20131212}
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
- 12th December 2013
|
||||
|
||||
Supported:
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60s
|
||||
|
||||
Development notes
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
- initial release
|
||||
- source code deblobbed
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20131213
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 13 December 2013
|
||||
|
||||
r20131213 (2nd release) {#release20131213}
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
- 13th December 2013
|
||||
|
||||
Supported:
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60s
|
||||
|
||||
Development notes
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
- added background image to GRUB2
|
||||
- added memtest86+ payload to grub2
|
||||
- improvements to the documentation
|
||||
- new grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20131214 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 14 December 2013
|
||||
|
||||
r20131214 (3rd release) {#release20131214}
|
||||
=======================
|
||||
|
||||
- 14th December 2013
|
||||
|
||||
Supported:
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60s
|
||||
|
||||
Development notes
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Added SeaBIOS payload to GRUB2 (for booting USB drives)
|
||||
- new grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140221 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 21 February 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Release 20140221 (4th release) {#release20140221}
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
- 21st February 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Officially supported
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60s
|
||||
|
||||
Development notes
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Removed SeaBIOS (redundant)
|
||||
- New GRUB version (2.02\~beta2)
|
||||
- Fixes some USB issues
|
||||
- Includes ISOLINUX/SYSLINUX parser
|
||||
- New grub.cfg
|
||||
- Removed useless options:
|
||||
- options for booting sda 2/3/4
|
||||
- seabios boot option
|
||||
- Added new menu entries:
|
||||
- Parse ISOLINUX config (USB)
|
||||
- Parse ISOLINUX config (CD)
|
||||
- Added 'cat' module for use on GRUB command line.
|
||||
- "set pager=1" is set in grub.cfg, for less-like functionality
|
||||
|
||||
The "Parse" options read ./isolinux/isolinux.cfg on a CD or USB, and
|
||||
automatically converts it to a grub config and switches to the boot menu
|
||||
of that distro. This makes booting ISOs \*much\* easier than before.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140309 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 9 March 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revision notes (9th March 2014):
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- recreated coreboot config from scratch
|
||||
- GRUB loads even faster now (less than 2 seconds).
|
||||
- Total boot time reduced by further \~5 seconds.
|
||||
- Added crypto and cryptodisk modules to GRUB
|
||||
- cbfstool now included in the binary archives
|
||||
|
||||
Development notes
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Binary archive now have 2 images:
|
||||
- With serial output enabled and memtest86+ included (debug level
|
||||
8 in coreboot)
|
||||
- With serial output disabled and memtest86+ excluded (faster boot
|
||||
speeds) (debugging disabled)
|
||||
- Reduced impact on battery life:
|
||||
- 'processor.max\_cstate=2' instead of 'idle=halt' for booting
|
||||
default kernel
|
||||
- coreboot.rom (faster boot speeds, debugging disabled):
|
||||
- Disabled coreboot serial output (Console-> in "make
|
||||
menuconfig")
|
||||
- Set coreboot debug level to 0 instead of 8 (Console-> in
|
||||
"make menuconfig")
|
||||
- Changed GRUB timeout to 1 second instead of 2 (in grub.cfg
|
||||
- Removed background image in GRUB.
|
||||
- Removed memtest86+ payload (since it relies on serial output)
|
||||
- coreboot\_serial.rom (slower boot speeds, debugging enabled):
|
||||
- Boot time still reduced, but only by \~2 seconds
|
||||
- has the memtest86+ payload included in the ROM
|
||||
- has serial port enabled. How this is achieved (from
|
||||
X60\_source): Turn on debugging level to 8, and enable serial
|
||||
output
|
||||
- (in Console-> in coreboot "make menuconfig")
|
||||
- (and build with grub\_serial.cfg and grub\_memdisk\_serial.cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140605 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 5 June 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revision notes (5th June 2014):
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- added backlight support (Fn+Home and Fn+End) on X60
|
||||
- fixed broken/unstable 3D when using kernel 3.12 or higher
|
||||
- (see 'BACKPORT' file)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140611 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 11 June 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revision notes (11th June 2014):
|
||||
--------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- removed 'CD' boot option from coreboot.rom (not needed)
|
||||
- removed 'processor.max\_cstate=2' and 'idle=halt' options (see
|
||||
README.powertop file)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140622 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 22 June 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Release 20140622 (5th release)
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
- 7th March 2014
|
||||
- revised 22nd June 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Officially supported
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60
|
||||
- ThinkPad X60s
|
||||
|
||||
Revision (22nd June 2014 - extra)
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Documentation: added X60 Unbricking tutorial
|
||||
- Documentation: added info about enabling or disabling wifi
|
||||
- Documentation: added info about enabling or disabling trackpoint
|
||||
|
||||
Revision (22nd June 2014 - extra)
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Documentation: Improved the instructions for using flashrom
|
||||
- Documentation: Improved the instructions for using cbfstool (to
|
||||
change the default GRUB menu)
|
||||
- Documentation: Numerous small fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
Revision notes (22nd June 2014)
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- updated GRUB (git 4b8b9135f1676924a8458da528d264bbc7bbb301, 20th
|
||||
April 2014)
|
||||
- Made "DeJavu Sans Mono" the default font in GRUB (fixes border
|
||||
corruption).
|
||||
- re-added background image in GRUB (meditating GNU)
|
||||
- added 6 more images:
|
||||
- coreboot\_ukqwerty.rom (UK Qwerty keyboard layout in GRUB)
|
||||
- coreboot\_serial\_ukqwerty.rom (UK Qwerty keyboard layout in
|
||||
GRUB)
|
||||
- coreboot\_dvorak.rom (US Dvorak keyboard layout in GRUB)
|
||||
- coreboot\_serial\_dvorak.rom (US Dvorak keyboard layout in GRUB)
|
||||
- coreboot\_ukdvorak.rom (UK Dvorak keyboard layout in GRUB)
|
||||
- coreboot\_serial\_ukdvorak.rom (UK Dvorak keyboard layout in
|
||||
GRUB)
|
||||
- (coreboot.rom and coreboot\_serial.rom have US Qwerty keyboard
|
||||
layout in GRUB, as usual)
|
||||
- improved the documentation:
|
||||
- removed FLASH\_INSTRUCTION and README.powertop and merged them
|
||||
with README
|
||||
- removed obsolete info from README and tidied it up
|
||||
- deleted README (replaced with docs/)
|
||||
- tidied up the menu entries in GRUB
|
||||
- tidied up the root directory of X60\_source/, sorted more files into
|
||||
subdirectories
|
||||
- improved the commenting inside the 'build' script (should make
|
||||
modifying it easier)
|
||||
- Renamed X60\_binary.tar.gz and X60\_source.tar.gz to
|
||||
libreboot\_bin.tar.gz and libreboot\_src.tar.gz, respectively.
|
||||
- Replaced "GNU GRUB version" with "FREE AS IN FREEDOM" on GNU
|
||||
GRUB start screen.
|
||||
- Added sha512.txt files in libreboot\_src and libreboot\_bin. (inside
|
||||
the archives)
|
||||
- Added libreboot\_bin.tar.gz.sha512.txt and
|
||||
libreboot\_src.tar.gz.sha512.txt files (outside of the archives)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,229 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140711 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 11 July 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140711 (1st beta) (11th July 2014)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Initial release (new coreboot base, dated 1st June 2014. See
|
||||
'getcb' script for reference)
|
||||
- DEBLOBBED coreboot
|
||||
- Removed the part from memtest86+ 'make' where it tried to connect
|
||||
to some scp server while compiling. (commented out line 24 in the
|
||||
Makefile)
|
||||
- X60 now uses a single .config (for coreboot)
|
||||
- X60 now uses a single grub.cfg (for grub memdisk)
|
||||
- X60 now uses a single grub.elf (payload)
|
||||
- Added new native graphics code for X60 (replaces the old 'replay'
|
||||
code) from Vladimir Serbinenko: 5320/9 from review.coreboot.org
|
||||
- T60 is now supported, with native graphics. (5345/4 from
|
||||
review.coreboot.org, cherry-picked on top of 5320/9 checkout)
|
||||
- Added macbook2,1 support (from Mono Moosbart and Vladimir
|
||||
Serbinenko) from review.coreboot.org (see 'getcb' script to know
|
||||
how that was done)
|
||||
- Documentation: added information linking to correct page and
|
||||
talking about which models are supported.
|
||||
- Added resources/libreboot/config/macbook21config
|
||||
- macbook21: Added 'build-macbook21' script and linked to it in
|
||||
'build' (ROMs included under bin/macbook21/)
|
||||
- macbook21: Removed dd instructions from build-macbook21 script
|
||||
(macbook21 does not need bucts when flashing libreboot while
|
||||
Apple EFI firmware is running)
|
||||
- Documentation: Added macbook21 ROMs to the list of ROMs in
|
||||
docs/\#rom
|
||||
- Documentation: Write documentation linking to Mono Moosbart's
|
||||
macbook21 and parabola page (and include a copy)
|
||||
- Documentation: added a copy of Mono's Parabola install guide (for
|
||||
macbook21 with Apple EFI firmware) and linked in in main index.
|
||||
- Documentation: added a copy of Mono's Coreboot page (for macbook21)
|
||||
and linked it in main index.
|
||||
- T60: Copy CD option from the grub.cfg files for T60 \*serial\*.rom
|
||||
images into the grub configs for non-serial images. (T60 laptops have
|
||||
CD/DVD drive on main laptop)
|
||||
- macbook21: remove options in build-macbook21 for \*serial\*.rom
|
||||
(there is no dock or serial port available for macbook21)
|
||||
- Added patches for backlight controls on X60 and T60 with help from
|
||||
Denis Carikli (see ./resources/libreboot/patch/gitdiff and ./getcb
|
||||
and docs/i945\_backlight.md)
|
||||
- Documentation: added docs/i945\_backlight.html showing how
|
||||
backlight controls were made to work on X60/T60
|
||||
- Documentation: Added info about getting LCD panel name based on EDID
|
||||
data.
|
||||
- Documentation: Added a link to this from the list of supported
|
||||
T60 laptopss and LCD panels for T60 (so that the user can check
|
||||
what LCD panel they have).
|
||||
- X60/T60: Merged patches for 3D fix (from Paul Menzel) when using
|
||||
kernel 3.12 or higher (see ./resources/libreboot/patch/gitdiff and
|
||||
./getcb)
|
||||
- based on 5927/11 and 5932/5 from review.coreboot.org
|
||||
- Improved thinkpad\_acpi support (from coreboot ): xsensors shows
|
||||
more information.
|
||||
- From 4650/29 in review.coreboot.org (merged in coreboot
|
||||
'master' on June 1st 2014)
|
||||
- Merged changes for digitizer (X60 Tablet) and IR (X60 and T60) based
|
||||
on 5243/17, 5242/17 and 5239/19 from review.coreboot.org
|
||||
- (see ./resources/libreboot/patch/gitdiff and ./getcb)
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about building flashrom using
|
||||
'builddeps-flashrom' script.
|
||||
- Re-created resources/libreboot/config/x60config
|
||||
- Re-created resources/libreboot/config/t60config
|
||||
- Added 'x60tconfig' in resources/libreboot/config (because X60
|
||||
Tablet has different information about serial/model/version in
|
||||
'dmidecode')
|
||||
- Added 'build-x60t' script
|
||||
- Updated 'build' script to use 'build-x60t'
|
||||
- Documentation: added to \#config section the section
|
||||
\#config\_x60t (libreboot configuration and dmidecode info)
|
||||
- Documentation: added x60t ROMs to the list of ROMs
|
||||
- Tidied up the 'builddeps' script (easier to read)
|
||||
- Tidied up the 'cleandeps' script (easier to read)
|
||||
- Annotated the 'buildall' script
|
||||
- Added 'getcb' script for getting coreboot revision used from git,
|
||||
and patching it.
|
||||
- Added 'getgrub' script for getting the GRUB revision used from
|
||||
git, and patching it.
|
||||
- Added 'getmt86' script for getting the memtest86+ version used,
|
||||
and patching it.
|
||||
- Added 'getbucts' script for getting the bucts version used.
|
||||
- Added 'getflashrom' script for getting the flashrom version used,
|
||||
and patching it
|
||||
- Added 'getall' script which runs all of the other 'get' scripts.
|
||||
- Add instructions to the 'build' script to prepare
|
||||
libreboot\_meta.tar.gz
|
||||
- New archive: libreboot\_meta.tar.gz - minimal archive, using the
|
||||
'get' scripts to download all the dependencies (coreboot,
|
||||
memtest, grub and so on).
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about where 'build' script
|
||||
prepares the libreboot\_meta.tar.gz archive.
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about how to use the 'get'
|
||||
scripts in libreboot\_meta.tar.gz (to generate
|
||||
libreboot\_src.tar.gz)
|
||||
- Documentation: mention that meta doesn't create libreboot\_src/
|
||||
directory, but that libreboot\_meta itself becomes the same.
|
||||
- Documentation: advise to rename libreboot\_meta to
|
||||
libreboot\_src after running 'getall'.
|
||||
- Annotated the 'builddeb' script, to say what each set of
|
||||
dependencies are for.
|
||||
- Separated bucts/flashrom builddeb sections into separate scripts:
|
||||
builddeb-flashrom, builddeb-bucts.
|
||||
- Documentation: Updated relevant parts based on the above.
|
||||
- Added instructions to 'build' script for including builddeb-bucts
|
||||
and builddeb-flashrom in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Updated flashrom checkout (r1822 2014-06-16) from SVN
|
||||
(http://flashrom.org/Downloads).
|
||||
- Updated flashing instructions in docs/ for new commands needed
|
||||
(Macronix chip on X60/T60)
|
||||
- For X60/T60 (flashrom): Patched
|
||||
flashchips.c\_lenovobios\_macronix and
|
||||
flashchips.c\_lenovobios\_sst executables for SST/macronix
|
||||
(included in resources/flashrom/patch)
|
||||
- Updated builddeps to build flashrom\_lenovobios\_sst and
|
||||
flashrom\_lenovobios\_macronix, for X60/T60 users with Lenovo
|
||||
BIOS
|
||||
- moved the flashrom build instructions from 'builddeps' and put
|
||||
them in 'builddeps-flashrom', excecuting that from
|
||||
'builddeps'.
|
||||
- Added builddeps-flashrom to libreboot\_bin.tar.gz
|
||||
- flashrom: added patched flashchips.c to resources/flashrom/patch
|
||||
(automatically use correct macronix chip on libreboot, without using
|
||||
'-c' switch)
|
||||
- removed 'MX25L1605' and 'MX25L1605A/MX25L1606E' entries in
|
||||
flashchips.c for the patched version of flashchips.c
|
||||
- added instructions to 'builddeps-flashrom' to automatically
|
||||
use this modified flashchips.c in the default build
|
||||
- Added builddeb to libreboot\_bin.tar.gz
|
||||
- Moved 'bucts' build instructions from builddeps to builddeps-bucts
|
||||
- builddeps now runs 'builddeps-bucts' instead
|
||||
- Added 'builddeps-bucts' to libreboot\_bin.tar.gz
|
||||
- Documentation: Added information about using 'builddep-bucts'
|
||||
to build the BUC.TS utility.
|
||||
- Added 'lenovobios\_firstflash' and 'lenovobios\_secondflash'
|
||||
scripts
|
||||
- Added instructions to 'build' script for including those files
|
||||
in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Documentation: Add tutorial for flashing while Lenovo BIOS is
|
||||
running (on X60/T60)
|
||||
- Added 'flash' script (make sure to run builddeps-flashrom first)
|
||||
which (while libreboot is already running) can use flashrom to flash
|
||||
a ROM
|
||||
- eg: "sudo ./flash bin/x60/coreboot\_serial\_ukdvorak.rom"
|
||||
equivalent to "sudo ./flashrom/flashrom -p internal -w
|
||||
bin/x60/coreboot\_uk\_dvorak.rom"
|
||||
- updated 'build' script to include the 'flash' script in
|
||||
libreboot\_bin.tar.gz
|
||||
- Documentation: replaced default flashrom tutorial to recommend the
|
||||
'flash' script instead.
|
||||
- Re-add cbfstool source code back into libreboot\_bin.tar.gz, as
|
||||
cbfstool\_standalone
|
||||
- Patched that version to work (able to be built and used) without
|
||||
requiring the entire coreboot source code.
|
||||
- Created patched version of the relevant source files and added
|
||||
it into resources/cbfstool/patch
|
||||
- see coreboot/util/cbfstool/rmodule.c and then the patched
|
||||
version in resources/cbfstool/patch/rmodule.c
|
||||
- see coreboot/src/include/rmodule-defs.h and the rule in
|
||||
'build' for including this in
|
||||
../libreboot\_bin/cbfstool\_standalone
|
||||
- Added instructions to 'build' script for applying this patch
|
||||
to the cbfstool\_standalone source in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Added instructions to 'build' script for then re-compiling
|
||||
cbfstool\_standalone in libreboot\_bin after applying the patch
|
||||
- Added a 'builddeps-cbfstool' script (in src, but only used in
|
||||
bin and put in bin by 'build') that compiles
|
||||
cbfstool\_standalone in libreboot\_bin (make), moves the
|
||||
cbfstool and rmodtool binaries into libreboot\_bin/ and then
|
||||
does 'make clean' in libreboot\_bin/cbfstool\_standalone
|
||||
- Updated the 'build' script to put 'builddeps-cbfstool' in
|
||||
libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Updated the 'build' script in the cbfstool (standalone) part
|
||||
to accomodate the above.
|
||||
- Documentation: added notes about cbfstool (standalone) in
|
||||
libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Documentation: made docs/gnulinux/grub\_cbfs.html slightly easier to
|
||||
follow.
|
||||
- Annotate the 'build\*' scripts with 'echo' commands, to help the
|
||||
user understand what it actually happening during the build process.
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about how 'dmidecode' data was
|
||||
put in the coreboot configs
|
||||
- Documentation: In fact, document how the 'config' files in
|
||||
resources/libreboot/config/ were created
|
||||
- Documentation: Added information about which ThinkPad T60 laptops are
|
||||
supported, and which are not.
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about LCD inverters (for upgrading
|
||||
the LCD panel on a T60 14.1' XGA or 15.1' XGA)
|
||||
- it's FRU P/N 41W1478 (on T60 14.1") so this was added to the
|
||||
docs.
|
||||
- it's P/N 42T0078 FRU 42T0079 or P/N 41W1338 (on T60 15.1") so
|
||||
this was added to the docs.
