297 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
297 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
|
|
% nonGeNUine Boot 20230717 released!
|
|||
|
|
% Leah Rowe in GNU Leah Mode™
|
|||
|
|
% 17 July 2023
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Original GNU Boot ("gnuboot") release
|
|||
|
|
=====================================
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This project was *originally* named GNU Boot or *gnuboot*, unofficially, with
|
|||
|
|
the intent that it would be re-used by the *real* GNU Boot project, to help them
|
|||
|
|
get in sync with modern Libreboot releases; on 17 July 2023, they still used
|
|||
|
|
very old Libreboot releases, with old coreboot revisions from around ~mid 2021.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This non-**G**e**NU**ine release was renamed to *nonGeNUine Boot* after
|
|||
|
|
receiving a [legal threat, citing trademark infringement](#update-21-july-2023)
|
|||
|
|
from the official GNU Boot project.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
More context for this is provided by the Libreboot project. See:
|
|||
|
|
[GNU Boot article on libreboot.org](https://libreboot.org/news/gnuboot.html)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Introduction
|
|||
|
|
============
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
nonGeNUine Boot provides boot firmware for supported x86/ARM machines, starting a
|
|||
|
|
bootloader that then loads your operating system. It replaces proprietary
|
|||
|
|
BIOS/UEFI firmware on x86 machines, and provides an *improved* configuration
|
|||
|
|
on [ARM-based chromebooks](../docs/install/chromebooks.html) supported
|
|||
|
|
(U-Boot bootloader, instead of Google's depthcharge bootloader). On x86
|
|||
|
|
machines, the GRUB and SeaBIOS coreboot
|
|||
|
|
payloads are officially supported, provided in varying configurations per
|
|||
|
|
machine. It provides an [automated build system](../docs/maintain/) for the
|
|||
|
|
[configuration](../docs/build/) and [installation](../docs/install/) of coreboot
|
|||
|
|
ROM images, making coreboot easier to use for non-technical people. You can find
|
|||
|
|
the [list of supported hardware](../docs/hardware/) in nonGeNUine Boot documentation.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
nonGeNUine Boot's main benefit is *higher boot speed*,
|
|||
|
|
[better](../docs/gnulinux/encryption.md)
|
|||
|
|
[security](../docs/gnulinux/grub_hardening.md) and more
|
|||
|
|
customisation options compared to most proprietary firmware. As a
|
|||
|
|
[libre](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.html) software project, the
|
|||
|
|
code can be audited, and coreboot does
|
|||
|
|
regularly audit code. The other main benefit is [*freedom* to study, adapt and
|
|||
|
|
share the code](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.en.html), a freedom
|
|||
|
|
denied by most boot firmware, but not nonGeNUine Boot! Booting GNU+Linux and BSD is
|
|||
|
|
also [well](../docs/gnulinux/) [supported](../docs/bsd/).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Changes, relative to Libreboot 20220710
|
|||
|
|
========================================
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
nonGeNUine Boot is a fork of Libreboot. This release is based on Libreboot 20230625,
|
|||
|
|
with certain boards/documentation removed so as to comply with the [GNU
|
|||
|
|
System Distribution Guidelines (GNU
|
|||
|
|
FSDG)](https://www.gnu.org/distros/free-system-distribution-guidelines.en.html).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
*Libreboot 20220710* was the *last* regular Libreboot release to comply
|
|||
|
|
with the old *Binary Blob Extermination Policy* adhering to GNU FSDG
|
|||
|
|
ideology. Read the [Libreboot 20220710 release
|
|||
|
|
announcement](https://libreboot.org/news/libreboot20220710.html).