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about names of LCD panels for T60
|
||||
to the relevant parts of the documentation.
|
||||
- Documentation: added information (with pictures) about the
|
||||
differences between T60 with Intel GPU and T60 with ATI GPU.
|
||||
- Documentation: added pictures of keyboard layouts (US/UK
|
||||
Qwerty/Dvorak) to the ROM list, to let the user compare with their
|
||||
own keyboard.
|
||||
- Move the coreboot build instructions in 'builddeps' into
|
||||
'builddeps-coreboot' and link it in 'builddeps'
|
||||
- Link to 'builddeps-coreboot' in final stage of 'getcb'
|
||||
- Move GRUB build instructions from 'builddeps' into
|
||||
'builddeps-grub', link from 'builddeps'
|
||||
- Link to 'builddeps-grub' in final stage of 'getgrub'
|
||||
- Move MemTest86+ build instructions from 'builddeps' into
|
||||
'builddeps-memtest86', link from 'builddeps'
|
||||
- Link to 'builddeps-memtest86' in final stage of 'getmt86'
|
||||
- made 'build' script put resources/ directory in libreboot\_bin, to
|
||||
make builddeps-flashrom work in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Removed instructions for building source code in the 'get' script
|
||||
(they don't really belong there)
|
||||
- Added libfuse-dev and liblzma-dev to the list of GRUB dependencies
|
||||
in 'builddeb' script.
|
||||
- Converted the 'RELEASE' file to 'docs/RELEASE.html'
|
||||
- Added those dependencies to builddeb script (for GRUB part): gawk
|
||||
libdevmapper-dev libtool libfreetype6-dev
|
||||
- Added to build script the instruction at the end to create a
|
||||
sha512sum.txt with a file manifest plus checksums.
|
||||
- Deleted the RELEASE and BACKPORT files (no longer needed)
|
||||
- Documentation: added information about X60/T60 dock (ultrabase x6
|
||||
and advanced mini dock) to relevant sections.
|
||||
- Added to docs/\#serial
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140716 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 16 July 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140716 (2nd beta) (16th July 2014)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Deleted all git-related files from the coreboot directory. This was
|
||||
necessary because with those it is possible to run 'git diff'
|
||||
which shows the changes made in the form of a patch (diff format);
|
||||
this includes the blobs that were deleted during deblobbing.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140720 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 20 July 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140720 (3rd beta) (20th July 2014)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixed typo that existed in 2nd beta where the release date of the
|
||||
2nd beta was listed as being in year 2016, when in actual fact it
|
||||
was 2014.
|
||||
- Documentation: added (preliminary) details about (rare) buggy CPUs
|
||||
on the ThinkPad T60 that were found to fail (instability, kernel
|
||||
panics, etc) without the microcode updates.
|
||||
- Documentation: added docs/hardware/x60\_heatsink.html for showing
|
||||
how to change the heatsink on the Thinkpad X60
|
||||
- Added ROM images for Azerty (French) keyboard layout in GRUB
|
||||
(courtesy of Olivier Mondoloni)
|
||||
- Tidied up some scripts:
|
||||
- ~~Re-factored those scripts (made easier to read/maintain):
|
||||
build-x60, build-x60t, build-t60, build-macbook21~~
|
||||
- ~~Reduced the number of grub configs to 2 (or 1, for macbook21),
|
||||
the build scripts now generate the other configs at build
|
||||
time.~~
|
||||
- Deleted build-x60, build-x60t, build-t60, build-macbook21 and
|
||||
replaced with intelligent (generic) buildrom-withgrub script
|
||||
- Updated build to use buildrom-withgrub script for building the
|
||||
ROM images.
|
||||
- coreboot.rom and coreboot\_serial.rom renamed to
|
||||
coreboot\_usqwerty.rom and coreboot\_serial\_usqwerty.rom
|
||||
- coreboot\_dvorak and coreboot\_serial\_dvorak.rom renamed to
|
||||
coreboot\_usdvorak.rom and coreboot\_serial\_usdvorak.rom
|
||||
- Renamed coreboot\*rom to libreboot\*rom
|
||||
- Made flash, lenovobios\_firstflash and lenovobios\_secondflash
|
||||
scripts fail if the specified file does not exist.
|
||||
- Updated all relevant parts of the documentation to reflect the
|
||||
above.
|
||||
- Replaced background.png with background.jpg. added gnulove.jpg.
|
||||
(resources/grub/background/)
|
||||
- Updated buildrom-withgrub to use background.jpg instead of
|
||||
background.png
|
||||
- Updated buildrom-withgrub to use gnulove.jpg aswell
|
||||
- Updated resources/grub/config/macbook21/grub\*cfg to use gnulove.jpg
|
||||
background.
|
||||
- Updated resources/grub/config/{x60,t60,x60t}/grub\*cfg to use
|
||||
background.jpg background.
|
||||
- Documentation: updated docs/\#grub\_custom\_keyboard to be more
|
||||
generally useful.
|
||||
- nvramtool:
|
||||
- Updated builddeps-coreboot script to build it
|
||||
- Updated build script to include it in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Documentation: added docs/security/x60\_security.html (security
|
||||
hardening for X60)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140729 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 29 July 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140729 (4th beta) (29th July 2014)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Documentation: improved (more explanations, background info) in
|
||||
docs/security/x60\_security.html (courtesy of Denis Carikli)
|
||||
- MacBook2,1 tested (confirmed)
|
||||
- macbook21: Added script 'macbook21\_firstflash' for flashing
|
||||
libreboot while Apple EFI firmware is running.
|
||||
- Documentation: macbook21: added software-based flashing instructions
|
||||
for flashing libreboot while Apple EFI firmware is running.
|
||||
- Reduced size of libreboot\_src.tar.gz:
|
||||
- Removed .git and .gitignore from grub directory
|
||||
(libreboot\_src); not needed. Removing them reduces the size of
|
||||
the archive (by a lot). GRUB development should be upstream.
|
||||
- Removed .git and .gitignore from bucts directory
|
||||
(libreboot\_src); not needed. Removing them reduces the size of
|
||||
the archive. bucts development should be upstream.
|
||||
- Removed .svn from flashrom directory (libreboot\_src); not
|
||||
needed. Removing it reduces the size of the archive. flashrom
|
||||
development should be upstream.
|
||||
- Added ROMs with Qwerty (Italian) layout in GRUB
|
||||
(libreboot\*itqwerty.rom)
|
||||
- Added resources/utilities/i945gpu/intel-regs.py for debugging issues
|
||||
related to LCD panel compatibility on X60 Tablet and T60. (courtesy
|
||||
of [Michał Masłowski](http://mtjm.eu))
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140811 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 11 August 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Corrections to r20140811 (5th beta) (11th August 2014)
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixed typo where revision list for 5th beta was listed as March 11th
|
||||
2014, when in fact it was August 11th 2014
|
||||
- Fixed incorrect grub.cfg that was actually placed in
|
||||
resources/grub/config/x60/grub\_usqwerty.cfg which broke the default
|
||||
GRUB menu entry on X60
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140811 (5th beta) (11th August 2014)
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- build: added 'luks', 'lvm', 'cmosdump' and 'cmostest' to the
|
||||
list of modules for grub.elf
|
||||
- Documentation: added pics showing T60 unbricking (still need to
|
||||
write a tutorial)
|
||||
- build: include cmos.layout
|
||||
(coreboot/src/mainboard/manufacturer/model/cmos.layout) files in
|
||||
libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Documentation: added **install/x60tablet\_unbrick.html**
|
||||
- Documentation: added **install/t60\_unbrick.html**
|
||||
- Documentation: added **install/t60\_lcd\_15.html**
|
||||
- Documentation: added **install/t60\_security.html**
|
||||
- Documentation: added **install/t60\_heatsink.html**
|
||||
- Documentation: Renamed RELEASE.html to release.html
|
||||
- Documentation: removed pcmcia reference in x60\_security.html (it's
|
||||
cardbus)
|
||||
- Documentation: added preliminary information about randomized seal
|
||||
(for physical intrusion detection) in x60\_security.html and
|
||||
t60\_security.html
|
||||
- Documentation: added preliminary information about
|
||||
preventing/mitigating cold-boot attack in x60\_security.html and
|
||||
t60\_security.html
|
||||
- Documentation: added info to \#macbook21 warning about issues with
|
||||
macbook21
|
||||
- Documentation: X60/T60: added information about checking custom ROMs
|
||||
using dd to see whether or not the top 64K region is duplicated
|
||||
below top or not. Advise caution about this in the tutorial that
|
||||
deals with flashing on top of Lenovo BIOS, citing the correct dd
|
||||
commands necessary if it is confirmed that the ROM has not been
|
||||
applied with dd yet. (in the case that the user compiled their own
|
||||
ROMs from libreboot, without using the build scripts, or if they
|
||||
forgot to use dd, etc).
|
||||
- Split resources/libreboot/patch/gitdiff into separate patch files
|
||||
(getcb script updated to accomodate this change).
|
||||
- Re-added .git files to bucts
|
||||
- Fixed the oversight where macbook21\_firstflash wasn't included in
|
||||
binary archives
|
||||
- Release archives are now compressed using .tar.xz for better
|
||||
compression
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140903 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 3 September 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140903 (6th beta) (3rd September 2014)
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Added modified builddeb\* scripts for Parabola GNU+Linux-libre:
|
||||
buildpac, buildpac-flashrom, buildpac-bucts (courtesy of Noah
|
||||
Vesely)
|
||||
- Documentation: updated all relevant areas to mention use of
|
||||
buildpac\* scripts for Parabola users.
|
||||
- Documentation: added information showing how to enable or disable
|
||||
bluetooth on the X60
|
||||
- MacBook1,1 tested! See **hardware/\#macbook11**
|
||||
- Documentation: fixed typo in \#get\_edid\_panelname (get-edit
|
||||
changed to get-edid)
|
||||
- Documentation: added images/x60\_lcd\_change/ (pics only for now)
|
||||
- Added gcry\_serpent and gcry\_whirlpool to the GRUB module list in
|
||||
the 'build' script (for luks users)
|
||||
- **Libreboot is now based on a new coreboot version from August 23rd,
|
||||
2014:\
|
||||
Merged commits (relates to boards that were already supported in
|
||||
libreboot):**
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6697/>
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6698/> (merged already)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6699/> (merged already)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6696/> (merged already)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6695/> (merged already)
|
||||
- **<http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/5927/> (merged already)**
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6717/> (merged already)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6718/> (merged already)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6723/> (merged already)
|
||||
(text-mode patch, might enable memtest. macbook21)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6732/> (MERGED) (remove useless
|
||||
ps/2 keyboard delay from macbook21. already merged)
|
||||
- These were also merged in coreboot (relates to boards that libreboot
|
||||
already supported):
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/5320/> (merged)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/5321/> (merged)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/5323/> (merged)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6693/> (merged)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/6694/> (merged)
|
||||
- <http://review.coreboot.org/#/c/5324/> (merged)
|
||||
- Documentation: removed the section about tft\_brightness on X60 (new
|
||||
code makes it obsolete)
|
||||
- Removed all patches from resources/libreboot/patch/ and added new
|
||||
patch: 0000\_t60\_textmode.git.diff
|
||||
- Updated getcb script and DEBLOB script.
|
||||
- Updated configuration files under resources/libreboot/config/ to
|
||||
accomodate new coreboot version.
|
||||
- Removed grub\_serial\*.cfg and libreboot\_serial\*.rom, all
|
||||
configs/rom files are now unified (containing same configuration as
|
||||
serial rom files from before).
|
||||
- Documentation: updated \#rom to reflect the above.
|
||||
- Updated GRUB to new version from August 14th, 2014.
|
||||
- Unified all grub configurations for all systems to a single grub.cfg
|
||||
under resources/grub/config/
|
||||
- Updated flashrom to new version from August 20th, 2014
|
||||
- Added getseabios and builddeps-seabios (builddeps and getall were
|
||||
also updated)
|
||||
- Added instructions to 'buildrom-withgrub' to include
|
||||
bios.bin.elf and vgaroms/vgabios.bin from SeaBIOS inside the
|
||||
ROM.
|
||||
- Added seabios (and sgavgabios) to grub as payload option in menu
|
||||
- Disabled serial output in Memtest86+ (no longer needed) to speed up
|
||||
tests.
|
||||
- MemTest86+ now works properly, it can output on the laptop
|
||||
screen (no serial port needed anymore).
|
||||
- Added getgrubinvaders, builddeps-grubinvaders scripts. Added these
|
||||
to getall and builddeps.
|
||||
- Added [GRUB Invaders](http://www.coreboot.org/GRUB_invaders)
|
||||
menu entry in resources/grub/config/grub.cfg
|
||||
- Added rules to builddeps-coreboot to build libpayload with
|
||||
TinyCurses. (added appropriate instructions to cleandeps script).
|
||||
- Commented out lines in resources/grub/config/grub.cfg for loading
|
||||
font/background (not useful anymore, now that GRUB is in text-mode).
|
||||
- Commented out lines in buildrom-withgrub that included
|
||||
backgrounds/fonts (not useful anymore, now that GRUB is in
|
||||
text-mode).
|
||||
- Added resources/utilities/i945-pwm/ (from
|
||||
git://git.mtjm.eu/i945-pwm), for debugging acpi brightness on i945
|
||||
systems.
|
||||
- Added instructions for it in builddeps, builddeps-i945pwm,
|
||||
builddeb and cleandeps
|
||||
- 'build' script: removed the parts that generated sha512sum
|
||||
manifests (not needed, since release tarballs are GPG-signed)
|
||||
- 'build' script: removed the parts that generated libreboot\_meta
|
||||
directory (not needed anymore, since \_meta will be hosted in git)
|
||||
- Updated \#build\_meta (and other parts of documentation) to
|
||||
accomodate this change.
|
||||
- Documentation: simplified (refactored) the notes in \#rom
|
||||
- 'build' script: removed the parts that generated libreboot\_bin
|
||||
and added them to a new script: 'build-release'
|
||||
- Documentation: \#build updated to reflect the above.
|
||||
- ~~Added all gcry\_\* modules to grub (luks/cryptomount):
|
||||
gcry\_arcfour gcry\_camellia gcry\_crc gcry\_dsa gcry\_md4
|
||||
gcry\_rfc2268 gcry\_rmd160 gcry\_seed gcry\_sha1 gcry\_sha512
|
||||
gcry\_twofish gcry\_blowfish gcry\_cast5 gcry\_des gcry\_idea
|
||||
gcry\_md5 gcry\_rijndael gcry\_rsa gcry\_serpent gcry\_sha256
|
||||
gcry\_tiger gcry\_whirlpool~~
|
||||
- Added GNUtoo's list of GRUB modules (includes all of the gcry\_\*
|
||||
modules above), cryptomount should be working now.
|
||||
- Removed builddeb-bucts and builddeb-flashrom, merged them with
|
||||
builddeb ( updated accordingly)
|
||||
- Removed buildpac-bucts and buildpac-flashrom, merged them with
|
||||
buildpac ( updated accordingly)
|
||||
- Renamed buildpac to deps-parabola ( updated accordingly)
|
||||
- Documentation: removed all parts talking about build dependencies,
|
||||
replaced them with links to \#build\_dependencies
|
||||
- Documentation: emphasized more strongly on the documentation, the
|
||||
need to re-build bucts and/or flashrom before flashing a ROM image.
|
||||
- build-release: flashrom, nvramtool, cbfstool and bucts are no longer
|
||||
provided pre-compiled in binary archives, and are now in source form
|
||||
only. (to maximize distro compatibility).
|
||||
- 'build' script: replaced grub.elf assembly instructons, it is now
|
||||
handled by a utility added under resources/utilities/grub-assemble
|
||||
- Moved resources/grub/keymap to
|
||||
resources/utilities/grub-assemble/keymap, and updated that utility
|
||||
to use it
|
||||
- Documentation: removed useless links to pictures of keyboard layouts
|
||||
and unmodified layouts.
|
||||
- Removed all unused fonts from dejavu-fonts-ttf-2.34/ directory
|
||||
- 'buildrom-withgrub' script: updated it to create 2 sets of ROMs
|
||||
for each system: one with text-mode, one with coreboot framebuffer.
|
||||
- Documentation: updated \#rom to reflect the above
|
||||
- Deleted unused README and COPYING file from main directory
|
||||
- Removed some rm -Rf .git\* instructions from the get\* scripts and
|
||||
moved them to build-release script
|
||||
- Split up default grub.cfg into 6 parts:
|
||||
extra/{common.cfg,txtmode.cfg,vesafb.cfg} and
|
||||
menuentries/{common.cfg,txtmode.cfg,vesafb.cfg}
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub script uses these to generate the correct
|
||||
grub.cfg for each type of configuration.
|
||||
- grub\_memdisk.cfg (used inside grub.elf) now only loads grub.cfg
|
||||
from cbfs. It no longer enables serial output or sets prefix.
|
||||
(menuentries/common.cfg does instead)
|
||||
- resources/grub/config/extra/common.cfg, added:
|
||||
- insmod instructions to load those modules: nativedisk, ehci,
|
||||
ohci, uhci, usb, usbserial\_pl2303, usbserial\_ftdi,
|
||||
usbserial\_usbdebug
|
||||
- set prefix=(memdisk)/boot/grub
|
||||
- For native graphics (recommended by coreboot wiki):\
|
||||
gfxpayload=keep\
|
||||
terminal\_output \--append gfxterm
|
||||
- Play a beep on startup:\
|
||||
play 480 440 1
|
||||
- Documentation: updated gnulinux/grub\_cbfs.html to make it safer
|
||||
(and easier) to follow.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20140911 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 11 September 2014
|
||||
|
||||
6th release (pre-release, 7th beta)
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
- Released 11th July 2014 (pre-release) 1st beta
|
||||
- Revised (pre-release, 2nd beta) 16th July 2014
|
||||
- Revised (pre-release, 3rd beta) 20th July 2014
|
||||
- Revised (pre-release, 4th beta) 29th July 2014
|
||||
- Revised (pre-release, 5th beta) 11th August 2014 (corrected 11th
|
||||
August 2014)
|
||||
- Revised (pre-release, 6th beta) 3rd September 2014
|
||||
- Revised (pre-release, 7th beta) 11th September 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Machines still supported (compared to previous release):
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard.
|
||||
|
||||
New systems supported in this release:
|
||||
--------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with
|
||||
digitizer support
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list** for list of supported LCD
|
||||
panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have its mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are issues; see below)
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
**hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list** for known working LCD panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have its mainboard replaced with
|
||||
a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 variants with ATI GPU) will likely never be supported:
|
||||
**hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel**
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook11**.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook21**.
|
||||
|
||||
Machines no longer supported (compared to previous release):
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- **All previous systems still supported!**
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20140911 (7th beta) (11th September 2014)
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- The changes below were made in a git repository, unlike in previous
|
||||
releases. Descriptions below are copied from 'git log'.
|
||||
- Update .gitignore for new dependencies.
|
||||
- Use a submodule for i945-pwm.
|
||||
- Don't clean packages that fail or don't need cleaning.
|
||||
- Don't clean i945-pwm, it's not needed.
|
||||
- Regression fix: Parabola live ISO boot issues
|
||||
- Re-enable background images in ISOLINUX/SYSLINUX GRUB parser menus
|
||||
- Regression fix: Re-add CD-ROM (ata0) in GRUB
|
||||
- Documentation: add notes about performance penalty when using
|
||||
ecryptfs.
|
||||
- Documentation: Fixed spelling and grammatical errors.
|
||||
- Documentation: macbook21: add new system as tested
|
||||
- Documentation: macbook21: add info about improving touchpad
|
||||
sensitivity
|
||||
- Documentation: X60 Tablet: add more information about finger input
|
||||
- Documentation: release.html: Add information about recently merged
|
||||
commit in coreboot
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20141015 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 15 October 2014
|
||||
|
||||
Machines supported in this release:
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard. An X60 Tablet motherboard will
|
||||
also fit inside an X60/X60s.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with
|
||||
digitizer support
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list** for list of supported LCD
|
||||
panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have its mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are issues; see below):
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
**hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list** for known working LCD panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have its mainboard replaced with
|
||||
a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- See **future/\#t60\_cpu\_microcode**.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 variants with ATI GPU) will likely never be supported:
|
||||
**hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel**
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook11**.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook21**.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes for this release (latest changes first, earliest changes last)
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Updated coreboot (git commit
|
||||
8ffc085e1affaabbe3dca8ac6a89346b71dfc02e), the latest at the time of
|
||||
writing.
|
||||
- Updated SeaBIOS (git commit
|
||||
67d1fbef0f630e1e823f137d1bae7fa5790bcf4e), the latest at the time of
|
||||
writing.
|
||||
- Updated Flashrom (svn revision 1850), the latest at the time of
|
||||
writing.
|
||||
- Updated GRUB (git commit 9a67e1ac8e92cd0b7521c75a734fcaf2e58523ad),
|
||||
the latest at the time of writing.
|
||||
- Cleaned up the documentation, removed unneeded files.
|
||||
- ec/lenovo/h8 (x60/x60s/x60t/t60): Enable
|
||||
wifi/bluetooth/wwan/touchpad/trackpoint by default.
|
||||
- Documentation: Updated list of T60 LCDs (Samsung LTN150XG 15" XGA
|
||||
listed as non-working).
|
||||
- builddeps-coreboot: Don't build libpayload (not needed. This was
|
||||
leftover by mistake, when trying out the TINT payload).
|
||||
- Replaced most diff files (patches) for coreboot with gerrit
|
||||
checkouts (cherry-pick).
|
||||
- Documentation: x60\_security.html and t60\_security.html: added
|
||||
links to info about the ethernet controller (Intel 82573).
|
||||
- Documentation: x60\_security.html and t60\_security.html: added
|
||||
notes about DMA and the docking station.
|
||||
- Documentation: configuring\_parabola.html: basic post-install steps
|
||||
for Parabola GNU+Linux (helpful, since libreboot development is
|
||||
being moved to Parabola at the time of writing).
|
||||
- builddeps-coreboot: use 'make crossgcc-i386' instead of 'make
|
||||
crossgcc'. Libreboot only targets x86 at the time of writing.
|
||||
- ROM images no longer include SeaBIOS. Instead, the user adds it
|
||||
afterwards. Documentation and scripts updated.
|
||||
- docs/images/encrypted\_parabola.html: Notes about linux-libre-grsec
|
||||
- Documentation: encrypted\_parabola.html: add tutorial for encrypted
|
||||
Parabola GNU+Linux installation.
|
||||
- Documentation: added more info about wifi chipsets
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,159 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20150124 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 24 January 2015
|
||||
|
||||
Machines supported in this release:
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard. An X60 Tablet motherboard will
|
||||
also fit inside an X60/X60s.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with
|
||||
digitizer support
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list** for list of supported LCD
|
||||
panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have it's mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are
|
||||
issuesinstall/x200\_external.html; see below):
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
**hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list** for known working LCD panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have it's mainboard replaced
|
||||
with a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- See **future/\#t60\_cpu\_microcode**.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 laptops with ATI GPU) will likely never be
|
||||
supported: **hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel**
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X200**
|
||||
- X200S and X200 Tablet are also supported, conditionally; see
|
||||
**hardware/x200.html\#x200s**
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
**hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html**
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad R400** (r20150208 and later, only)
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
**hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html**
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook11**.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook21**.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes for this release (latest changes first, earliest changes last)
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Added (ahci1) to list of devices for ISOLINUX parser
|
||||
(CD/DVD) (this is needed for the X200 docking station).
|
||||
- grub.cfg: ISOLINUX parsing is now done on all USB partitions.
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Automatically switched to /boot/grub/libreboot\_grub.cfg
|
||||
on a partition, if it exists.
|
||||
- libreboot\_bin: added static ARM binaries for flashrom, cbfstool,
|
||||
ich9gen and ich9deblob (tested on beaglebone black).
|
||||
- Flashrom: removed redundant Macronix flashchip definitions (for X200
|
||||
owners).
|
||||
- Flashrom: added whitelist for ThinkPad X200.
|
||||
- X200: fixed uneven backlight (at low levels)
|
||||
- ich9macchange (new script, uses ich9gen): for changing the default
|
||||
MAC address on X200 ROM images.
|
||||
- ich9gen: added capability to change the default MAC address (and
|
||||
update the checksum)
|
||||
- ich9deblob: added new utility ich9gen: this can generate a
|
||||
descriptor+gbe image without a factory.rom dump present.
|
||||
- Modified ich9deblob to use a struct for Gbe, documenting everything.
|
||||
- Massively updated the ich9deblob utility: re-factored everything
|
||||
completely.
|
||||
- Enabled cstates 1 and 2 on macbook21. This reduces idle heat / power
|
||||
consumption.
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub: disabled creation of \*txtmode\*.rom for X200
|
||||
(only framebuffer graphics work)
|
||||
- Updated SeaBIOS (again)
|
||||
- docs/install/\#flashrom\_x200: improve instructions
|
||||
- Updated flashrom (again) - patches updated
|
||||
- Updated GRUB (again)
|
||||
- Updated coreboot (again)
|
||||
- build-release: not all files were copied to libreboot\_src. fix
|
||||
that.
|
||||
- build-release: include cbmem (statically compiled) in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- Documentation (X200): added software-based flashing instructions
|
||||
- Documentation: remove all references to the bus pirate (replaced
|
||||
with BBB flashing tutorials)
|
||||
- **New board:** ThinkPad X200S and X200 Tablet support added to
|
||||
libreboot
|
||||
- build: automatically find board names (configs) to build for
|
||||
- **New board:** ThinkPad X200 support added to libreboot
|
||||
- coreboot-libre config (all boards): enable USB dongle log output
|
||||
(for BeagleBone Black)
|
||||
- cleandeps: actually clean grubinvaders
|
||||
- .gitignore: add powertop directory
|
||||
- cleandeps: clean i945-pwm utility
|
||||
- scripts (all): fix typos
|
||||
- Documentation: general cleanup.
|
||||
- builddeps-flashrom: reduce build commands to a single for loop
|
||||
- scripts (all): replace unnecessary rm -Rf with rm -f
|
||||
- docs/release.html: add lenovo g505s to the list of candidates
|
||||
- .gitignore: add libreboot\_bin.tar.xz and libreboot\_src.tar.xz
|
||||
- libreboot\_bin.tar.xz: Include utils as statically linked binaries
|
||||
- This means that the user does not have to install build
|
||||
dependency or build from source anymore.
|
||||
- deps-parabola (removed) Remove Parabola dependencies script. Will
|
||||
re-add later (properly tested)
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Add more path checks to isolinux parser (more ISOs should
|
||||
work now)
|
||||
- Update SeaBIOS
|
||||
- x60flashfrom5 (new), for X60 users upgrading from 5th/early release
|
||||
- Update flashrom
|
||||
- Update GRUB
|
||||
- Updated coreboot-libre
|
||||
- i945: permanently set tft\_brightness to 0xff (fixes bug on X60
|
||||
where turning up brightness at max would make it loop back to
|
||||
low brightness)
|
||||
- getcb: Revert X60/T60 to legacy backlight controls
|
||||
- The ACPI brightness patches were abandoned and obsolete.
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Only load initrd.img if it exists. Add rw to linux line
|
||||
(for ProteanOS)
|
||||
- build: Only generate the GRUB configurations once (re-use on all
|
||||
images)
|
||||
- Only build 2 GRUB payload executables, re-use on all boards.
|
||||
- resources/utilities/grub-assemble/gen.txtmode.sh: Use GNU BASH\
|
||||
resources/utilities/grub-assemble/gen.vesafb.sh: Use GNU BASH
|
||||
- scripts (error handling): Replace exit with exit 1 (make debugging
|
||||
easier)
|
||||
- Move most files in CBFS to GRUB memdisk, except grub.cfg and
|
||||
grubtest.cfg
|
||||
- docs/release.html Add DMP vortex86ex to list of candidates.
|
||||
- docs/release.html Add ThinkPad X201 to list of candidates.
|
||||
- New links added to docs/security/x60\_security and
|
||||
docs/security/t60\_security
|
||||
- lenovobios\_secondflash: Warn if BUCTS is not present. (not a
|
||||
dealbreaker. Can just pull out nvram battery/coin).
|
||||
- lenovobios\_firstflash: Fail if BUCTS fails. (anti-bricking
|
||||
precaution)
|
||||
- Removed obnoxious warnings from flashing scripts, improved
|
||||
documentation instead.
|
||||
- scripts (all): add proper error checking (fail fast, fail early. Do
|
||||
not continue if there are errors)
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub: rename image to boardname\_layout\_romtype.rom
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub: don't move cbfstool, execute directly
|
||||
- resources/utilities/grub-assemble: add French Dvorak (BEPO) keyboard
|
||||
layout.
|
||||
- Documentation: add docs/hardware/x60\_keyboard.html (show how to
|
||||
replace keyboard on X60/X60T)
|
||||
- Documentation: major cleanup (better structure, easier to find
|
||||
things)
|
||||
- docs/release.html: Remove Acer CB5 from list of future candidates.
|
||||
- Too many issues. Chromebooks are crippled (soldered
|
||||
RAM/storage/wifi) and have too many usability issues for the
|
||||
libreboot project.
|
||||
- docs/gnulinux/grub\_cbfs.html Major cleanup. Usability improvements.
|
||||
- flash (flashrom script): remove boardmismatch=force
|
||||
- This was put there before for users upgrading from libreboot r5
|
||||
to r6, but also allows the user to flash the wrong image. For
|
||||
example, the user could flash a T60 image on an X60, thus
|
||||
bricking the system. It's almost certain that most people have
|
||||
upgraded by now, so remove this potentially dangerous option.
|
||||
- Documentation: update compatibility list for X60T LCD panels.
|
||||
- docs/release.html: add note about X60 Tablet board in X60/X60s
|
||||
- docs/howtos/grub\_boot\_installer.html: small corrections
|
||||
- docs/howtos/grub\_boot\_installer.html: improved readability, fixed
|
||||
html errors
|
||||
- Documentation (macbook21 related): clean up
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20150126 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 26 January 2015
|
||||
|
||||
Machines supported in this release:
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard. An X60 Tablet motherboard will
|
||||
also fit inside an X60/X60s.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with
|
||||
digitizer support
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list** for list of supported LCD
|
||||
panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have it's mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are
|
||||
issuesinstall/x200\_external.html; see below):
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
**hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list** for known working LCD panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have it's mainboard replaced
|
||||
with a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- See **future/\#t60\_cpu\_microcode**.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 laptops with ATI GPU) will likely never be
|
||||
supported: **hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel**
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X200**
|
||||
- X200S and X200 Tablet are also supported, conditionally; see
|
||||
**hardware/x200.html\#x200s**
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
**hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html**
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad R400** (r20150208 and later, only)
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
**hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html**
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook11**.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook21**.
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20150126 (relative to r20150124)
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This is a bug fix release based on r20150124. It contains a few small
|
||||
changes:
|
||||
|
||||
- grub.cfg: hardcode the list of partitions to search (speeds up
|
||||
booting considerably. GRUB regexp isn't very well optimized)
|
||||
- Docs (x200.html hcl): Remove incorrect information
|
||||
- Documentation (bbb\_setup.md): Fix typos
|
||||
- build-release: delete ich9fdgbe\_{4m,8m}.bin files from ich9gen
|
||||
- These were accidentically included in the r20150124 release.
|
||||
They are generated from ich9gen so it's ok, but they don't
|
||||
need to be in the archive.
|
||||
- Documentation (grub\_cbfs.md): Looping in libreboot\_grub.cfg (Add
|
||||
notes about it if the user copied from grub.cfg in CBFS.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20150208 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 8 February 2015
|
||||
|
||||
Machines supported in this release:
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard. An X60 Tablet motherboard will
|
||||
also fit inside an X60/X60s.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with
|
||||
digitizer support
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list** for list of supported LCD
|
||||
panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have it's mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are
|
||||
issuesinstall/x200\_external.html; see below):
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
**hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list** for known working LCD panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have it's mainboard replaced
|
||||
with a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- See **future/\#t60\_cpu\_microcode**.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 laptops with ATI GPU) will likely never be
|
||||
supported: **hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel**
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad X200**
|
||||
- X200S and X200 Tablet are also supported, conditionally; see
|
||||
**hardware/x200.html\#x200s**
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
**hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html**
|
||||
- **Lenovo ThinkPad R400** (r20150208 and later, only)
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
**hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html**
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook11**.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See **hardware/\#macbook21**.
|
||||
|
||||
Revisions for r20150208 (relative to r20150126)
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This is a maintenance release (polishing) based on r20150126. Users who
|
||||
installed r20150126 don't really need to update to this release.
|
||||
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub: use gnulove.jpg background on 16:10 laptops
|
||||
(MacBook2,1 and X200)
|
||||
- build-release: include grub-background script in libreboot\_bin
|
||||
- grub-background (new): lets user change GRUB background image
|
||||
- grub-assemble: Add link to original utility.
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub: Put background.jpg in CBFS, not GRUB memdisk
|
||||
- grub-assemble: merge scripts into a single script gen.sh
|
||||
- Documentation: implement theme, drastically improve readability
|
||||
- docs/hardware/: update list of compatible T60 LCD panels
|
||||
- docs/: more clarification of libreboot's stated purpose.
|
||||
- build-release: include the commitid file in the release archives
|
||||
- docs/: Further emphasize the GNU+Linux requirement.
|
||||
- lenovobios\_firstflash: fix BASH errors
|
||||
- lenovobios\_secondflash: fix BASH errors
|
||||
- docs/install/x200\_external.html: Tell user to switch MAC address.
|
||||
- docs/git/: Add to the list of x86\_64 compatible hosts.
|
||||
- docs/install/: Remove old (obsolete) information.
|
||||
- docs/git/: Say that the build dependencies are for src (and not
|
||||
nedeed for libreboot\_bin)
|
||||
- build: re-factor the descriptor/gbe generating loop for GM45/ICH9M
|
||||
- X60, X60S and X60 Tablet now the same ROM images.
|
||||
- Add QEMU (q35/ich9) support to libreboot.
|
||||
- Add QEMU (i440fx/piix4) support to libreboot
|
||||
- docs/: Re-write the description of what libreboot is.
|
||||
- docs/release.html: Add notes about how to use GPG.
|
||||
- build-release: delete the commitid file from release archives
|
||||
- build-release: create file named commitid after build-release
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,224 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20150518 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 18 May 2015
|
||||
|
||||
Installation instructions can be found at ***docs/install/***. Building
|
||||
instructions (for source code) can be found at ***docs/git/\#build***.
|
||||
|
||||
Machines supported in this release:
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- **ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard. An X60 Tablet motherboard will
|
||||
also fit inside an X60/X60s.
|
||||
- **ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with digitizer
|
||||
support
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list*** for list of supported
|
||||
LCD panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have it's mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are issues; see below):
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
***docs/hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list*** for known working LCD
|
||||
panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have it's mainboard replaced
|
||||
with a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- See ***docs/future/\#t60\_cpu\_microcode***.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 laptops with ATI GPU) will likely never be
|
||||
supported: ***docs/hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad X200**
|
||||
- X200S and X200 Tablet are also supported, conditionally; see
|
||||
***docs/hardware/x200.html\#x200s***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad R400**
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/r400.html***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad T400**
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/t400.html***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad T500**
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/t500.html***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/\#macbook11***.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/\#macbook21***.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes for this release, relative to r20150208 (earliest changes last, recent changes first)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- Add a whitelist entry to board\_enable.c in flashrom, for the
|
||||
ThinkPad R400, T400 and T500
|
||||
- Updated flashrom (to SVN revision 1889)
|
||||
- X200 whitelist patch removed (merged upstream)
|
||||
- X200 whitelist modified to include X200S and X200 Tablet
|
||||
- libreboot\_util: don't include cmos layout files (not needed
|
||||
anymore)
|
||||
- **coreboot-libre: backport patches for X200 Tablet digitizer
|
||||
support**
|
||||
- build/release/archives: create SHA512 sum manifest file of the
|
||||
release archives
|
||||
- build/release/archives: separate crossgcc into a new archive
|
||||
- disabled generation of txtmode ROM images for now (they will be back
|
||||
again in the next release)
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: delete unused code (reduce size of src archive)
|
||||
- Flashing guides: make them more friendly to colourblind people
|
||||
- docs/gnulinux/encrypted\_\*.html: Remove mention of password
|
||||
length - it was arbitrary and pointless.
|
||||
- docs/maintain/: Finish the guide
|
||||
- scripts/download/coreboot: use diffs included in libreboot, not
|
||||
external gerrit cherry-picks - review.coreboot.org (gerrit) being
|
||||
down no longer kills libreboot (backup mirrors of the master
|
||||
repository exist)
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: Add info about wp/hold and pinouts
|
||||
- docs/: improve the description of libreboot
|
||||
- docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html: notes about the demefactory utility
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: EHCI debug: recommend linux-libre
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: EHCI Debug logging setup guide
|
||||
- docs/hardware/t500.html: Add screen compatibility report (TODO: fix
|
||||
incompatible screens)
|
||||
- Update coreboot(again) + merge GM45 hybrid GPU patches - means that
|
||||
T400/T500 with the ATI+Intel hybrid GPU setup will work (ATI
|
||||
disabled, Intel permanently enabled). power\_on\_after\_fail nvram
|
||||
option added to all GM45 boards, defaulting to No, so that plugging
|
||||
it AC doesn't boot up the system against the users will. Net20DC is
|
||||
now the default debug dongle on all boards (compatible with BBB).
|
||||
- demefactory (new utility): create GM45 factory.rom without the ME
|
||||
- ich9deblob: re-factor descriptor.c functions
|
||||
- docs/hardware/t500.html: add hardware logs
|
||||
- docs/gnulinux/encrypted\_\*.html: No password for default entry
|
||||
- docs/git/: Add more details about BUC.TS
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Also scan for grub2/grub.cfg, not just grub/grub.cfg
|
||||
- docs/maintain/ (new section. WIP!): Maintaining libreboot
|
||||
- docs/gnulinux/grub\_boot\_installer.html: Fix hazardous instruction
|
||||
- docs/tasks.html: Better categorization between intel/amd/arm
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: notes about SPI flashing stability
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: more names for the 0.1" cables
|
||||
- docs/install/\*\_external.html: add disclaimer about thermal paste
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: Fix broken links
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: preliminary notes about EHCI debug
|
||||
- docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html: Link to websites talking about the
|
||||
ME
|
||||
- docs/install/{t400,t500,r400}\_external.html: Notes about CPU
|
||||
compatibility
|
||||
- Delete the ich9macchange script. It's useless, and confuses people
|
||||
- docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html: prioritize ich9gen executable path
|
||||
- docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html: prioritize changing mac address
|
||||
- docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html: less confusing notes about ich9gen
|
||||
- build/dependencies/parabola: Add dependencies for x86\_64
|
||||
- scripts/dependencies/paraboladependencies: build dependencies
|
||||
(32-bit Parabola)
|
||||
- **New board**: ThinkPad T500
|
||||
- Add diffs for descriptor/gbe differences between T500 and X200
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: provide better blob categorization
|
||||
- docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html: add notes about flash write protect
|
||||
- **New board**: ThinkPad T400
|
||||
- GRUB: add partial vesamenu.c32 support (fixes tails ISOLINUX menu)
|
||||
- Update GRUB (to revision fa07d919d1ff868b18d8a42276d094b63a58e299)
|
||||
- Update coreboot (to revision
|
||||
83b05eb0a85d7b7ac0837cece67afabbdb46ea65)
|
||||
- Intel CPU microcode (most of it) no longer deleted, because it
|
||||
was deleted upstream (moved to a 3rd party repository).
|
||||
- MacBook2,1 cstate patch is no longer cherry picked (merged
|
||||
upstream)
|
||||
- Patch to disable use of timestamps in coreboot no longer
|
||||
included (merged upstream)
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: don't list vortex86ex kbd firmware as microcode
|
||||
(list it separately)
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: don't rm \*/early\_setup\_ss.h (these are not
|
||||
blobs)
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: add GPLv3 license to the findblobs script
|
||||
- coreboot-libreboot: don't rm raminit\_tables (nahelem/sandybridge)
|
||||
(they are not blobs)
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: don't delete the .spd.hex files (they are not
|
||||
blobs)
|
||||
- build/release/archives: don't put rmodtool in libreboot\_util
|
||||
- docs/install/x200\_external.html: recommend installing GNU+Linux at
|
||||
the end
|
||||
- docs/install/x200\_external.html: add more photos, improve
|
||||
instructions
|
||||
- build/clean/grub: use distclean instead of clean
|
||||
- grub-assemble: Add the *bsd* and *part\_bsd* modules
|
||||
- build/roms/withgrub: Only run ich9gen if gm45/gs45 images exist
|
||||
- docs/git/: Add notes about building for specific boards
|
||||
- build/roms/withgrub: Allow building for a custom range of boards
|
||||
- grub-assemble: Disable verbose output
|
||||
- Add documentation on how to unlock root encrypted fs with key in
|
||||
initramfs in Parabola Linux
|
||||
- docs/gnulinux/grub\_cbfs.html: Improve structure (easier to use)
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Disable the beep on startup
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: Make the guide easier to use
|
||||
- docs/gnulinux/grub\_cbfs.html: Remove redundant instructions
|
||||
- docs/install/x200\_external.html: Mark pins in the images
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: Replace 3.3V PSU photo with ATX PSU
|
||||
- docs/hardware/x200.html: Add dumps from 4-MiB X200 with Lenovo BIOS 3.22
|
||||
- docs/hardware/x200.html: Add dumps from 4-MiB X200 with Lenovo BIOS 3.18
|
||||
- grub.cfg: add syslinux\_configfile menuentry for ahci0
|
||||
- grub.cfg: Add more paths for syslinux\_configfile
|
||||
- docs/future.html: T60: Add EDID dump from LG-Philips LP150E05-A2K1
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: Further clarify which clip is needed
|
||||
- bash scripts: Make script output more user-friendly in general
|
||||
- bash scripts: Only enable verbose output if DEBUG= is used
|
||||
- build: Support multiple extra options - now possible to build
|
||||
multiple images for arbitrary boards (configs), but without building
|
||||
the entire collection.