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
For the purpose of *continuity*, this release will list changes relative to that
|
|||
|
|
version. Future releases of nonGeNUine Boot will reference past releases of *itself*.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
New mainboards supported
|
|||
|
|
------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
These laptops would have been compatible with Libreboot, under the old
|
|||
|
|
policy, and they were added in this release of nonGeNUine Boot:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* [Dell Latitude E6400](../docs/hardware/e6400.md)
|
|||
|
|
* [ASUS Chromebook Flip C101 (gru-bob)](../docs/install/chromebooks.md)
|
|||
|
|
* [Samsung Chromebook Plus (v1) (gru-kevin)](../docs/install/chromebooks.md)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
KFSN4-DRE, KCMA-D8, KGPE-D16 *update*
|
|||
|
|
-------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
FUN FACT: This includes building of ASUS KFSN4-DRE, KCMA-D8 and KGPE-D16
|
|||
|
|
boards, which were updated based on coreboot `4.11_branch`. ROM images are
|
|||
|
|
provided for these boards, in this nonGeNUine Boot release. The toolchain in
|
|||
|
|
this coreboot version would not build on modern GNU+Linux distributions, so I
|
|||
|
|
spent time patching it.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Coreboot, GRUB, U-Boot and SeaBIOS revisions
|
|||
|
|
------------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In nonGeNUine Boot 20230717:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot (default): commit ID `e70bc423f9a2e1d13827f2703efe1f9c72549f20`, 17 February 2023
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot (cros): commit ID `8da4bfe5b573f395057fbfb5a9d99b376e25c2a4` 2 June 2022
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot (fam15h\_udimm): commit ID `1c13f8d85c7306213cd525308ee8973e5663a3f8`, 16 June 2021
|
|||
|
|
* GRUB: commit ID `f7564844f82b57078d601befadc438b5bc1fa01b`, 14 February 2023
|
|||
|
|
* SeaBIOS: commit ID `ea1b7a0733906b8425d948ae94fba63c32b1d425`, 20 January 2023
|
|||
|
|
* U-Boot (for coreboot/cros): commit ID `890233ca5569e5787d8407596a12b9fca80952bf`, 9 January 2023
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
In Libreboot 20220710:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot (default): commit ID `b2e8bd83647f664260120fdfc7d07cba694dd89e`, 17 November 2021
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot (cros): **did not exist** (no ARM/U-Boot support in Libreboot 20220710)
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot (fam15h\_udimm): commit ID `ad983eeec76ecdb2aff4fb47baeee95ade012225`, 20 November 2019
|
|||
|
|
* GRUB: commit ID `f7564844f82b57078d601befadc438b5bc1fa01b`, 25 October 2021
|
|||
|
|
* SeaBIOS: commit ID `1281e340ad1d90c0cc8e8d902bb34f1871eb48cf`, 24 September 2021
|
|||
|
|
* U-Boot: **did not exist** (no ARM/U-Boot support in Libreboot 20220710)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Build system changes
|
|||
|
|
--------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The changes are *vast*, and most of them visible directly by viewing the
|
|||
|
|
Libreboot git history; for reference, this nonGeNUine Boot release corresponds
|
|||
|
|
approximately to `lbmk` (LibreBoot MaKe)
|
|||
|
|
revision `8c7774289ca60a1144b3151344eb400a059390e0` from 16 July 2023.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
And now, the changes (summarised, relative to Libreboot 20220710):
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot crossgcc downloads: when coreboot downloads `acpica` (for use
|
|||
|
|
of `iasl`), the old upstream links to tarballs are no longer online. Newer
|
|||
|
|
versions of coreboot pull from github, but nonGeNUine Boot is still using some
|
|||
|
|
older coreboot revisions prior to that change. The corresponding tarballs
|
|||
|
|
are now hosted on Libreboot rsync, and used by nonGeNUine Boot's build
|
|||
|
|
system, [gbmk](../docs/maintain/) (itself a fork of the Libreboot build
|
|||
|
|
system, named `lbmk`).
|
|||
|
|
* A [HUGE build system audit](https://libreboot.org/news/audit.html) inherited
|
|||
|
|
from Libreboot, has been assimilated by nonGeNUine Boot; the entire build system was
|
|||
|
|
re-written in a much cleaner coding style, with much stricter error handling
|
|||
|
|
and clear separation of logic. A *lot* of bugs were fixed. A *LOT* of bugs.
|
|||
|
|
Build system auditing has been the *main* focus, in these past 12 months.