|
||||
- Deleted the signing archive key - the finger print and ID is given
|
||||
instead, so that the user can download it from a key server
|
||||
- scripts/helpers/build/release: Move docs to separate archive -
|
||||
reduces the size of the other archives considerably
|
||||
- Move DEBLOB to resources/utilities/coreboot-libre/deblob
|
||||
- scripts/helpers/build/release: Delete DEBLOB from libreboot\_src/ -
|
||||
not needed in libreboot\_src (release archive) because it contains a
|
||||
coreboot revision that has already been deblobbed.
|
||||
- flash (script): Use *build* instead of *DEBLOB* to know if in src
|
||||
- docs/install/r400\_external.html: Show images, don't link.
|
||||
- docs/install/x200\_external.html: Show images, don't link.
|
||||
- docs/install/bbb\_setup.html: Show images, instead of linking
|
||||
- Documentation: optimize all images (reduce file sizes)
|
||||
- Remove download links from the release page (and the archive page) -
|
||||
release archives are hosted differently following this release,
|
||||
which means that the old methods are no longer viable.
|
||||
- Moved ich9macchange to resources/scripts/misc/ich9macchange
|
||||
- ich9macchange: assume that the script is being run from \_util (act
|
||||
only on one ROM image, defined by a user-provided path)
|
||||
- Move grub-background to resources/scripts/misc/grub-background
|
||||
- grub-background: assume that it is being run from libreboot\_util
|
||||
- grub-background: change only one ROM image, specified by path
|
||||
- build (release archives): Add the commitid file to release/
|
||||
- build-release: Move the release archives to release/
|
||||
- Merge all build scripts into a single generic script, with helpers
|
||||
in resources/scripts/helpers/build/
|
||||
- Replace *getall* with *download*, which takes as input an argument
|
||||
specifying which program the user wants to download.
|
||||
- Moved the get scripts to resources/scripts/helpers/download/
|
||||
- build-release: Remove the powertop entries
|
||||
- Documentation: general improvements to the flashing instructions
|
||||
- Merged all flashing scripts into a single script
|
||||
- Updated GRUB
|
||||
- bucts: Make it build without git
|
||||
- Moved dejavu-fonts-ttf-2.34/AUTHORS to resources/grub/font/
|
||||
- Deleted GRUB Invaders from libreboot
|
||||
- Deleted SeaBIOS from libreboot
|
||||
- build-release: optimize use of tar (reduced file sizes)
|
||||
- grub.cfg: add another SYSLINUX config location
|
||||
(/syslinux/syslinux.cfg)
|
||||
- build-release: remove the bin/ directory from libreboot\_util
|
||||
- cleandeps: delete the bin/ directory
|
||||
- buildrom-withgrub: create the bin directory if it does not exist
|
||||
- coreboot-libre: don't use git for version timestamp
|
||||
- i945-pwm: add clean command to Makefile
|
||||
- i945-pwm: add -lz to Makefile
|
||||
- docs/install/x200\_external: Mention GPIO33 non-descriptor mode
|
||||
- docs/hardware/: Remove redundant links
|
||||
- ich9macchange: Add R400
|
||||
- build-release: Separate ROM images into individual archives
|
||||
- build-release: rename libreboot\_bin to libreboot\_util
|
||||
- **New board:** ThinkPad R400 support added to libreboot.
|
||||
- bbb\_setup.html: tell user to use libreboot's own flashrom
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,169 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20160818 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 18 August 2016
|
||||
|
||||
This is in comparison to the Libreboot 20150518 release.
|
||||
|
||||
Installation instructions can be found at `docs/install/`. Building
|
||||
instructions (for source code) can be found at `docs/git/\#build`.
|
||||
|
||||
Machines supported in this release:
|
||||
-----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- **ASUS Chromebook C201**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/c201.html***
|
||||
- **Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L desktop motherboard**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/ga-g41m-es2l.html***
|
||||
- **Intel D510MO desktop motherboard**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/d510mo.html***
|
||||
- **Intel D945GCLF desktop motherboard**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/d945gclf.html***
|
||||
- **Apple iMac 5,2**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/imac52.html***
|
||||
- **ASUS KFSN4-DRE server board**
|
||||
- PCB revision 1.05G is the best version (can use 6-core CPUs)
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/kfsn4-dre.html***
|
||||
- **ASUS KGPE-D16 server board**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/kgpe-d16.html***
|
||||
- **ASUS KCMA-D8 desktop/workstation board**
|
||||
- Check notes in ***docs/hardware/kcma-d8.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad X60/X60s**
|
||||
- You can also remove the motherboard from an X61/X61s and replace
|
||||
it with an X60/X60s motherboard. An X60 Tablet motherboard will
|
||||
also fit inside an X60/X60s.
|
||||
- **ThinkPad X60 Tablet** (1024x768 and 1400x1050) with digitizer
|
||||
support
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/\#supported\_x60t\_list*** for list of supported
|
||||
LCD panels
|
||||
- It is unknown whether an X61 Tablet can have it's mainboard
|
||||
replaced with an X60 Tablet motherboard.
|
||||
- **ThinkPad T60** (Intel GPU) (there are issues; see below):
|
||||
- See notes below for exceptions, and
|
||||
***docs/hardware/\#supported\_t60\_list*** for known working LCD
|
||||
panels.
|
||||
- It is unknown whether a T61 can have it's mainboard replaced
|
||||
with a T60 motherboard.
|
||||
- See ***docs/future/\#t60\_cpu\_microcode***.
|
||||
- T60p (and T60 laptops with ATI GPU) will likely never be
|
||||
supported: ***docs/hardware/\#t60\_ati\_intel***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad X200**
|
||||
- X200S and X200 Tablet are also supported, conditionally; see
|
||||
***docs/hardware/x200.html\#x200s***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad R400**
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/r400.html***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad T400**
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/t400.html***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **ThinkPad T500**
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/t500.html***
|
||||
- **ME/AMT**: libreboot removes this, permanently.
|
||||
***docs/hardware/gm45\_remove\_me.html***
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook1,1** (MA255LL/A, MA254LL/A, MA472LL/A)
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/\#macbook11***.
|
||||
- **Apple MacBook2,1** (MA699LL/A, MA701LL/A, MB061LL/A, MA700LL/A,
|
||||
MB063LL/A, MB062LL/A)
|
||||
- See ***docs/hardware/\#macbook21***.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes for this release of Libreboot, relative to Libreboot version 20150518 (earliest changes are shown last and the most recent changes are shown first first)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
- NEW BOARDS ADDED:
|
||||
- ASUS Chromebook C201 (ARM laptop) (thanks to Paul Kocialkowski)
|
||||
- Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L motherboard (desktop) (thanks to Damien
|
||||
Zammit)
|
||||
- Intel D510MO motherboard (desktop) (thanks to Damien Zammit)
|
||||
- ASUS KCMA-D8 motherboard (desktop) (thanks to Timothy Pearson)
|
||||
- ASUS KFSN4-DRE motherboard (server) (thanks to Timothy Pearson)
|
||||
- ASUS KGPE-D16 motherboard (server) (thanks to Timothy Pearson)
|
||||
|
||||
For details development history on these boards, refer to the git log
|
||||
and documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
For boards previously supported, many fixes from upstream have been
|
||||
merged.
|
||||
|
||||
Other changes (compared to libreboot 20150518), for libreboot in general
|
||||
or for previously supported systems: (this is a summary. For more
|
||||
detailed change list, refer to the git log)
|
||||
|
||||
256MiB VRAM allocated on GM45 (X200, T400, T500, R400) instead of 32MiB.
|
||||
This is an improvement over both Lenovo BIOS and Libreboot 20150518,
|
||||
allowing video decoding at 1080p to be smoother. (thanks Arthur Heymans)
|
||||
To clarify, GM45 video performance in libreboot 20160818 is better than
|
||||
on the original BIOS and the previous libreboot release.
|
||||
|
||||
64MiB VRAM on i945 (X60, T60, MacBook2,1) now supported in
|
||||
coreboot-libre, and used by default (in the previous release, it was
|
||||
8MiB allocated). Thanks to Arthur Heymans.
|
||||
|
||||
Higher battery life on GM45 (X200, T400, T500, R400) due to higher
|
||||
cstates now being supported (thanks Arthur Heymans). C4 power states
|
||||
also supported.
|
||||
|
||||
Higher battery life on i945 (X60, T60, MacBook2,1) due to better CPU
|
||||
C-state settings. (Deep C4, Dynamic L2 shrinking, C2E).
|
||||
|
||||
Text mode on GM45 (X200, T400, T500, R400) now works, making it possible
|
||||
to use MemTest86+ comfortably. (thanks to Nick High from coreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
Dual channel LVDS displays on GM45 (T400, T500) are now automatically
|
||||
detected in coreboot-libre. (thanks Vladimir Serbinenko from coreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
Partial fix in coreboot-libre for GRUB display on GM45, for dual channel
|
||||
LVDS higher resolution LCD panels (T400, T500). (thanks Arthur Heymans)
|
||||
|
||||
Massively improved GRUB configuration, making it easier to boot more
|
||||
encrypted systems automatically, and generally a more useful menu for
|
||||
booting the system (thanks go to Klemens Nanni of the autoboot project).
|
||||
Libreboot now uses the grub.cfg provided by the installed GNU+Linux
|
||||
distribution automatically, if present, switching to that configuration.
|
||||
This is done across many partitions, where libreboot actively searches
|
||||
for a configuration file (also on LVM volumes and encrypted volumes).
|
||||
This should make libreboot more easy to use for non-technical users,
|
||||
without having to modify the GRUB configuration used in libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Utilities archives is now source only. You will need to compile the
|
||||
packages in there (build scripts included, and a script for installing
|
||||
build dependencies). (binary utility archives are planned again in the
|
||||
next release, when the new build system is merged)
|
||||
|
||||
SeaGRUB is now the default payload on all x86 boards. (SeaBIOS
|
||||
configured to load a compressed GRUB payload from CBFS immediately,
|
||||
without providing an interface in SeaBIOS. This way, GRUB is still used
|
||||
but now BIOS services are available, so you get the best of both
|
||||
worlds). Thanks go to Timothy Pearson of coreboot for this idea.
|
||||
|
||||
crossgcc is now downloaded and built as a separate module to
|
||||
coreboot-libre, with a universal revision used to build all boards.
|
||||
|
||||
Individual boards now have their own coreboot revision and patches,
|
||||
independently of each other board. This makes maintenance easier.
|
||||
|
||||
Updated all utilities, and modules (coreboot, GRUB, etc) to newer
|
||||
versions, with various bugfixes and improvements upstream.
|
||||
|
||||
RTC century byte issue now fixed on GM45 in coreboot-libre, so the date
|
||||
should now be correctly displayed when running the latest linux kernel,
|
||||
instead of seeing 1970-01-01 when you boot (thanks to Alexander Couzens
|
||||
from coreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
Build system now uses multiple CPU cores when building, speeding up
|
||||
building for some people. Manually specifying how many cores are needed
|
||||
is also possible, for those using the build system in a chroot
|
||||
environment. (thanks go to Timothy Pearson from coreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
In the build system (git repository), https:// is now used when cloning
|
||||
coreboot. http:// is used as a fallback for GRUB, if git:// fails.
|
||||
|
||||
New payload, the depthcharge bootloader (free bootloader maintained by
|
||||
Google) for use on the ASUS Chromebook C201. (thanks go to Paul
|
||||
Kocialkowski)
|
||||
|
||||
Various fixes to the ich9gen utility (e.g. flash component density is
|
||||
now set correctly in the descriptor, gbe-less descriptors now supported)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20160902 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 2 September 2016.
|
||||
|
||||
This fixes build issues in the previous 20160818 release
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20160907 release
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 7 September 2016
|
||||
|
||||
In comparison to Libreboot 20160902:
|
||||
|
||||
For existing boards, there are no new board specific changes.
|
||||
|
||||
This release adds one new mainboard to libreboot:
|
||||
|
||||
- Intel D945GCLF desktop motherboard (thanks to Arthur Heymans)
|
||||
|
||||
Other bugfixes:
|
||||
|
||||
- Various improvements to the documentation
|
||||
- re-added "unset superusers" to the grub.cfg, which was needed for
|
||||
some users depending on the distros that they used
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
|
|
@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20211122 released!
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 22 November 2021
|
||||
|
||||
Free your BIOS today!
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is free (as in freedom) boot firmware, which initializes the hardware
|
||||
(e.g. memory controller, CPU, peripherals) in your computer so that software
|
||||
can run. Libreboot then starts a bootloader to load your operating system. It
|
||||
replaces the proprietary BIOS/UEFI firmware typically found on a computer.
|
||||
Libreboot is compatible with specifical computer models that use the Intel/AMD
|
||||
x86 architecture. Libreboot works well with GNU+Linux and BSD operating systems.
|
||||
|
||||
The last Libreboot release, version 20210522, was released on May 22nd
|
||||
in 2021. *This* new release, Libreboot 20211122, is released today on November
|
||||
22nd, 2021. This is yet another *testing* release, so expect there to be some
|
||||
bugs. Every effort has been made to ensure reliability on all boards, however.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find this release in the `testing` directory on Libreboot release
|
||||
mirrors. If you check in the `stable` directory, you'll still only find
|
||||
the 20160907 release in there, so please ensure that you check the `testing`
|
||||
directory!
|
||||
|
||||
This is a *bug fix* release, relative to 20210522. No new boards or major
|
||||
features have been added, but several problems that existed in the previous
|
||||
release have now been fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
Work done since the 20210522 release:
|
||||
-------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
* Updated to newer coreboot, SeaBIOS and GRUB versions. The 20210522
|
||||
release was using coreboot 4.14, on most boards, from May 2021. This release
|
||||
is using a coreboot revision from November 2021.
|
||||
* Tianocore dropped from the build system. It was planned that this would be
|
||||
provided in ROM images, but Tianocore is very bloated and buggy, and not
|
||||
worth maintaining. It was supported in the build system, but not actually
|
||||
enabled on any boards. Instead, a future release of Libreboot will include
|
||||
a busybox+linux payload with the u-root bootloader:
|
||||
<https://github.com/u-root/u-root>
|
||||
* New upstream used for SeaBIOS: <https://review.coreboot.org/seabios>
|
||||
* Dummy PIKE2008 option ROM now automatically inserted into ASUS KGPE-D16 and
|
||||
KCMA-D8 ROM images. It is literally an empty file. This disables the option
|
||||
ROM from being loaded, which is known to hang SeaBIOS on these boards.
|
||||
* 16MB configs now available, for more boards. For instance, ThinkPad X60 and
|
||||
T60, ASUS KGPE-D16, etc. It's always possible to upgrade the flash, and
|
||||
information about this is provided in the documentation.
|
||||
* `memtest86+` included on more ROMs by default (where text mode startup is used)
|
||||
* `memtest86+`: Now coreboot's own fork is used, instead of upstream. This fork
|
||||
works much more reliably on coreboot targets, when running on bare metal.
|
||||
* More 16MB configs added, for more boards. This will be finished by the time
|
||||
of the next release. Already, several older laptops such as the ThinkPad X60
|
||||
or T60, have these configs in the latest `lbmk.git`. If you upgrade the
|
||||
default SPI flash to 16MByte / 128MBit (maximum size possible), you can then
|
||||
easily put an entire busybox+linux system in the flash.
|
||||
* `coreboot`: Added persmule's 2016 patch to enable more SATA/eSATA ports on
|
||||
ThinkPad T400. This change benefits T400S users.
|
||||
* `grub.cfg`: LUKS setups are now detected on mdraid setups.
|
||||
* `grub.cfg`: Default timeout changed to 10 seconds, instead of 1. This benefit
|
||||
desktop users, who previously complained about not having time to respond if
|
||||
they wanted to interact with the boot menu.
|
||||
* `grub.cfg`: Performance optimization when scanning for encrypted LUKS volumes.
|
||||
GRUB will stall a lot less often, and feel more responsive, when dealing with
|
||||
LUKS-encrypted setups.
|
||||
* `coreboot`: cstate 3 now supported on MacBook2,1 and Macbook1,1. This results
|
||||
in lower CPU temperatures and higher battery life on idle. Thanks go to
|
||||
vitali64 on IRC for this fix
|
||||
* Reset bug fixed, on GM45 platforms (ThinkPad X200/T400/T500 and so on). These
|
||||
laptops did not reliably reboot, on the Libreboot 20210522 testing release.
|
||||
They now reboot reliably, with this fix. See:
|
||||
<https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbmk/issues/3>
|
||||
* `lbmk`: Use `env` instead of hardcoding the bash path, in bash scripts. This
|
||||
should make the build system slightly more portable between distros.
|
||||
* Turkish keyboard layout added on GRUB payloads
|
||||
|
||||
New release schedule under consideration
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
|
||||
The 20210522 release happened to coincide with coreboot 4.14's release, more
|
||||
or less.
|
||||
|
||||
This release also coincides roughly with the coreboot 4.15 release, which came
|
||||
out on November 5th. See:
|
||||
<https://doc.coreboot.org/releases/coreboot-4.15-relnotes.html>
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot has, since the 4.15 release, decided to release every 3 months instead
|
||||
of every 6. That means the coreboot 4.16 release is planned for February 2022.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm considering this: 2 releases every 3 months, of Libreboot. A testing release
|
||||
and then a fork of that is created, to fix bugs ready for a stable release 3
|
||||
months later, while simultaneously working (in the lbmk master branch) towards
|
||||
another testing release. *If no stable release is available at the same time as
|
||||
a testing release, then delay it if the delay will be minimal, otherwise
|
||||
cancel and abandon that particular stable branch.*
|
||||
|
||||
So: if I do this, the next stable release of Libreboot could be in February
|
||||
2022 based on bug fixes of this November 2021 release, using coreboot 4.15.
|
||||
A testing release could be simultaneously made, with perhaps extra features,
|
||||
and based on coreboot 4.16.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm considering it. In general, I do want Libreboot to be in sync with the
|
||||
coreboot project, but coreboot does not guarantee stability in their releases.
|
||||
Rather, releases are regarded as *milestones* for the coreboot developers to
|
||||
reflect on current developments, and plan the next few months.
|
||||
|
||||
When Libreboot first started, coreboot did not have a fixed release scheduled.
|
||||
It was purely rolling release. Coreboot however has been quite reliable with
|
||||
its own release schedules in the past few years, making it viable for Libreboot
|
||||
to also have a fixed schedule.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,243 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% Libreboot 20220710 released!
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 10 July 2022
|
||||
|
||||
Free your BIOS today!