|
|||
|
|
* `cros`: Disable coreboot-related BL31 features. This fixes poweroff on gru
|
|||
|
|
chromebooks. Patch courtesy of Alper Nebi Yasak.
|
|||
|
|
* `u-boot`: Increase EFI variable buffer size. This fixes an error where
|
|||
|
|
Debian's signed shim allocates too many EFI variables to fit in the space
|
|||
|
|
provided, breaking the boot process in Debian. Patch courtesy Alper Nebi Yasak
|
|||
|
|
* Coreboot build system: don't warn about no-payload configuration. nonGeNUine Boot
|
|||
|
|
compiles ROM images *without* using coreboot's payload support, instead it
|
|||
|
|
builds most payloads by itself and inserts them (via cbfstool) afterwards.
|
|||
|
|
This is more flexible, allowing greater configuration; even U-Boot is
|
|||
|
|
handled this way, though U-Boot at least still uses coreboot's crossgcc
|
|||
|
|
toolchain collection to compile it. Patch courtesy Nicholas Chin.
|
|||
|
|
* `util/spkmodem-recv`: New utility, forked from GNU's implementation, then
|
|||
|
|
re-written to use OpenBSD style(9) programming style instead of the
|
|||
|
|
originally used GNU programming style, and it is uses
|
|||
|
|
OpenBSD `pledge()` when compiled on OpenBSD. Generally much cleaner coding
|
|||
|
|
style, with better error handling than the original GNU version (it is forked
|
|||
|
|
from coreboot, who forked it from GNU GRUB, with few changes made). This
|
|||
|
|
is a receiving client for spkmodem, which is a method coreboot provides to
|
|||
|
|
get a serial console via pulses on the PC speaker.
|
|||
|
|
* download/coreboot: Run `extra.sh` directly from given coreboot tree. Unused
|
|||
|
|
by any boards, but could allow expanding upon patching capabilities in lbmk
|
|||
|
|
for specific mainboards, e.g. apply coreboot gerrit patches in a specific
|
|||
|
|
order that is not easy to otherwise guarantee in more generalised logic of
|
|||
|
|
the nonGeNUine Boot build system.
|
|||
|
|
* `util/e6400-flash-unlock`: New utility, that disables flashing protections
|
|||
|
|
on Dell's own BIOS firmware, for Dell Latitude E6400. This enables nonGeNUine Boot
|
|||
|
|
installation *without* disassembling the machine (external flashing equipment
|
|||
|
|
is *not required*). Courtesy Nicholas Chin.
|
|||
|
|
* Build dependencies scripts updated for more modern distros. As of this day's
|
|||
|
|
release, nonGeNUine Boot compiles perfectly in bleeding edge distros e.g. Arch
|
|||
|
|
Linux, whereas the previous 20220710 required using old distros e.g.
|
|||
|
|
Debian 10.
|
|||
|
|
* `cbutils`: New concept, which implements: build coreboot utilities like
|
|||
|
|
cbfstool and include the binaries in a directory inside lbmk, to be re-used.
|
|||
|
|
Previously, they would be compiled in-place within the coreboot build system,
|
|||
|
|
often re-compiled needlessly, and the checks for whether a given util are
|
|||
|
|
needed were very ad-hoc: now these checks are much more robust.
|
|||
|
|
Very centralised approach, per coreboot tree, rather than selectively
|
|||
|
|
compiling specific coreboot utilities, and makes the build system logic in
|
|||
|
|
nonGeNUine Boot much cleaner.
|
|||
|
|
* GRUB config: 30s timeout by default, which is friendlier on some desktops
|
|||
|
|
that have delayed keyboard input in GRUB.
|
|||
|
|
* ICH9M/GM45 laptops: 256MB VRAM by default, instead of 352MB. This fixes
|
|||
|
|
certain performance issues, for some people, as 352MB can be very unstable.