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is free (as in freedom) boot firmware, which initializes the hardware
|
||||
(e.g. memory controller, CPU, peripherals) in your computer so that software
|
||||
can run. Libreboot then starts a bootloader to load your operating system. It
|
||||
replaces the proprietary BIOS/UEFI firmware typically found on a computer.
|
||||
Libreboot is compatible with specifical computer models that use the Intel/AMD
|
||||
x86 architecture. Libreboot works well with GNU+Linux and BSD operating systems.
|
||||
|
||||
The last Libreboot release, version 20211122, was released on November 22nd
|
||||
in 2021. *This* new release, Libreboot 20220710, is released today on July
|
||||
10th, 2022. This is intended to be a *stable* release, with some caveats.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a *bug fix* release, relative to 20211122. No new boards or major
|
||||
features have been added, but several problems that existed in the previous
|
||||
release have now been fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
Build from source
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
*This* release was build-tested on Debian 11. Your mileage may vary, with
|
||||
other distros. Portability is very much a goal for a future release; in
|
||||
particular, I want to port the Libreboot build system and everything it uses
|
||||
to build properly on OpenBSD, but I'm also interested in non-GNU Linux distros
|
||||
such as Alpine Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Much of the Libreboot build system relies on GNU-specific features, in the
|
||||
BASH implementation of `sh`.
|
||||
|
||||
Work done since the 20211122 release:
|
||||
-------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
* Lots and lots of improvements to the documentation. Previous 2021 testing
|
||||
releases did not include snapshots of the documentation (which is actually
|
||||
the Markdown source files for the website), but this release *does* include
|
||||
now a snapshot of the current Libreboot documentation, as per the time of
|
||||
release.
|
||||
* grub.cfg: Many performance improvements, improving the boot speeds
|
||||
when using the GNU GRUB payload (courtesy Ferass 'Vitali64' EL HAFIDI with
|
||||
additional improvements made by Leah Rowe)
|
||||
* GM45/ICH9M laptops: Disable PECI in coreboot, to work around a microcode bug
|
||||
causing SpeedStep (and possibly other CPU features) to fail.
|
||||
* Do not treat warnings as errors when building flashrom (fixes building on
|
||||
newer versions of GCC).
|
||||
* Macbook2,1: 16MB configurations now available (you must first upgrade the
|
||||
SPI flash)
|
||||
* Build system improvement: automated scripts for modifying coreboot configs.
|
||||
* Disable (by default) serial output on all boards, to prevent boot speed
|
||||
issues.
|
||||
* grub.cfg: Actually enable USB keyboards, explicitly (works around bug seen
|
||||
on some laptops, when using the GRUB payload).
|
||||
* Coreboot configs: Do not enable wifi during early init (security liability)
|
||||
* Preliminary u-boot integration; not used in any boards yet, but future
|
||||
full integration is planned, for several ARM platforms. U-boot is not
|
||||
included in the release archives, but logic does exist in the build system.
|
||||
Courtesy of Denis 'GNUtoo' Carikli.
|
||||
* Scripts in lbmk: improved help output, courtesy of Denis 'GNUtoo' Carikli.
|
||||
* scripts: process git versions when lbmk is a worktree or submodule. Courtesy
|
||||
John Doe (cool guy)
|
||||
* Updated to newer flashrom, in the build system
|
||||
* Perform silentoldconfig in seabios before full make. This fixes a race
|
||||
condition when rebuilding SeaBIOS with a high CPU count, resulting in failure
|
||||
with the error message (fix courtesy of John Doe):
|
||||
|
||||
cc1: fatal error: can't open 'out/src/asm-offsets.s' for writing: No such file or directory
|
||||
|
||||
* lbmk: Specifically call python3, when python3 is to be used instead of 2.
|
||||
* lbmk: Preliminary fix for git credentials check. Set a placeholder name/email
|
||||
if one is not set.
|
||||
|
||||
Caveats
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
Due to reported issues by users, these boards do not have ROM images
|
||||
available in the Libreboot 20220710 release:
|
||||
|
||||
* KGPE-D16 ROM images not included
|
||||
* ditto KCMA-D8
|
||||
* ditto GA-G41M-ES2L
|
||||
|
||||
GA-G41M-ES2L works *for me* but jxself on FSF IRC reported video init issues.
|
||||
If you have this board, and the 2021 releases don't work either, you might
|
||||
consider using upstream coreboot or the September 2016 Libreboot release.
|
||||
I will investigate this, and re-include ROMs for this board on the next
|
||||
release of Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
The boards listed above can still be compiled, from the source code archive
|
||||
in this release and from the Libreboot git repository; additionally, ROM images
|
||||
are provided for these in the previous release. D8/D16 continue to have raminit
|
||||
issues; for now, use the 2021 releases. The next Libreboot release will
|
||||
merge newer patches that are available for this board, improving raminit
|
||||
reliability (among other things); that new release will, when available, have
|
||||
D16 ROMs included.
|
||||
|
||||
All other boards are reasonably stable, and shouldn't provide any issues (no
|
||||
major issues reported, and/or non-blocking issues only).
|
||||
|
||||
Planned future work
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
In general, you should also check the issue tracker to find other notes.
|
||||
There is always more work to do, to improve Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Support for non-x86 platforms
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This is still on hold, but will be done as part of a future release.
|
||||
The coreboot firmware does support other platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux distro in flash
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This is another project that has been on hold for a while. The issue
|
||||
has been that I need a decent userland project. I've looked at many
|
||||
different userlands and recently (as of late June) decided to make
|
||||
my own. I want a BusyBox-like solution, but based on code from OpenBSD,
|
||||
ported to run under Linux with musl libc.
|
||||
|
||||
I want this distro to provide a kexec bootloader in flash, similar to Heads,
|
||||
and I also want it to use apk-tools, pointing at Alpine Linux repositories
|
||||
so as to allow any number of packages to be downloaded. It could also provide
|
||||
lots of utils in general, to be a live *rescue system* of sorts. Linux system
|
||||
in flash, that can bootstrap other systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Re-factor and optimize GRUB
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB is full of unused bloat that almost nobody uses, yet is in the current
|
||||
Libreboot builds. It's been on TODO for some time, but work has not yet
|
||||
begun on this project. My efforts are currently focused on the Linux distro.
|
||||
|
||||
What I want is a fork of GRUB, optimized to run on bare metal as a coreboot
|
||||
payload, on x86 and ARM platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
Planned osboot/Libreboot merger
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
*The plans below are a guiding principle, but the details may change, when
|
||||
or if (most likely when) this decision is implemented.*
|
||||
|
||||
In general, more hardware support is always a focus of the Libreboot project.
|
||||
With this in mind, a fundamental policy change in planned in the next release.
|
||||
|
||||
Read the policies of Libreboot and osboot. They differ, but the guiding
|
||||
philosophy behind them is exactly the same:
|
||||
|
||||
* <https://libreboot.org/news/policy.html>
|
||||
* <https://osboot.org/news/policy.html> (this will redirect to _newpolicy.html_
|
||||
on libreboot.org, and the current _policy.html_ will redirect
|
||||
to _oldpolicy.html_, on the libreboot site, when the decision is implemented)
|
||||
|
||||
The differences are clear, but they are not entirely irreconcilable. I had
|
||||
initially started *osboot* to be its own project, but I have concluded for some
|
||||
time now that this level of separation is inefficient. I've thought of a better
|
||||
way to run both projects. I initially planned to do an osboot release at the
|
||||
same time as a new Libreboot release, but this will no longer be done.
|
||||
|
||||
*This is the last Libreboot release*, under the current policy. The next
|
||||
Libreboot release will be conducted under a new policy, that accomodates both
|
||||
the current Libreboot policy and current osboot policy.
|
||||
|
||||
Basically, the differences between lbmk and osbmk are quite minor and osboot
|
||||
merely adds a few new features for platforms it supports that Libreboot does
|
||||
(can)not under current policy. This is not to say that the differences are
|
||||
not substantial, for those parts of osboot that do differ, but the overall
|
||||
structure and design of both build systems (libreboot and osboot) is exactly
|
||||
the same, and they're both easily adaptable.
|
||||
|
||||
What I want to do is refactor parts of the osboot build system so that you
|
||||
can pass an option (e.g. environmental variable) at build-time, which will
|
||||
dictate that any modules downloaded/built, and any ROMs built, will be created
|
||||
under current Libreboot policy.
|
||||
|
||||
Example, Libreboot-style, blobless:
|
||||
|
||||
FSDG= ./build boot roms all
|
||||
|
||||
Example, Osboot-style:
|
||||
|
||||
./build boot roms all
|
||||
|
||||
An option in `board.cfg` for each board would specify whether the given board
|
||||
can actually be built and booted this way, per current Libreboot policy.
|
||||
Therefore, a version of the current guidelines will still be made available.
|
||||
The *new* osboot-derived guidelines would be a separate document.
|
||||
|
||||
Where `board.cfg` does specify that FSDG is possible, non-FSDG configs can
|
||||
still be made available (for example: include microcode updates and don't
|
||||
provide microcode-related mitigations), while also providing FSDG compliant
|
||||
configs (no microcode updates, and related issues mitigated via patches if
|
||||
possible, e.g. PECI disable patch to fix SpeedStep on GM45/ICH9M machines).
|
||||
|
||||
This would then become the Libreboot build system, and the documentation on
|
||||
libreboot would integrate everything from osboot too, accomodating this new
|
||||
policy change. The Libreboot project would therefore have two policies:
|
||||
|
||||
* Current one, if building with FSDG option
|
||||
* Osboot one, if building without FSDG option
|
||||
|
||||
FSDG is the FSF guideline that Libreboot currently complies with, and which
|
||||
this release (Libreboot 20220710) adheres to.
|
||||
|
||||
Under this planned change, *two* sets of ROM images would be provided in
|
||||
the next Libreboot release:
|
||||
|
||||
* Limited subset, built based on current Libreboot policy. These sets would
|
||||
be similar to what you currently see in Libreboot releases.
|
||||
* Expanded set, based on current osboot policy
|
||||
|
||||
Under that next release, with the change made, both sets of ROM images would
|
||||
be built from the same source archive.
|
||||
|
||||
When this merger is conducted, the <https://osboot.org/> site will shut down
|
||||
and redirect (HTTP 301) to <https://libreboot.org/>. A new fusion of Libreboot
|
||||
and osboot will be born, continuing on *libreboot.org*.
|
||||
|
||||
This would then open up the Libreboot project to support more hardware, far
|
||||
more than it currently supports. The documentation would also be greatly
|
||||
improved, to more thoroughly specify what issues exist (if any) on a given
|
||||
board, as per *current Libreboot blob policy* and from an OSHW perspective.
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for this planned merger is pragmatic: I want to help more people
|
||||
to increase the amount of freedom they have, and most hardware currently
|
||||
supported by Libreboot is nearly impossible to find these days. In other words,
|
||||
it's a choice between abandoning Libreboot and focusing only on osboot, which
|
||||
itself is a new project that has to completely establish itself again, or to
|
||||
instead continue using the Libreboot name, and implementing this newly
|
||||
pragmatic decision as a means of *continuity*.
|
||||
|
||||
Even if more hardware is added to Libreboot under the current policy, I think
|
||||
this new change of direction is fundamentally *good*, because Libreboot is
|
||||
mainly about making coreboot as easy to use as possible. My feelings about
|
||||
this are already written in the current osboot policy.
|
||||
|
||||
I believe the Libreboot project is in a position to help people regardless, by
|
||||
focusing on the wider set of supported coreboot hardware while still catering
|
||||
to the existing Libreboot users (precisely the reason why the merger is
|
||||
planned, in exactly the manner as described above).
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Libreboot news
|
||||
title: osboot news
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
News about libreboot, both technical and organisational. Releases are also
|
||||
News about osboot, both technical and organisational. Releases are also
|
||||
announced here.
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
|
|||
BLOGTITLE="News for Libreboot.org"
|
||||
BLOGDESCRIPTION="News for Libreboot.org"
|
||||
BLOGTITLE="News for osboot.org"
|
||||
BLOGDESCRIPTION="News for osboot.org"
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,33 +1,51 @@
|
|||
% Binary blob extermination policy
|
||||
% Binary blob minimalisation policy
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 2 January 2022 (updated 23 January 2022)
|
||||
|
||||
This article was written by Leah Rowe, the founder and current lead developer
|
||||
of Libreboot.
|
||||
% 4 January 2022 (updated 23 January 2022)
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot intentionally *de-blobs* coreboot, which is to say that it does not
|
||||
include binary blobs. The coreboot software otherwise requires binary blobs on
|
||||
most systems that it has support for. Libreboot's version of coreboot is
|
||||
entirely *free*, on its consequently reduced set of supported mainboards.
|
||||
In the beginning Libreboot intentionally *de-blobbed* coreboot, which is to say that it did not
|
||||
include binary blobs. Coreboot, on the other hand, requires binary blobs on
|
||||
most systems that it has support for. Libreboot's
|
||||
entirely *"free"* version of coreboot consequently supported fewer mainboards.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot is designed to comply with the Free Software Foundation's
|
||||
[Respects Your Freedom criteria](https://ryf.fsf.org/about/criteria) and
|
||||
the [GNU Free System Distribution Guidelines (GNU FSDG)](https://www.gnu.org/distros/free-system-distribution-guidelines.en.html),
|
||||
ensuring that it is entirely [Free Software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html).
|
||||
Libreboot's zero blobs policy has
|
||||
been scrapped, entirely. The goal of current libreboot is simply to support every single
|
||||
system from coreboot, to provide pre-configured, automated compiling of ROM
|
||||
images for *all* of them. This is quite a lot more ambitious in terms of sheer
|
||||
workload, and maintenance. It is expected that the project will *grow* in the
|
||||
future, to accomodate *board maintainers*, just like you have *package
|
||||
maintainers* in Debian; the analogy is highly appropriate, given the nature
|
||||
of the libreboot build system, which you can learn more about on the [lbmk maintenance manual](../docs/maintain/).
|
||||
|
||||
It was decided that a formal policy should be written, because there is quite
|
||||
a bit of nuance that would otherwise not be covered. Libreboot's policies in
|
||||
this regard were previously ill defined.
|
||||
**Freedom is very much preferable and a world where everyone can use Free
|
||||
Software, exclusively, is to be welcomed. However, we do not yet live in that
|
||||
world.**
|
||||
|
||||
Background information
|
||||
======================
|
||||
The libreboot position is more like an opinion, as opposed to an actual policy.
|
||||
That opinion is this: *some* freedom is better than *zero* freedom. There are
|
||||
plenty of people with coreboot-compatible hardware, who wish to move away from
|
||||
otherwise fully proprietary boot firmware (usually supplied by the manufacturer
|
||||
of the hardware). The libreboot project is here to help! It provides a fully
|
||||
automated build system, making coreboot much easier to use, and it provides
|
||||
user-friendly [installation guides](../docs/install/) to help you get started.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot concerns itself only with what goes in the main boot flash IC, but
|
||||
Supporting more hardware, even if the hardware is less
|
||||
friendly to software freedom, will provide a path towards coreboot for more
|
||||
people, and it may lead to more coreboot development in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
Freedom is still the ultimate goal, and *coreboot* provides a lot more freedom
|
||||
to the user compared to fully proprietary vendor firmware. Making coreboot
|
||||
easier to use is a noble goal, and the result is that more people can achieve
|
||||
a level of computing freedom that they would otherwise not have.
|
||||
|
||||
Current project scope
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot project is concerned with what goes in the main boot flash IC, but
|
||||
there are other pieces of firmware to take into consideration, as covered
|
||||
in the [Libreboot FAQ](../faq.md#what-other-firmware-exists-outside-of-libreboot).
|
||||
in the [libreboot FAQ](../faq.md#what-other-firmware-exists-outside-of-osboot).
|
||||
|
||||
Most critical of these are:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,68 +54,103 @@ Most critical of these are:
|
|||
* Intel Management Engine / AMD PSP firmware
|
||||
|
||||
Specific binary blobs are also problematic, on most coreboot systems, but they
|
||||
differ per machine. Libreboot *excludes* binary blobs in releases, so it only
|
||||
supports a handful of machines from coreboot.
|
||||
differ per machine.
|
||||
|
||||
For information about Intel Management Engine and AMD PSP, refer to the FAQ.
|
||||
|
||||
So what *is* Libreboot's policy?
|
||||
================================
|
||||
Blob *minimalization* policy
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot follows a very conservative and *light touch* approach, when it comes
|
||||
to deblobbing coreboot.
|
||||
Default configurations
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot only excludes *software* binary blobs, plus CPU microcode updates,
|
||||
completely in line with FSF policy. *In practise, it is mostly microcode
|
||||
updates that Libreboot's build system deletes, along with coreboot Git history
|
||||
so that no traces remain of old revisions; older revisions had many blobs in
|
||||
the main repository, but modern coreboot moved almost all of them to third
|
||||
party submodule repositories.*.
|
||||
The libreboot project has the following policy:
|
||||
|
||||
*Non-software* blobs are permitted, so long as they are in an easily understood
|
||||
and/or well-documented format. For example, DDR training data is permitted
|
||||
(patterns used during memory controller initialization, specifically training,
|
||||
where the precise timings for the RAM are brute-forced); this is not software.
|
||||
* If a blob *can* be avoided, it should be avoided. For example, if VGA ROM
|
||||
initialization otherwise does a better job but coreboot has *free* init code
|
||||
for a given graphics device, that code should be used in libreboot, when
|
||||
building a ROM image. Similarly, if *memory controller initialization* is
|
||||
possible with a binary blob *or* free code in coreboot, the *free* code
|
||||
should be used in ROMs built by `lbmk`, and the *blob* for raminit should
|
||||
not be used; however, if no free init code is available for said raminit,
|
||||
it is permitted and lbmk will use the *blob*.
|
||||
* Some nuance is to be observed: on some laptop or desktop configurations, it's
|
||||
common that there will be *two* graphics devices (for example, an nvidia and
|
||||
an intel chip, using nvidia optimus technology, on a laptop). It may be that
|
||||
one of them has free init code in coreboot, but the other one does not. It's
|
||||
perfectly acceptable, and desirable, for libreboot to support both devices,
|
||||
and accomodate the required binary blob on the one that lacks native
|
||||
initialization.
|
||||
* An exception is made for CPU microcode updates: they are permitted, and in
|
||||
fact *required* as per libreboot policy. These updates fix CPU bugs, including
|
||||
security bugs, and since the CPU already has non-free microcode burned into
|
||||
ROM anyway, the only choice is either *x86* or *broken x86*. Thus, libreboot
|
||||
will only allow coreboot mainboard configurations where microcode updates
|
||||
are *enabled*, if available for the CPU on that mainboard.
|
||||
* Intel Management Engine: in the libreboot documentation, words *must* be written
|
||||
to tell people how to *neuter* the ME, if possible on a given board.
|
||||
The `me_cleaner` program is very useful, and provides a much more secure ME
|
||||
configuration.
|
||||
* Binary blobs should *never* be deleted, even if they are unused. In the
|
||||
coreboot project, a set of `3rdparty` submodules are available, with binary
|
||||
blobs for init tasks on many boards. These must *all* be included in libreboot
|
||||
releases, even if unused. That way, even if `lbmk` does not yet integrate
|
||||
support for a given board, someone who downloads libreboot can still make
|
||||
changes to their local version of the build system, if they wish, to provide
|
||||
a configuration for their hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
SPD data stored in the coreboot Git repository is in all cases some format
|
||||
that's simply more efficient to store as a binary, in a format that is in fact
|
||||
known/understood (see: coreboot source code and data sheets); in many cases,
|
||||
there's only *one* correct way to write such data, making even the question of
|
||||
copyright a moot point. Data is data, and code is code; the two are *separate*.
|
||||
Generally speaking, common sense is applied. For example, an exception to the
|
||||
minimalization might be if *blob* raminit and *free* raminit are available, but
|
||||
the *free* one is so broken so as to be unusable. In that situation, the blob
|
||||
one should be used instead, because otherwise the user might switch back to an
|
||||
otherwise fully proprietary system, instead of using coreboot (via libreboot).
|
||||
|
||||
Non-software blobs must be redistributable under a free license, and must not
|
||||
be encumbered by DRM, or they will not be included in Libreboot.
|
||||
Configuration
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Logic (in coreboot) for *loading or executing* binary blobs should not
|
||||
be removed/disabled. Libreboot merely *excludes* the blobs themselves. Most
|
||||
of the blobs that Libreboot removes (when downloading coreboot, in the build
|
||||
system) are CPU microcode updates; Libreboot leaves the code for loading
|
||||
microcode updates intact, and you can in fact insert microcode updates into
|
||||
your ROM image. This behaviour is intentional, and must not be removed. The
|
||||
only job Libreboot has is to not *distribute* those blobs itself!
|
||||
The principles above should apply to *default* configurations. However, libreboot
|
||||
is to be *configurable*, allowing the user to do whatever they like.
|
||||
|
||||
*That's all*. Furthermore, Libreboot must only support systems where *all* of
|
||||
the main boot flash can be free. For example, ivybridge and sandybridge intel
|
||||
platforms are completely libre in coreboot, but you still need neutered Intel
|
||||
ME firmware in the flash, making those machines unsuitable for Libreboot.