|
|||
|
|
* U-Boot patches: for `gru_bob` and `gru_kevin` chromebooks, U-Boot is used
|
|||
|
|
instead of Google's own *depthcharge* bootloader. It has been heavily
|
|||
|
|
modified to avoid certain initialisation that is replaced by coreboot, in
|
|||
|
|
such a way that U-Boot is mainly used as a bootloader providing UEFI for
|
|||
|
|
compliant GNU+Linux distros and BSDs. Courtesy Alper Nebi Yasak.
|
|||
|
|
* lbmk: The entire nonGeNUine Boot build system has, for the most part, been made
|
|||
|
|
portable; a lot of scripts now work perfectly, on POSIX-only implementations
|
|||
|
|
of `sh` (though, many dependencies still use GNU extensions, such as GNU
|
|||
|
|
Make, so this portability is not directly useful yet, but a stepping stone.
|
|||
|
|
nonGeNUine Boot eventually wants to be buildable on non-GNU, non-GNU/Linux systems,
|
|||
|
|
e.g. BSD systems)
|
|||
|
|
* nvmutil: Lots of improvements to code quality, features, error handling. This
|
|||
|
|
utility was originally its own project, started by Leah Rowe, and later
|
|||
|
|
imported into the nonGeNUine Boot build system.
|
|||
|
|
* build/boot/roms: Support cross-compiling coreboot toolchains for ARM platforms,
|
|||
|
|
in addition to regular x86 that was already supported. This is used for
|
|||
|
|
compiling U-boot as a payload, on mainboards.
|
|||
|
|
* U-boot integration: at first, it was just downloading U-Boot. Board integration
|
|||
|
|
for ARM platforms (from coreboot) came later, e.g. ASUS Chromebook Flip C101
|
|||
|
|
as mentioned above. The logic for this is forked largely from the handling
|
|||
|
|
of coreboot, because the interface for dealing with their build systems is
|
|||
|
|
largely similar, and they are largely similar projects. Courtesy Denis Carikli
|
|||
|
|
and Alper Nebi Yasak.
|
|||
|
|
* New utility: `nvmutil` - can randomise the MAC address on Intel GbE NICs, for
|
|||
|
|
systems that use an Intel Flash Descriptor
|
|||
|
|
* General build system fixes: better (and stricter) error handling
|
|||
|
|
* Fixed race condition when building SeaBIOS in some setups.
|
|||
|
|
* GRUB configs: only scan ATA, AHCI or both, depending on config per board.
|
|||
|
|
This mitigates performance issues in GRUB on certain mainboards, when
|
|||
|
|
scanning for `grub.cfg` files on the HDD/SSD.
|
|||
|
|
* GRUB configs: speed optimisations by avoiding slow device enumeration in
|
|||
|
|
GRUB.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Hardware supported in nonGeNUine Boot 20230717
|
|||
|
|
==================================================
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
All of the following are believed to *boot*, but if you have any issues,
|
|||
|
|
please contact the nonGeNUine Boot project. They are:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Servers (AMD, x86)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- [ASUS KGPE-D16 motherboard](../docs/hardware/kgpe-d16.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [ASUS KFSN4-DRE motherboard](../docs/hardware/kfsn4-dre.md)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Desktops (AMD, Intel, x86)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- [ASUS KCMA-D8 motherboard](../docs/hardware/kcma-d8.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Gigabyte GA-G41M-ES2L motherboard](../docs/hardware/ga-g41m-es2l.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Acer G43T-AM3](../docs/hardware/acer_g43t-am3.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Intel D510MO and D410PT motherboards](../docs/hardware/d510mo.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Apple iMac 5,2](../docs/hardware/imac52.md)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Laptops (Intel, x86)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- **[Dell Latitude E6400](../docs/hardware/e6400.md) (easy to flash, no disassembly, similar
|
|||
|
|
hardware to X200/T400)**
|
|||
|
|
- ThinkPad X60 / X60S / X60 Tablet
|
|||
|
|
- ThinkPad T60 (with Intel GPU)
|
|||
|
|
- [Lenovo ThinkPad X200 / X200S / X200 Tablet](../docs/hardware/x200.md)
|
|||
|
|
- Lenovo ThinkPad X301
|
|||
|
|