|
||||
It's natural that the user may want to create a setup that is *less* free than
|
||||
the default one in libreboot. This is perfectly acceptable; freedom is superior,
|
||||
and should be encouraged, but the user's freedom to choose should also be
|
||||
respected, and accomodated.
|
||||
|
||||
Other firmware, such as Embedded Controller firmware, is currently outside the
|
||||
scope of the Libreboot project, but not due to lack of desire; rather, these
|
||||
are not yet possible on most supported or otherwise capable platforms, at least
|
||||
not with free software. Other examples of firmware outside of the main boot
|
||||
flash is covered in the Libreboot FAQ.
|
||||
In other words, do not lecture the user. Just try to help them with their
|
||||
problem! The goal of the libreboot project is simply to make coreboot more
|
||||
accessible for otherwise non-technical users.
|
||||
|
||||
FREEDOM CATALOG
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
A *blob status* page should also be made available, educating people about the
|
||||
status of binary blobs on each machine supported by `lbmk`.
|
||||
|
||||
It is desirable to see a world where all hardware and software is free.
|
||||
Hardware!?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, hardware. RISC-V is a great example of a modern attempt at free hardware.
|
||||
It is a free ISA for the manufacture of a microprocessor. Many real-world
|
||||
implementations of it already exist, that can be used, and there will only be
|
||||
more.
|
||||
|
||||
Free *hardware* is still in its infancy. We should start a project that will
|
||||
catalog the status of various efforts, including at the hardware level (even
|
||||
the silicon level). Movements like OSHW and Right To Repair are extremely
|
||||
important, including to the Free Software movement which otherwise will
|
||||
typically think less about hardware freedom (even though it really, really
|
||||
should!)
|
||||
|
||||
Problems with RYF criteria
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
You can read those guidelines by following these hyperlinks:
|
||||
|
||||
* [GNU Free System Distribution Guidelines (GNU FSDG)](https://www.gnu.org/distros/free-system-distribution-guidelines.en.html)
|
||||
* [FSF Respects Your Freedom (RYF) guidelines](https://ryf.fsf.org/about/criteria)
|
||||
|
||||
The FSF RYF guidelines state the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*"However, there is one exception for secondary embedded processors. The exception applies to software delivered inside auxiliary and low-level processors and FPGAs, within which software installation is not intended after the user obtains the product. This can include, for instance, microcode inside a processor, firmware built into an I/O device, or the gate pattern of an FPGA. The software in such secondary processors does not count as product software."*
|
||||
* "However, there is one exception for secondary embedded processors. The exception applies to software delivered inside auxiliary and low-level processors and FPGAs, within which software installation is not intended after the user obtains the product. This can include, for instance, microcode inside a processor, firmware built into an I/O device, or the gate pattern of an FPGA. The software in such secondary processors does not count as product software."
|
||||
|
||||
This is a violation of every principle the FSF stands for, *and it should be
|
||||
rejected on ideological grounds*. The rest of libreboot's policy and overall
|
||||
|
|
@ -139,11 +192,11 @@ to user freedom, and ought to be free, but it is completely disregarded by
|
|||
the FSF as *part of the hardware*. This is wrong, and the FSF should actively
|
||||
actively encourage people to free it, on every laptop!
|
||||
|
||||
Other firmware currently outside the reach of the Libreboot project are covered
|
||||
in the Libreboot FAQ. For example, HDD/SSD firmware is covered in the FAQ.
|
||||
Other firmware currently outside the reach of the libreboot project are covered
|
||||
in the libreboot FAQ page. For example, HDD/SSD firmware is covered in the FAQ.
|
||||
Again, completely disregarded and shrugged off by the FSF.
|
||||
|
||||
The Libreboot project will not hide or overlook these issues, because they are
|
||||
The libreboot project will not hide or overlook these issues, because they are
|
||||
indeed critical, but again, currently outside the scope of what lbmk does.
|
||||
At the moment, lbmk concerns itself just with coreboot, but this ought to
|
||||
change in the future.
|
||||
|
|
@ -176,7 +229,7 @@ provide incentive for levels of software freedom, such as:
|
|||
blobs in a format fully documented by Intel (they are just binary configuration
|
||||
files), but I went ahead and wrote ich9gen anyway. With ich9gen, you can
|
||||
more easily modify the descriptor/gbe regions for your firmware image. See:
|
||||
<https://libreboot.org/docs/install/ich9utils.html> - osboot also has this
|
||||
<https://libreboot.org/docs/install/ich9utils.html> - libreboot also has this
|
||||
* FSF once endorsed the ThinkPad T400 with Libreboot, as sold by Minifree. This
|
||||
machine comes in two versions: with ATI+Intel GPU, or only Intel GPU. If ATI
|
||||
GPU, it's possible to configure the machine so that either GPU is used. If the
|
||||
|
|
@ -250,9 +303,10 @@ To be clear: it is preferable that microcode be free. The microcode on Intel
|
|||
and AMD systems *are* non-free. Facts and feelings rarely coincide; the
|
||||
purpose of this section is to spread *facts*.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot build system enables microcode updates *by default.*
|
||||
|
||||
Not including CPU microcode updates is an absolute disaster for system
|
||||
stability and security, and yet, this is one of Libreboot's key policies, to
|
||||
comply with FSF criteria.
|
||||
stability and security.
|
||||
|
||||
Making matters worse, that very same text quoted from the FSF RYF criteria in
|
||||
fact specifically mentions microcode. Quoted again for posterity:
|
||||
|
|
@ -290,18 +344,6 @@ To once again get in the head-space of the FSF: these updates cannot do the CPU
|
|||
equivalent of re-factoring an entire codebase. They are *hot fixes*, nothing
|
||||
more!
|
||||
|
||||
These processors provide a way to supply microcode *updates*. These updates
|
||||
are volatile, and consequently must be applied during every boot cycle. The
|
||||
updates fix stability/reliability/security bugs, and their *absence*
|
||||
is *technically incorrect*, but Libreboot excludes them anyway, because that is
|
||||
FSF policy. Examples of where these updates fix bugs: on ASUS KCMA-D8/KGPE-D16
|
||||
and ThinkPad X200/T400/T500/W500/X200T/X200/R500/X301, the updates make
|
||||
hardware-based virtualization (via `kvm`) completely stable, where it would
|
||||
otherwise lead to a kernel panic. They allow those same thinkpads to be run with
|
||||
high CPU usage and I/O (RAM usage), without crashing (otherwise, it's very
|
||||
likely to encounter a kernel panic caused by a
|
||||
[Machine Check Exception](../faq.html#machine-check-exceptions-on-some-montevina-penryn-cpu-laptops)).
|
||||
|
||||
Not including these updates will result in an unstable/undefined state. Intel
|
||||
themselves define which bugs affect which CPUs, and they define workarounds, or
|
||||
provide fixes in microcode. Based on this, software such as the Linux kernel
|
||||
|
|
@ -310,7 +352,7 @@ can update the microcode at boot time (however, it is recommend still to do it
|
|||
from coreboot, for more stable memory controller initialization or “raminit”).
|
||||
Similar can be said about AMD CPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some examples of where lack of microcode updates affected Libreboot,
|
||||
Here are some examples of where lack of microcode updates affected *Libreboot*,
|
||||
forcing Libreboot to work around changes made upstream in coreboot, changes
|
||||
that were *good* and made coreboot behave in a more standards-compliant manner
|
||||
as per Intel specifications. Libreboot had to *break* coreboot to retain
|
||||
|
|
@ -325,38 +367,45 @@ functionality but only when microcode updates are excluded. The most
|
|||
technically correct solution is to *not* apply the above patches, and instead
|
||||
supply microcode updates!
|
||||
|
||||
Pick your poison. Libreboot does not disable the mechanism in coreboot to load
|
||||
these updates. At boot time, coreboot can supply such updates to the CPU, if
|
||||
present in CBFS. Libreboot merely excludes them, but you can add them to your
|
||||
Libreboot ROM image. A fork of Libreboot, named osboot, includes them by
|
||||
default; it does this, even on libreboot-compatible hardware. Not adding the
|
||||
updates is *irresponsible*, but a promise was made to the FSF back in 2013
|
||||
when the Libreboot project started, precisely that it would not add microcode
|
||||
to ROM images by default. It is Libreboot's policy to keep that promise,
|
||||
despite the *obvious* flaw of that policy.
|
||||
Pick your poison. Not adding the updates is *irresponsible*, and ultimately
|
||||
futile, because you still end up with non-free microcode anyway, just you get
|
||||
an older, buggier version instead!
|
||||
|
||||
More info about osboot is available on <https://osboot.org/> - osboot's policy
|
||||
is the same as Libreboot, except that it does *not* delete blobs; the goal is
|
||||
still software freedom, but it provides those users who are not willing/able
|
||||
to use libreboot hardware to otherwise still have some freedoms compared to
|
||||
otherwise fully proprietary *vendor* firmware. osboot and libreboot are two
|
||||
sides of a coin; neither should exist alone.
|
||||
The libreboot build system does not apply the two patches linked above! Instead,
|
||||
CPU microcode updates are enabled by default, on the affected boards. The
|
||||
result is superior IA32 feature control and added PECI support.
|
||||
|
||||
The osboot firmware is far superior to Libreboot, in terms of reliability, due
|
||||
The libreboot project rejects the FSF's narrow, dogmatic view entirely.
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot firmware is far superior to Libreboot, in terms of reliability, due
|
||||
to the presence of microcode updates in the firmware, and with zero practical
|
||||
change to your freedom, on libreboot-compatible hardware. However, I will say:
|
||||
change to your freedom, on libreboot-compatible hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
People have been using Libreboot for years, on these machines, and most people
|
||||
don't really have *that* many issues, most of the time. My opposition to FSF's
|
||||
microcode policy is out of principle. *Logical*, common sense principle. I
|
||||
simply cannot compute that microcode updates are an attack on your freedom,
|
||||
because:
|
||||
However:
|
||||
|
||||
Microcode updates are not an attack on your freedom. The FSF's opposition to
|
||||
these updates is both symbolic and *ignorant*; it is ultimately futile, but I
|
||||
digress.
|
||||
**I will continue to develop Libreboot and libreboot, in parallel.**
|
||||
|
||||
**I will continue to develop Libreboot and osboot, in parallel.**
|
||||
There are some people who still want Libreboot, who believe in FSF principles
|
||||
on this subject, and I believe it would ultimately be damaging if I were to
|
||||
just *shut down* the Libreboot project. I do not agree with the policies of
|
||||
the Libreboot project; I was only following the FSF's instructions when I made
|
||||
it, all those years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
If I were to cancel Libreboot, my fear is that such people would be stubborn
|
||||
and end up, ironically, being less likely to use coreboot-based firmware. This
|
||||
is for a very human reason: such people might try (fail) to make their *own*
|
||||
Libreboot instead. I believe I'm in the best position to run such a project, to
|
||||
ensure that a good job is being performed. I *want* to help people, even those
|
||||
people, *because I want everyone to have freedom*. I also believe in freedom of
|
||||
choice, and Libreboot is an excellent choice for those who wish to use something
|
||||
that complies with FSF criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
Thus, I continue developing Libreboot in parallel with libreboot, even though
|
||||
Libreboot is technically *inferior* to libreboot. The *osboot* project is where
|
||||
my heart truly lies. I'm completely in it, whereas Libreboot is something I
|
||||
also maintain on the side. I try to do my best, when working on both projects.
|
||||
I really don't mind maintaining both of them, because they are actually very
|
||||
similar anyway, on relevant hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
Other considerations
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
|
@ -395,7 +444,9 @@ completely disregards many things that are now possible, including freedoms at
|
|||
the hardware level (the RYF criteria only covers *software*). Those guidelines
|
||||
are written with assumptions that were still true in the 1990s, but the world
|
||||
has since evolved. As of 2 January 2022, Libreboot still complies strictly with
|
||||
RYF, and will continue to do so, at least for the time being.
|
||||
RYF, and will continue to do so, at least for the time being. The libreboot
|
||||
project rejects those policies in their entirety, and instead takes a pragmatic
|
||||
approach.
|
||||
|
||||
The conclusion that should be drawn from all of this is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -407,7 +458,7 @@ As has always been the case, Libreboot tries to always go above and beyond, but
|
|||
the Libreboot project does not see RYF as a *gold standard*. There are levels
|
||||
of freedom possible now that the RYF guidelines do not cover at all, and in
|
||||
some cases even actively discourage/dis-incentivize because it makes compromises
|
||||
based on assumptions that are no longer true.
|
||||
based on assumptions that are no longer true.
|
||||
|
||||
Sad truth: RYF actively encourages *less* freedom, by not being bold enough.
|
||||
It sets a victory flag and says *mission accomplished*, despite the fact
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
|||
% Translations wanted
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 11 December 2021
|
||||
% 4 January 2022
|
||||
|
||||
The libreboot website is currently only available in English.
|
||||
|
||||
I've recently added support for translations to
|
||||
the [Untitled Static Site Generator](https://untitled.vimuser.org/), which the
|
||||
Libreboot website uses. Pages on libreboot.org are written in Markdown, and
|
||||
libreboot website uses. Pages on libreboot.org are written in Markdown, and
|
||||
this software generates HTML pages.
|
||||
|
||||
This very page that you are reading was created this way!
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,16 +14,16 @@ This very page that you are reading was created this way!
|
|||
Getting started
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
The Libreboot website is available, in Markdown, from a Git repository:\
|
||||
<https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww>
|
||||
The libreboot website is available, in Markdown, from a Git repository:\
|
||||
<https://notabug.org/libreboot/osbwww>
|
||||
|
||||
Instructions for how to send patches are available here:\
|
||||
<https://libreboot.org/git.html>
|
||||
|
||||
If you're working on a translation, make note of the commit ID from `lbwww.git`
|
||||
If you're working on a translation, make note of the commit ID from `osbwww.git`
|
||||
and keep track of further changes (to the English website) in that repository.
|
||||
|
||||
When you send the translation, please specify what commit ID in `lbwww.git` it
|
||||
When you send the translation, please specify what commit ID in `osbwww.git` it
|
||||
is up to date with. From then on, I will keep track of changes to the English
|
||||
website, which is what I work on. My native language is English. When the first
|
||||
translation is made available on libreboot.org, I will create a new page (in
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,290 +0,0 @@
|
|||
% New Hampshire (USA) may soon enshrine Software Freedom into law. YOUR HELP IS NEEDED!
|
||||
% Leah Rowe
|
||||
% 8 January 2022
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction
|
||||
============
|
||||
|
||||
This event of such global importance to [Free
|
||||
Software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) projects, and the Free
|
||||
Software movement as a whole, has made me decide to write an article. **The
|
||||
events in question, covered by this article, will occur on 11 January 2022.
|
||||
This is just three days away from today, 8 January 2022 when this article was
|
||||
written, so if you make a decision, you should make it now, today, and prepare.
|
||||
Please continue reading.**
|
||||
|
||||
If you live in New Hampshire or in one of the neighbouring states, especially
|
||||
Massachusetts, please listen up! If you are further away and unable to reach
|
||||
New Hampshire all that easily, please spread the following news anyway. It's
|
||||
important. As alien as it may seem to many of my readers, I'm actually writing
|
||||
parts of this article as though someone who has never heard of Free Software is
|
||||
reading it, because I expect precisely that such people *will* read this
|
||||
particular article.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the term *Free Software* used in this article, but some people
|
||||
call it Open Source Software. [However, you should call it Free
|
||||
Software.](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/open-source-misses-the-point.html)
|
||||
The word "free" refers to freedom, not price, though the software is usually
|
||||
also free as in gratis / zero price.
|
||||
|
||||
The opposite of Free Software is called *proprietary software*, or *non-free
|
||||
software*. Proponents of Open Source sometimes call non-free software *Closed
|
||||
Source*, but you should call it *non-free* or proprietary, to highlight the
|
||||
fact that it isn't free.
|
||||
|
||||
What's happening in New Hampshire?
|
||||
==================================
|
||||
|
||||
An important bill is being proposed in New Hampshire, which would enshrine
|
||||
much of what we know as Free Software *into law*. Here is the proposed bill,
|
||||
technically named "HB1273":\
|
||||
<https://gencourt.state.nh.us/bill_status/legacy/bs2016/billText.aspx?sy=2022&id=1363&txtFormat=html>
|
||||
|
||||
You can read it for yourself, but here is a paraphrasing of what it proposes:
|
||||
|
||||
* *Specifically* bans state-run websites from serving non-free javascript to
|
||||
clients
|
||||
* Creates a commission to provide oversight, watching the use of Free Software by state agencies
|
||||
* Bans state agencies from using proprietary software - maybe this could include schools, in the future!
|
||||
* If a person is tried in a criminal case, they have the right to audit the source code of any proprietary software that collects evidence against them
|
||||
* Encourages data portability (able to transfer data from one program to another)
|
||||
* Bans certain non-compete clauses and NDAs (non-disclosure agreements) pertaining to Free Software projects
|
||||
* Bans state/local law enforcement from assisting with the enforcement of copyright claims against Free Software projects
|
||||
* Bans state agencies from purchasing non-free software if free software exists, for a given task
|
||||
|
||||
However, this is only a short summary. You are advised to read the bill in
|
||||
detail. It's not very long.
|
||||
|
||||
At first glance, it may not seem that the bill affects individuals, but don't
|
||||
be fooled; this is a hugely positive step forward for everyone! If the state is
|
||||
using Free Software, that most likely means it'll be used in education aswell.
|
||||
|
||||
Although perhaps not immediately and readily apparent, this is a stake in the
|
||||
heart of proprietary software's current dominance, because it would remove one
|
||||
key element of its attack against us; its abuse of education services.
|
||||
|
||||
If education services are using Free Software, that means they'll probably have
|
||||
children (the ones being educated) using it too. This is a *huge* step, and it
|
||||
will result in more Free Software developers in the future. Free Software will
|
||||
become more and more mainstream to the masses, which can surely only be a good
|
||||
thing!
|
||||
|
||||
Freedom is always superior. The more people that have it, the better off we all
|
||||
are, because freedom is also collective; it relies on others around us also
|
||||
having it, so that we can defend each other. If more people have it, especially
|
||||
if it results in more Free Software developers in the future, that's one thing,
|
||||
but imagine if *more* states like what they see and start to copy the new
|
||||
legislation.
|
||||
|
||||
Now imagine that countries besides the US start doing it, inspired by the US's
|
||||
success (and I think it will be a resounding success).
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine a world where [Free
|
||||
Software](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html), free as in freedom, is
|
||||
the default everywhere. Imagine a world where [Free Software
|
||||
licensing](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.html) is required reading
|
||||
material in schools. *Imagine a world where any five year old can install a
|
||||
free operating system such as GNU+Linux, and Computer Science is mandatory in
|
||||
schools from a young age. Imagine filing your tax returns with Free Software,
|
||||
exclusively. Imagine not even thinking about that, because it became the norm.*
|
||||
|
||||
*Imagine a world where proprietary software doesn't exist, because it is
|
||||
obsolete; entire generations of people are taught to value freedom, and to
|
||||
staunchly defend it, helping each other learn and grow (and produce better
|
||||
software in the process, with less bugs, because people are now free to do
|
||||
that, without relying on some evil company).*
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine a world where you're no longer being spied on because NSA, Apple and
|
||||
Microsoft no longer have backdoor access to your computer. *Imagine having the
|
||||
ability to say no, because that's what freedom is. Try to imagine it!*
|
||||
|
||||
Free Software is a revolution that we in the Free Software movement have
|
||||
rigorously upheld and fought for, over many years, but we still face an uphill
|
||||
battle because children are not taught in schools about free computing, nor are
|
||||
they encouraged to learn; they are taught to view computers as *products* to
|
||||
throw away every 1-2 years, that they can run a few *apps* on but otherwise are
|
||||
not allowed to do anything with. The *concept* of a *general purpose, fully
|
||||
reprogrammable computer* is heavily suppressed in mainstream culture. *Most*
|
||||
people in the world do not run a free operating system; the idea of a computer
|
||||
being a mere *appliance* is normalized (as opposed to the idea of it being a
|
||||
highly liberating tool for development and the expansion of human knowledge).
|
||||
|
||||
*This* is what we in the Free Software movement have fought for over the years.
|
||||
We believe that knowledge is a human right, that the ability to share, study,
|
||||
learn, adapt and modify the software is an inalienable right that everyone must
|
||||
have. [The four freedoms are absolute.](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html)
|
||||
|
||||
One of our biggest problem has been simply that schools and governments do not
|
||||
teach people about free computing. The right to learn, the right to read and
|
||||
the right to hack. Our governments are made up of human beings just like you or
|
||||
me, and they can be bought/corrupted; Microsoft, Apple and many others (such as
|
||||
IBM) have done this for years, having the national infrastructures governing us
|
||||
run on their proprietary systems, instead of systems that respect freedom; it
|
||||
is essential that these systems run free software, because a free and democratic
|
||||
society should expect nothing less. Those companies buy influence *and they own
|
||||
your politicians*.
|
||||
|
||||
All of this could change very soon. Something is happening in New Hampshire,
|
||||
which could redefine our movement and give *free software* real power
|
||||
instead.
|
||||
|
||||
HOW TO HELP
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
TESTIFY IN SUPPORT OF THE BILL
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
**The reading of the bill is happening on 11 January 2022. This is when you
|
||||
should go to New Hampshire.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Location of hearing: Legislative Office Building in Concord, New Hampshire:\
|
||||
<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Hampshire_Legislative_Office_Building>**
|
||||
|
||||
The organizer of the proposed bill, *Eric Gallager*, has left instructions on
|
||||
Twitter. The following is a *nitter* link, which lets you view the relevant
|
||||
Twitter thread without running non-free Javascript in your browser:\
|
||||
<https://nitter.net/cooljeanius/status/1479663133207764992>
|
||||
|
||||
The original Twitter URL is:\
|
||||
<https://twitter.com/cooljeanius/status/1479663133207764992>
|
||||
|
||||
Further instructions for what room to go to, when you get there:\
|
||||
|
||||
See Nitter link:\
|
||||
<https://nitter.net/cooljeanius/status/1479062316532604930>
|
||||
|
||||
(original twitter link: <https://twitter.com/cooljeanius/status/1479062316532604930>)
|
||||
|
||||
**Please read both threads very carefully!**
|
||||
|
||||
**YOU NEED TO GO TO NEW HAMPSHIRE IN PERSON!**
|
||||
|
||||
If you're able to go to New Hampshire to attend the reading of the bill, please
|
||||
do so! Voice your support of the bill, and say why you think it's important.
|
||||
|
||||
Tell the lawmakers that you demand freedom!
|
||||
|
||||
This thread on Twitter is where Eric announced that the reading of the bill is
|
||||
to proceed (original Twitter URL):\
|
||||
<https://twitter.com/cooljeanius/status/1479555737223413760>
|
||||
|
||||
More states/countries will follow
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
If this bill is passed in New Hampshire, more states will likely follow. It
|
||||
will lead to a massively renewed drive to liberate all computer users, and US
|
||||
laws tend to be copied/pasted around the world too.
|
||||
|
||||
This bill, if passed, will have a hugely positive impact on Free Software at a
|
||||
global level.
|
||||
|
||||
You *must* support this bill. If you want to see it pass, please go to New
|
||||
Hampshire on 11 January 2022 to make sure your voice is heard.
|
||||
|
||||
OUR ENEMIES WILL BE THERE
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The *proprietary* software companies like Microsoft and Apple will also be
|
||||
there, trying to argue the case *against* the use of Free Software.
|
||||
|
||||
There is already precedent; please watch this video, which shows how Microsoft
|
||||
(for example) might behave in the reading of the bill. This video is from a
|
||||
discussion within the European Union, several years ago:\
|
||||
<https://vid.puffyan.us/watch?v=W_S0k1sx8EM> (invidious link. works without
|
||||
javascript enabled, if you wish)
|
||||
|
||||
They will try to trick the law makers by claiming things such as:
|
||||
|
||||
* **"Free software is insecure / you will get hacked"** - nothing could be
|
||||
further from the truth! Free operating systems such as GNU+Linux, FreeBSD and
|
||||
especially OpenBSD, are among the most secure operating systems available.
|
||||
* **"Free software is used by criminal hackers"** - here, they use the
|
||||
term *hacker* to describe someone who illegally gains access to someone
|
||||
elses computer. Don't fall for it. Maintainers of free operating systems
|
||||
like GNU+Linux distros or the BSDs are actively working to make the internet
|
||||
and computers in general *more secure*
|
||||
* **"Software authors deserve to be paid!"** - In fact, many free software devs
|
||||
are *paid* to work on Free Software! Many companies, including big ones,
|
||||
work on it. There are also hobbyists or otherwise unpaid people, who might
|
||||
work on Free Software for a number of reasons (wanting to make the world a
|
||||
better place, wanting the glory of recognition for solving a major problem,
|
||||
and more often than not, simply because *it is fun to do so and you make a
|
||||
lot of friends too!*) - No, these companies (e.g. Microsoft) are only arguing
|
||||
in reality for the ability to pay their *shareholders*, and they control the
|
||||
software exclusively. In fact, free software has repeatedly and consistently
|
||||
over the years *defined* the computing industry, creating all kinds of new
|
||||
employment opportunities; for example, docker is widely used today and it is
|
||||
free software, used by millions of companies for commercial gain, and the
|
||||
apache web server revolutionized the web back in the day, enabling lots of
|
||||
ISPs to easily host websites - many of the common protocols that we depend
|
||||
upon today, that businesses depend upon (and get paid to maintain or provide
|
||||
services/support for) are in fact free as in freedom!
|
||||
* **"Developers should get recognition for their work"** - in free software, you
|
||||
can easily make a name for yourself with relatively few resources except your
|
||||
own computer and an internet connection, plus some cheap hosting. When most
|
||||
developers work on *proprietary* software such as Windows, they don't get
|
||||
recognition; their copyright is assigned to their employer (e.g. Microsoft)
|
||||
who will take all the credit!
|
||||
* **"Free software is unreliable / costly to maintain"** - actually, it has been
|
||||
well known for years that free software is generally more stable and reliable
|
||||
than proprietary. In cases where it isn't, it is quickly improved, and in
|
||||
complete freedom. Free software has a lower cost to maintain and service, and
|
||||
you have a free market where you can choose who you hire to write/maintain it
|
||||
for you (if you won't do that yourself); meanwhile, proprietary software
|
||||
such as Windows is often full of bugs, crashes often and there is only one
|
||||
provider of support most of the time, who will charge a heavy price, while
|
||||
also charging a lot of money for the software itself - free software
|
||||
is *free as in freedom*, but also usually *free as in zero price*.
|
||||
* **"Free software comes from potentially untrustworthy sources"** - This is
|
||||
pure nonsense, because the very freedoms provided by free software (access
|
||||
to source code, ability to work on it yourself, and see what others did)
|
||||
means that people generally do not add malware to public software sources,
|
||||
because they'd be discovered instantly. *Distributions* of GNU+Linux and
|
||||
other free operating systems are often maintained by many people, who verify
|
||||
the safety of each software package that they provide; they are also usually
|
||||
provided by each *distro*, in a central repository unlike with, say, Windows
|
||||
where you really *are* randomly executing binaries from all kinds of
|
||||
locations (often even without checking the cryptographic checksums of those
|
||||
files, to verify their integrity). It's very hard to become infected with
|
||||
malware on a free system, precisely because security is handled much better;
|
||||
the design of unix-like operating systems in particular is also naturally
|
||||
more secure, due to better separation of root/user privileges.
|
||||
* **"Free software isn't controlled, and is unknown."** - this is completely
|
||||
false. These non-free software companies are only talking about *their*
|
||||
control, and it's quite telling that they completely disregard yours, in this
|
||||
very sentence. In fact, Free Software *is* controlled, but it's not controlled
|
||||
by some external entity; *your* installation of free software is controlled
|
||||
by *you*.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're familiar with the *Matrix* films, proprietary operating systems like
|
||||
Windows/MacOS are basically like the Matrix; bland, no individuality, no
|
||||
independent thought, everything tightly controlled. By contrast, free operating
|
||||
systems (such as GNU+Linux distributions or the BSDs) are like zion/io; vibrant,
|
||||
full of life, buzzing with activity, everything loose and free, and everyone
|
||||
is different (a highly diverse culture of people from all walks of life, acting
|
||||
in common cause but nonetheless individuals).
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, Windows is known to have backdoors. Microsoft actively informs the
|
||||
NSA about how to exploit them, so that it can break into people's computers
|
||||
and steal private data.
|
||||
|
||||
Proprietary software companies are evil, and must be opposed. They know that
|
||||
if this bill passes, their days are numbered.
|
||||
|
||||
Defend freedom! Don't listen to any of the arguments against it by proprietary
|
||||
software companies; they don't care about you, and instead only care about
|
||||
profit. They fundamentally do not want you to have any sort of freedom over
|
||||
your own computer, and they actively pursue tactics (such as DRM) to thwart you.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft and Apple are not your friends. There is no such thing as the
|
||||
Windows community. When you use proprietary systems, you are isolated from
|
||||
everyone around you, and so are they. *You* are the product, for the non-free
|
||||
software to exploit at the behest of their developers who only care
|
||||
about *money*.
|
||||
|
||||
However, there *is* such a thing as the Free Software community. It is a
|
||||
vibrant community, consisting of millions of people collectively all over the
|
||||
world, and they are all free to work with each other infinitely. It gave us
|
||||
most of the technology that we take for granted today, including *the modern
|
||||
internet, where ISPs run free software almost exclusively!*
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2,8 +2,7 @@
|
|||
title: Site map
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Explore the vast mountains of libreland that is libreboot.org!
|
||||
Bots are very much welcome, in this land.
|
||||
Site map of osboot.org
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,751 +0,0 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Tasks
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Help the Libreboot project
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
This page is very new. It's intended to serve those who ask: what can I do to
|
||||
help Libreboot? You could try implementing some of the tasks listed on this page
|
||||
or you could submit new tasks to this page!
|
||||
|
||||
Current tasks (more will be added soon)
|
||||
=======================================
|
||||
|
||||
Move all distro FDE+/boot/ guides to distro wiki/manuals
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The Guix, Fedora, Parabola and Trisquel guides were outdated and therefore
|
||||
deleted. The Debian guide should also be deleted, even though it's up to date.
|
||||
The hyperbola one is actually a link to a guide on the Hyperbola site.
|
||||
|
||||
These are guides for fully encrypted GNU+Linux systems, including /boot, but
|
||||
it's desirable for these to be documented instead by each distro, because then
|
||||
they will more likely be properly maintained.
|
||||
|
||||
We constantly have to update them, on libreboot.org. It is unsustainable. Move
|
||||
them to other projects and let them deal with it. Libreboot's only job is to
|
||||
boot you into a payload. The rest is up to you!
|
||||
|
||||
This concerns GRUB payload on x86 targets. For SeaBIOS, it's fairly easy to
|
||||
just push a button and the distro installer boots, or the installed distro
|
||||
just boots up as normal.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are links to the guides that were deleted:
|
||||
|
||||
* <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww/src/8844c201ef0d1ab856fed2aa5148b89100fffe0d/site/docs/gnulinux/guix_system.md>
|
||||
* <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww/src/8844c201ef0d1ab856fed2aa5148b89100fffe0d/site/docs/gnulinux/encrypted_trisquel.md>
|
||||
* <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww/src/8844c201ef0d1ab856fed2aa5148b89100fffe0d/site/docs/gnulinux/encrypted_parabola.md>
|
||||
* <https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww/src/8844c201ef0d1ab856fed2aa5148b89100fffe0d/site/docs/gnulinux/configuring_parabola.md>
|
||||
|
||||
The Trisquel one will be almost identical to the Debian one, with perhaps a few
|
||||
extra considerations taken. It's recommended to focus on Debian first, and
|
||||
then adapt that to Trisquel. However, Trisquel is based on Ubuntu, so the
|
||||
guide can also be adapted for the Ubuntu site. This will cover most Ubuntu and
|
||||
Debian based distros.
|
||||
|
||||
The remaining Debian guide is here:
|
||||
<https://notabug.org/libreboot/lbwww/src/8844c201ef0d1ab856fed2aa5148b89100fffe0d/site/docs/gnulinux/encrypted_debian.md>
|
||||
|
||||
Document other RPi GNU+Linux distros for SPI flashing
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See:
|
||||
[../docs/install/spi.md#caution-about-rpi](../docs/install/spi.md#caution-about-rpi)
|
||||
|
||||
RPi's default distro, Raspbian, no longer can be trusted to be secure. TODO:
|
||||
document how to use other distros, to configure the RPi for SPI flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
bug: crossgcc not included in src archive if not already build
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
fix this. in practise, i always build the roms and then run the release scripts
|
||||
which means crossgcc will have been built, but this bug should still be fixed.
|
||||
this is so that you can simply run the release build scripts right after
|
||||
downloading the git repository
|
||||
|
||||
ThinkPad R60 support
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
macc24 on IRC ported it. add it!
|
||||
|
||||
Investigate u-boot
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
e.g. Pine64 ROCKPro64, which was added in coreboot 4.14
|
||||
but it's also supported by uboot
|
||||
|
||||
Lots of ARM hardware supported in coreboot, and lots of non-coreboot hardware
|
||||
out there with free firmware, but using uboot (not coreboot)
|
||||
|
||||
Pinebook computers look interesting:
|
||||
|
||||
Some of their computers look like they will be suitable for Libreboot, but they
|
||||
are ARM and most of them don't have coreboot support (instead, they use uboot
|
||||
exclusively).
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB: add BLS support
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
Resources:
|
||||
|
||||
* [The systemd's Boot Loader Specification](https://systemd.io/BOOT_LOADER_SPECIFICATION)
|
||||
* [The freedesktop.org's Boot Loader Specification](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/MatthewGarrett/BootLoaderSpec/)
|
||||
* [systemd-boot](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd-boot.html) - uefi app
|
||||
|
||||
Create a board-status repo, like coreboot
|
||||
-----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See: <https://review.coreboot.org/plugins/gitiles/board-status/>
|
||||
|
||||
For testing boards in Libreboot (and osboot-libre), it would be nice to have
|
||||
reports like on coreboot board-status entries.
|
||||
|
||||
This is especially important *now*, because lots of boards are being added to
|
||||
both Libreboot and osboot-libre. It will *especially* be important for
|
||||
osboot-libre, after the Libreboot release, because osboot-libre will start to
|
||||
focus on being a rolling release, bleeding edge coreboot distro, while
|
||||
Libreboot focuses on stable release. *board-status* entries like these will be
|
||||
invaluable to both projects.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: i945: test framebuffer(non-i915) init during S3 resume
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See notes here: <https://doc.coreboot.org/releases/coreboot-4.8.1-relnotes.html>
|
||||
|
||||
video init is skipped on i945 now, during S3 resume, to save time, and the i915
|
||||
linux kernel driver can handle that, but other drivers should be tested. e.g.
|
||||
generic corebootfb driver, drivers in various BSD systems, etc
|
||||
|
||||
61a3c8a005 payloads/tianocore: Add Kconfig to set boot timeout
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
this is from the coreboot git log. looks interesting. investigate
|
||||
|
||||
Document the following boards
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
These boards are added, but not documented yet
|
||||
|
||||
### Acer G43T-AM3
|
||||
|
||||
See: [flashrom_read_me_disable.log.txt](flashrom_read_me_disable.log.txt)\
|
||||
This is from Michael Büchler, whom I emailed, asking for info about this board.
|
||||
This is the person who ported the board to coreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Michael states the following:\
|
||||
````
|
||||
I'm also attaching a flashrom read log. The filename suggests that I
|
||||
had the ME disable pin set.. so this was with the "-p internal"
|
||||
flasher, but the SPI_ROM1 header also works. The pinout is 1:1 the same
|
||||
as the EEPROM.
|
||||
|
||||
This reminds me that I wanted to create a page for this board on the
|
||||
coreboot documentation. There you would have found this info. I should
|
||||
do it soon.
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
ME disable pin? Probably setting GPIO33 or something. I've replied to Michael,
|
||||
encouraging that person to document this board on the coreboot website.
|
||||
|
||||
indeed, next to the southbridge is a jumper and the silk screen says "ME disable"
|
||||
so I'm guessing this is actually just GPIO33 being grounded. so it's not simply
|
||||
disabling the ME, but the intel flash descriptor (which also disables NVM, not
|
||||
just the ME)
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some photos:
|
||||
TODO: add photos that michael sent me. i'm waiting for michael to confirm what
|
||||
license. for now see these photos that i pulled from a search engine:
|
||||
|
||||
* <ttps://pc-1.ru/pic/big/1186411.jpg>
|
||||
* <https://i5.walmartimages.com/asr/7ded9e88-73e6-4bc4-9b2a-ff22313c7172_2.9abea30734ddf03fc15b7188cb3e92cd.jpeg>
|
||||
|
||||
For flashing instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
* Refer to <https://av.libreboot.org/g43t-am3/soic8.jpg> - a proper photo is
|
||||
not available under a free license, or could not be found, so this diagram
|
||||
was made
|
||||
* NOTE: It might not be possible to do ISP flashing. Several other X4X desktop
|
||||
mainboards are problematic.
|
||||
* FOR EXAMPLE: <https://doc.coreboot.org/mainboard/intel/dg43gt.html>
|
||||
* That's another X4X board, and it recommends to de-solder the flash
|
||||
* It might be that this board, linked above, can be flashed ISP-style, but
|
||||
the person who wrote that page was using a 3.3V rail from a flasher like RPi
|
||||
or whatever, and maybe the flash chip shares a common rail with the southbridge
|
||||
or something else that draws a lot of current
|
||||
* On GA-G41M-ES2L, it's possible to power on the board, then turn it off but
|
||||
leave it plugged in, and a 3.3V rail from the ATX PSU will be active, powering
|
||||
the chip and providing more than enough current. In that situation, you connect
|
||||
your SPI flasher without using your SPI flasher's 3.3V rail. That may also be
|
||||
the case on this board, and the one linked dabove.
|
||||
|
||||
I couldn't find exact schematics/boardviews, but I did find this:
|
||||
|
||||
* <http://download.ecs.com.cn/dlfileecs/manual/mb/eng/p4/G43T_MV10/G43T-M_V20.pdf>
|
||||
|
||||
2MiB flash chip according to:\
|
||||
<https://review.coreboot.org/plugins/gitiles/board-status/+/refs/heads/master/acer/g43t-am3/4.12-4089-gb7e591e2da/2020-11-17T18_20_46Z/config.txt> and
|
||||
<https://review.coreboot.org/plugins/gitiles/board-status/+/refs/heads/master/acer/g43t-am3/4.12-3211-gfb623a02c5/2020-10-11T11_24_19Z/config.txt>
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: i think this is ICH10. Kconfig mentions IFD. flash it descriptorless
|
||||
based on intel/dg43gt port using "motherboard porting guide"
|
||||
|
||||
coreboot ba49d859eeaeced032403b2da6a5f34ea2a93a94 added it. The following is
|
||||
from that coreboot revision, in the commit log:
|
||||
|
||||
* Same board as Aspire M5800 (same vendor BIOS image)
|
||||
* Similar mainboards by Acer: G41T-AM, G43T-AM, G43T-AM4, Q45T-AM, to name a few.
|
||||
* ECS has some models that are obiously based on the same design, e.g. G43T-WM and G43T-M.