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R400](../docs/hardware/r400.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T400 / T400S](../docs/hardware/t400.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Lenovo ThinkPad T500](../docs/hardware/t500.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Lenovo ThinkPad W500](../docs/hardware/t500.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Lenovo ThinkPad R500](../docs/hardware/r500.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Apple MacBook1,1 and MacBook2,1](../docs/hardware/macbook21.md)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Laptops (ARM, with U-Boot payload)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- [ASUS Chromebook Flip C101 (gru-bob)](../docs/install/chromebooks.md)
|
|||
|
|
- [Samsung Chromebook Plus (v1) (gru-kevin)](../docs/install/chromebooks.md)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Downloads
|
|||
|
|
=========
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
You can find the release here, along with documentation:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
<https://av.vimuser.org/notgnuboot/20230717/>
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Happy... hacking.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
UPDATE (21 July 2023)
|
|||
|
|
=====================
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This website, that you are reading now, and the nonGeNUine release itself,
|
|||
|
|
was originally *named* GNU Boot, but clearly marked as *unofficial*, with the
|
|||
|
|
hope that the GNU project would adapt and re-use it for their project. I did
|
|||
|
|
this, specifically to help them get up to date. They currently use Libreboot
|
|||
|
|
from about 8 months ago (late 2022), and that revision used *coreboot* releases
|
|||
|
|
from ~mid 2021.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Modern Libreboot uses coreboot from early 2023, and contains many bug fixes
|
|||
|
|
in its build system, owing to an extensive [build system
|
|||
|
|
audit](https://libreboot.org/news/audit.html); GNU Boot still contains all of
|
|||
|
|
the bugs that existed, prior to the audit. Bugs such as: errors literally not
|
|||
|
|
being handled, in many critical areas of the build system, due to improper use
|
|||
|
|
of subshells within shell scripts (Libreboot's build system is implemented with
|
|||
|
|
shell scripts), improper handling of git credentials in the coreboot build
|
|||
|
|
system, fam15h boards no longer compiling correct on modern Linux distros...
|
|||
|
|
the list goes on. All fixed, in newer Libreboot, including the recent release.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
GNU Boot cease and desist email
|
|||
|
|
-------------------------------
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
The GNU Boot people actually sent me a cease and desist email, citing trademark
|
|||
|
|
infringement. Amazing.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Despite the original site clearly stating that it's unofficial. I literally made
|
|||
|
|
it to help them. You know, to help them use newer Libreboot because they use old
|
|||
|
|
Libreboot and even older coreboot.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Anyway, I complied with their polite request and have renamed the project to
|
|||
|
|
nonGeNUine Boot. The release archive was re-compiled, under this new brand
|
|||
|
|
name and this nonGeNUine website was re-written accordingly.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Personally, I like the new name better.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Here is a screenshot of the cease and desist request that I received,
|
|||
|
|
from *Adrien ‘neox’ Bourmault* who is a founding member of the GNU Boot
|
|||
|
|
project:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
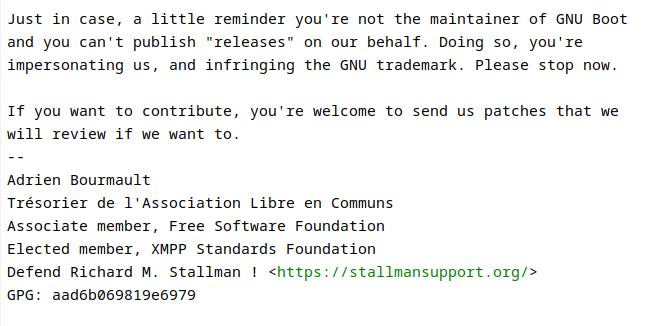
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
This, after they themselves tried to steal the name *Libreboot* for their
|
|||
|
|
fork, when they first announced themselves on 19 March 2023 at LibrePlanet,
|
|||
|
|
only renaming to *GNU Boot* months later (on 11 June 2023). Utter hypocrisy,
|
|||
|
|
and a great irony to boot.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
I may very well send patches. *If I want to*.
|