|
||||
|
||||
Working (ignore the note about Windows. Libreboot project doesn't care about
|
||||
that. This is just copied from the coreboot git log):
|
||||
|
||||
* CPUs from Pentium Dual-Core E2160 to Core 2 Quad Q9550 at FSB1333
|
||||
* Native raminit
|
||||
* All four DIMM slots at 1066 MHz (tested 2x2GB + 2x4GB)
|
||||
* PS/2 mouse
|
||||
* PS/2 keyboard (needs CONFIG\_SEABIOS\_PS2\_TIMEOUT, tested: 500)
|
||||
* USB ports (8 internal, 4 external)
|
||||
* All six SATA ports
|
||||
* Intel GbE
|
||||
* Both PCI ports with various cards (Ethernet, audio, USB, VGA)
|
||||
* Integrated graphics (libgfxinit)
|
||||
* HDMI and VGA ports
|
||||
* boot with PCIe graphics and SeaBIOS
|
||||
* boot with PCI VGA and SeaBIOS
|
||||
* Both PCIe ports
|
||||
* Flashing with flashrom
|
||||
* Rear audio output
|
||||
* SeaBIOS 1.14.0 to boot slackware64
|
||||
* SeaBIOS 1.14.0 to boot Windows 10 (needs VGA BIOS)
|
||||
* Temperature readings (including PECI)
|
||||
* Super I/O EC automatic fan control
|
||||
* S3 suspend/resume
|
||||
* Poweroff
|
||||
|
||||
Not working:
|
||||
|
||||
* Resource issues with the VGA BIOS of a PCI rv100-based card
|
||||
* Super I/O voltage reading conversions
|
||||
|
||||
Untested:
|
||||
|
||||
* The other audio jacks or the front panel header
|
||||
* On-board Firewire
|
||||
* EHCI debug
|
||||
* VBT (was extracted and added, but don't know how to test)
|
||||
* Super I/O GPIOs
|
||||
|
||||
Generate ICH10 descriptor/nvm
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Coreboot has a few Intel X4X boards with ICH10 southbridge. These can be booted
|
||||
descriptorless, but in some cases those boards will use an Intel gigabit NIC,
|
||||
which means that the NIC will be useless in a descriptorless setup.
|
||||
|
||||
Basically `ich9utils` but for ich10. However, it's preferable to generate it
|
||||
using bincfg. Intel provides some limited information about ICH10 descriptors
|
||||
in public datasheets. The rest can be guessed at like it was for ICH9M in
|
||||
libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Re-do desktop boards
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Right now, the configs make no sense. VGA ROM setup (for external GPU) also
|
||||
runs libgfxinit, and vice versa, on KCMA-D8 / KGPE-D16, and in many
|
||||
configs, both coreboot and seabios run pci roms. There needs to be consistency
|
||||
here.
|
||||
|
||||
I think there should be separation:
|
||||
|
||||
* libgfxinit. coreboot doesn't load pci roms. seabios loads them
|
||||
* vgarom-only setup, where coreboot runs pci roms. seabios doesn't load them
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following boards
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: some of these might not be suitable for Libreboot. Each one will be
|
||||
checked, before adding it to Libreboot.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: also check under "variants" for each board, and add more to this list if
|
||||
any are found. These lists are generated by greping Kconfig files but sometimes
|
||||
multiple boards are specified in a single Kconfig file. For example, macbook21
|
||||
Kconfig also specifies imac52 and macbook11 without any code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
### lenovo/g505s
|
||||
|
||||
Last I checked, video init was a problem on this laptop. (binary blob, but
|
||||
there was some work to implement free video initialization)
|
||||
|
||||
It might still be worth looking into
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel x4x platform
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: some use ICH7 southbridge.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: others use ICH10, and some of *those* have Intel ME + descriptor. others
|
||||
have descriptorless setup (no Intel ME). *all* of them can boot descriptorless,
|
||||
so it's possible to nuke the Intel ME on all of them (ICH7 ones never have ME
|
||||
to begin with)
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: this is the same platform used by Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L which Libreboot
|
||||
already supports. that one uses an ICH7 southbridge
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dell Optiplex 760
|
||||
|
||||
vitali64 on IRC is porting this to coreboot, and has it almost fully working
|
||||
|
||||
#### asrock/g41c-gs
|
||||
|
||||
Variants:
|
||||
|
||||
* g41c-gs-r2
|
||||
* g41m-gs
|
||||
* g41m-s3
|
||||
* g41m-vs3-r2
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/p5qc
|
||||
|
||||
Variants:
|
||||
|
||||
* p5q\_pro
|
||||
* p5ql\_pro
|
||||
* p5q
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/p5ql-em
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified in Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/p5qpl-am
|
||||
|
||||
Variants:
|
||||
|
||||
* p5g41t-m\_lx
|
||||
|
||||
#### foxconn/g41s-k
|
||||
|
||||
Variants:
|
||||
|
||||
* g41m
|
||||
|
||||
#### intel/dg41wv
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified in Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### intel/dg43gt
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified in Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### lenovo/thinkcentre\_a58
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified in Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel Pineview platform
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: same platform as Intel D510MO / D410PT
|
||||
|
||||
* foxconn/d41s
|
||||
|
||||
### GM45 / ICH9M
|
||||
|
||||
#### lenovo/x301 (thinkpad x200 variant)
|
||||
|
||||
ThinkPad X200 variant. Use standand ICH9M descriptor+nvm image
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel i945
|
||||
|
||||
same platform as X60/T60 thinkpads. some of these are desktops, so there will
|
||||
be some differences. it's unlikely that Intel ME will be an issue on any of
|
||||
them.
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/p5gc-mx
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### getac/p470
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### gigabyte/ga-945gcm-s2l
|
||||
|
||||
Variants:
|
||||
|
||||
* ga-945gcm-s2c
|
||||
|
||||
#### ibase/mb899
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### kontron/986lcd-m
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### roda/rk886ex
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
### AMD Fam10h / Fam15h
|
||||
|
||||
These boards are not a priority at the moment, but they will be added at some
|
||||
point (*after* the post-2016 release). These were all deleted from coreboot in
|
||||
version 4.11 (they are fam10h/15h boards). On this TODO page is an entry
|
||||
asking whether to fork coreboot 4.11 and maintain it, backporting newer features
|
||||
from coreboot, making it work with newer GCC toolchains, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: some of these are a *big* if, but many of them will work nicely without
|
||||
binary blobs when booting. NOTE: use of a VGA option ROM is implied, and
|
||||
Libreboot won't provide these, but the user could install an add-on graphics
|
||||
card and coreboot/seabios would just run whatever is on the card. There is no
|
||||
problem with Libreboot running those, because they could be free or non-free,
|
||||
we just don't know.
|
||||
|
||||
In practise, most of these probably don't have native video initialization in
|
||||
coreboot for the onboard GPU (if present), because it's probably an AMD/ATI
|
||||
one and libgfxinit doesn't have good support for those (it mostly has
|
||||
excellent support for Intel video chipsets).
|
||||
|
||||
This doesn't mean Libreboot can't support them. It just means that we will have
|
||||
to provide ROM images that don't use libgfxinit. Instead, the ROMs provided
|
||||
will always run VGA option ROMs present on the GPU. Here we mean add-on video
|
||||
cards, which means there's no way for the Libreboot project to predict what
|
||||
hardware will be used. It means that any GPU could be used. It probably implies
|
||||
use of SeaBIOS, but coreboot itself is able to run those VGA ROMs which enables
|
||||
other payloads (such as GNU GRUB) to be used reliably (with text mode startup).
|
||||
|
||||
Where external VGA ROMs are concerned, Libreboot prefers for coreboot to run
|
||||
them, and for SeaBIOS to run run them, OR, for SeaBIOS to run it but be the
|
||||
main payload.
|
||||
|
||||
In cases where coreboot runs the VGA ROM, it can also run other PCI ROMs, and
|
||||
SeaBIOS doesn't need to do anything (and in fact shouldn't do anything).
|
||||
|
||||
On boards that *do* have libgfxinit support, coreboot isn't running any PCI
|
||||
ROMs, which means no PCI ROMs for GRUB, which means you should use the SeaBIOS
|
||||
payload, either as the main payload or chainloaded from GRUB.
|
||||
|
||||
Also: it's still possible to use a serial console. You could use any of these
|
||||
boards in a headless server setup, with no graphics card.
|
||||
|
||||
Also: there are USB VGA adapters available. Driver support in the Linux kernel
|
||||
is flaky for a lot of them, but you might be able to get some sort of desktop
|
||||
usage out of these boards, if you used one of them (there would be no display
|
||||
during early boot, but you would see something when booting your kernel). With
|
||||
llvmpipe driver you could actually get good use out of these. They are usually
|
||||
a simple framebuffer chip inside.
|
||||
|
||||
#### advansus/a785e-i
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### amd/bimini\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### amd/mahogany\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### amd/serengeti\_cheetah\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### amd/tilapia\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/m4a785-m
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/m4a785t-m
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/m4a78-em
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### asus/m5a88-v
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### avalue/eax-785e
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### gigabyte/ma785gm
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### gigabyte/ma785gmt
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### gigabyte/ma78gm
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### hp/dl165\_g6\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### iei/kino-780am2-fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### jetway/pa78vm5
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### msi/ms9652\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### supermicro/h8dmr\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### supermicro/h8qme\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### supermicro/h8scm\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### tyan/s2912\_fam10
|
||||
|
||||
No variants specified by Kconfig
|
||||
|
||||
### gm45
|
||||
|
||||
#### thinkpad w700
|
||||
|
||||
<http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/Category:W700>
|
||||
|
||||
might be fun to work on. probably doesn't require much modification in
|
||||
coreboot, if any. buy one and port it to coreboot
|
||||
|
||||
There are photos on this page:
|
||||
|
||||
<http://web.archive.org/web/20210510205738/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/573>
|
||||
|
||||
Linuxboot payload
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
Linuxboot is a busybox+linux system available here:\
|
||||
<https://www.linuxboot.org/>
|
||||
|
||||
It goes in bootflash. It provides a bootloader program called u-root, which
|
||||
uses kexec to boot other kernels. It also provides some UEFI features, and it
|
||||
can parse GNU GRUB configuration files. It requires a large amount of flashing
|
||||
space (at least 12MiB, but it might be possible to squeeze it into 8MiB).
|
||||
|
||||
The problem is: it is using the upstream Linux kernel. TODO: fork Linuxboot and
|
||||
make the fork use linux-libre. Check other packages too. With this, a fully
|
||||
libre (by FSF standards) busybox+linux distro can be made, based on Linuxboot.
|
||||
|
||||
Linuxboot-libre is the working name for this new project. It will absolutely
|
||||
knock the wind out of GRUB and anything else, on setups where it's possible to
|
||||
use this payload.
|
||||
|
||||
Other payloads will still be retained, of course.
|
||||
|
||||
Fork coreboot 4.11 and maintain, for fam10h/15h boards
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Nowadays, coreboot removes boards. For example, KCMA-D8 and KGPE-D16 (and others
|
||||
were removed) from coreboot because they don't support relocatable ramstage,
|
||||
`C_ENVIRONMENTAL_BOOTBLOCK`, postcar and a few other features are required now
|
||||
in coreboot ports.
|
||||
|
||||
For libreboot purposes, it's mostly AMD Fam10/15h boards that were removed.
|
||||
These were maintained based on AMD's AGESA codebase, which was never properly
|
||||
integrated. It was just bolted on to coreboot, without honouring coreboot's
|
||||
native coding style and maintaining it was very difficult. The person maintaining
|
||||
fam10h/15h boards (in particular KCMA-D8 and KGPE-D16) had stopped doing work
|
||||
on those boards at that point.
|
||||
|
||||
Libreboot currently does not fork coreboot, and it never has. Rather, it has
|
||||
been a downstream distribution of coreboot, de-blobbing it and patching it
|
||||
when necessary. This was sustainable before, because more or less just one
|
||||
revision could be used.
|
||||
|
||||
There are mainly 2 choices:
|
||||
|
||||
* Re-add deleted boards to coreboot
|
||||
* Fork older coreboot revisions with those other boards, and keep backporting
|
||||
newer features from later coreboot revisions
|
||||
(for instance, coreboot now has the ability to clear all DRAM on every bootup
|
||||
but this configuration option is unavailable on KCMA-D8 and KGPE-D16 mainboards)
|
||||
|
||||
In practise, since this mostly affects fam10h/fam15h boards, it's probably
|
||||
*easier* to do the latter; fork older coreboot revision (version 4.11 in this
|
||||
case) and start backporting newer features; the current code works well, and
|
||||
only minor fixes will be needed here and there over time (e.g. patch it up to
|
||||
work on newer GCC versions when building).
|
||||
|
||||
Forking the *entire* coreboot project and maintaining it for more than just a
|
||||
few boards isn't really practical. It is best to cooperate with upstream, but
|
||||
in this case we are talking only about boards that were deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
It's always possible to bring the code on those deleted boards up to date again
|
||||
in the future, for re-entry into the coreboot master repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Test SeaBIOS option: etc/usb-time-sigatt
|
||||
----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
default is 500ms. setting it higher like 1000s might make USB drives work in
|
||||
SeaBIOS on KFSN4-DRE. see notes
|
||||
on <https://www.seabios.org/Runtime_config#Option_ROMs>
|
||||
|
||||
SST+macronix patches for flashrom on X60/T60
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
These binaries are referenced in the documentation currently not actually
|
||||
available and the build system (lbmk) does not produce them.
|
||||
|
||||
Warnings about option ROMs
|
||||
--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
They're bad because they're non-free. They violate the four freedoms.
|
||||
Libreboot enables automatic loading of PCI option ROMs in some setups, simply
|
||||
for the purpose of technical correctness, because there's no rule that says an
|
||||
option ROM must be non-free. It's possible that an option ROM might actually be
|
||||
free software.
|
||||
|
||||
Banning option ROMs in Libreboot desktops would be like banning all software
|
||||
from executing in an operating system, just because those programs might be
|
||||
non-free.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, the *correct* solution ethically is to just tell people not to use
|
||||
non-free software, and for the *libreboot project* to never directly recommend,
|
||||
distribute or document non-free software.
|
||||
|
||||
Use coreboot's memtest86+ fork
|
||||
------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The current version used does build, but it doesn't run, or it glitches out.
|
||||
That version of memtest is designed to be run on a normal BIOS system, so it
|
||||
might actually work with the SeaBIOS payload, but we want to use a memtest
|
||||
version that is guaranteed to work on bare metal, which is more common on
|
||||
Libreboot systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini site for libreboot
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini is a popular alternative to the web. See:
|
||||
<https://gemini.circumlunar.space/>
|
||||
|
||||
I've noticed a lot of projects starting to offer this, in addition to a regular
|
||||
website.
|
||||
|
||||
pandox2gem i'm told is a good tool that could integrate with the current static
|
||||
site generator, which uses pandoc (the pages are written in markdown)
|
||||
|
||||
Tor site for libreboot
|
||||
----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
hidden onion service
|
||||
|
||||
host it separately from the main site, on a different server. that way, there
|
||||
is another website just in case
|
||||
|
||||
2nd HTTP site
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Have different DNS records for ns2. specifically, different IPv4+6 for the site.
|
||||
When the main ns1 is down, the new website will kick in. (ns1 and ns2 are both
|
||||
currently hosted on the same network as the website)
|
||||
|
||||
i2p site
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
I probably won't, but someone is welcome to do this and libreboot.org will
|
||||
link to it
|
||||
|
||||
Fix GRUB bugs
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
Many of these bugs only happen in bare metal, and only on devices supported by
|
||||
libreboot. See:
|
||||
|
||||
<http://web.archive.org/web/20210510213902/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/561>
|
||||
|
||||
Security patch: spectre MSR fixes for Fam15h boards
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See: <http://web.archive.org/web/20210510214458/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/440>
|
||||
|
||||
Document teensy SPI flasher
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The following page has information, which can be assimilated:
|
||||
<https://trmm.net/SPI_flash/>
|
||||
|
||||
Also see:
|
||||
<https://www.flashrom.org/Teensy_3.1_SPI_%2B_LPC/FWH_Flasher>
|
||||
|
||||
Also see this interesting firmware here:
|
||||
<https://github.com/urjaman/frser-teensyflash>\
|
||||
NOTE: i've made a local git clone of this
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: document use of schottky diode for VCC on SPI flash (ISP)
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
this type of diode has minimal voltage drop. most flashes run close to their
|
||||
specified 3.3v, sometimes a bit higher, but the tolerated range is between 2.7
|
||||
and 3.6v
|
||||
|
||||
notes about use of a diode is already specified in the external flashing guide
|
||||
but those notes should be improved
|
||||
|
||||
* x200 (after cutting solder bridge - R405 - between flash chip and ICH9M)
|
||||
* x200s/x200t/w700 - 25xx flash Vcc is hardwired :( (to be confirmed on production board)
|
||||
* t400/t400s/t500/x301 - 25xx flash Vcc is hardwired, as everything else on UCI/lenovo boards
|
||||
|
||||
Document alternative external flashing method for X200S/X200T
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
GNUtoo wrote this interested guide:
|
||||
<https://framagit.org/GNUtoo/coreboot-scripts/-/tree/master/flash-wson8>
|
||||
|
||||
It still requires external flashing, but no soldering.
|
||||
|
||||
TODO: what about bucts? the bootblock is protected by PR4, but is it possible
|
||||
to use BUCTS and init from another bootblock?
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE TO SELF: a local git clone has been made of the above
|
||||
|
||||
Handle SATA power in ultrabay on gm45 thinkpads
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See:
|
||||
<http://web.archive.org/web/20201022210929/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/484>
|
||||
|
||||
document serial/lpt/pcie bus enable/disable on GA-G41M-ES2L
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
See:
|
||||
<http://web.archive.org/web/20210510214317/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/469>
|
||||
|
||||
This might be why graphics cards and add-on network cards didn't work on mine,
|
||||
last time i tested it. it's a config option that must be enabled in coreboot?
|
||||
|
||||
Document quad-core mods on GM45 thinkpads
|
||||
-----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: MAX\_CPUS=4 is now the default, in coreboot, for these machines.
|
||||
|
||||
There's a mod for T500 thinkpads, but it will
|
||||
work on any gm45 thinkpad supported in libreboot.
|
||||
Just have to study the schematics and boardview,
|
||||
then adapt the info available online for T500.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: max CPUs has to be set in coreboot
|
||||
|
||||
Document a *clean* way to do it. The current guides online have you drilling
|
||||
holes in the CPU socket! That's why they won't be linked here.
|
||||
|
||||
Some notes are already written here. expand upon them:
|
||||
<http://web.archive.org/web/20210307234010/https://notabug.org/libreboot/libreboot/issues/340>
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ The file `template.include` is the modified version (modified by Leah Rowe).
|
|||
The original version can be found here: [/template.original](/template.original)
|
||||
|
||||
Other modified templates may be used, on specific pages. Check for this on the
|
||||
Git repository for the Libreboot website.
|
||||
Git repository for the libreboot website.
|
||||
|
||||
The original template file named `template.original` by John MacFarlane was
|
||||
released under these conditions:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
28
site/who.md
28
site/who.md
|
|
@ -1,31 +1,37 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Who develops Libreboot?
|
||||
title: Who develops libreboot?
|
||||
x-toc-enable: true
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
The purpose of this page is to clearly define who works on Libreboot, who runs
|
||||
The purpose of this page is to clearly define who works on libreboot, who runs
|
||||
the project, how decisions are made, and in general how the project functions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find information about major contributions made to Libreboot, on this
|
||||
You can find information about major contributions made to libreboot, on this
|
||||
page which lists such people: [List of contributors](contrib.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Leah Rowe (founder, lead developer)
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
Leah Rowe is the founder of the Libreboot project, and currently the only
|
||||
full-time developer. Leah oversees all development of Libreboot, reviewing
|
||||
Leah Rowe is the founder of the libreboot project. Leah oversees all development of libreboot, reviewing
|
||||
outside contributions, and has the final say over all decisions. Leah owns and
|
||||
operates the libreboot.org servers from her lab in the UK. The servers are
|
||||
running Libreboot of course!
|
||||
operates the libreboot.org servers from her lab in the UK.
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about Leah's involvement with Libreboot, by reading her
|
||||
You can learn more about Leah's involvement with libreboot, by reading her
|
||||
entry on the [page listing all contributors, past and present](contrib.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Caleb La Grange
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
Caleb goes by the screen name `shmalebx9`.
|
||||
Caleb mainly deals with improvements to the lbmk build system, board porting,
|
||||
and documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about Caleb's involvement with libreboot, by reading his
|
||||
entry on the [page listing all contributors, past and present](contrib.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Developers wanted!
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
Leah is the only developer right now. This section will be updated when more
|
||||
developers join the
|
||||
project. **Learn how to contribute patches on the [git page](git.md)**
|
||||
**Learn how to contribute patches on the [git page](git.md)**
|
||||
|
||||
All are welcome to join in on development.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue